acupuncture
The first major victory in the battle for the integrity of universities seems to have been won. This email was sent by Kate Chatfield who is module leader for the “BSc” in homeopathic medicine at the University of Central Lancashire (UCLAN).
| from Kate Chatfield…
Dear All, It’s a sad day for us here at UCLan because we have taken the decision not to run a first year this year due to low recruitment. The course will be put ‘on hold’ for this year and next until we see what happens with the general climate. Fortunately our masters course is thriving and we have been asked to focus upon this area and homeopathy research for the time being. Of late UCLan has been the subject of many attacks by the anti-homeopathy league. Colquhoun et al have kept the university lawyers and us quite fruitlessly busy by making claims for very detailed course information under the Freedom of Information Act. The latest demand is for 32 identified lesson plans with teaching notes, power points, handouts etc. The relentless attacks have taken their toll and it appears that they have won this small victory. The university has been very clear that this decision has been taken solely on the grounds of poor educational experience and is nothing to do with the current furore. They continue to be supportive of us and our efforts. Best wishes Kate and Jean |
There is some background here. In July 2006 I made a request to UCLAN under the Freedom of Information Act 2000, in which I asked to see some of their teaching materials. I appealed to UCLAN but Professor Patrick McGhee, Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Academic), also turned down two appeals. A letter sent directly to Professor Malcolm McVicar, vice-chancellor and president of UCLAN, failed to elicit the courtesy of a reply (standard practice I’m afraid, when a vice chancellor is faced with a difficult question). (Ironically, McVicar lists one of his interests as “health policy”.) So then I appealed to the Office of the Information Commissioner, in November 2006. Recently the case got to the top of the pile, and a judgment is expected any moment now.
Kate Chatfield’s letter to her colleagues is interesting. She describes a request ro see some of her teaching materials as an “attack”. If someone asks to see my teaching materials, I am rather flattered, and I send them. Is she not proud of what she teaches? Why all the secrecy? After all, you, the taxpayer, are paying for this stuff to be taught, so why should you not be able see it? Or is the problem that she feels that the “alternative reality” in which homeopaths live is just too complicated for mortals to grasp? Perhaps this attitude should be interpreted as flattering to the general public, because somewhere deep down she knows that the public will be able to spot gobbledygook when they see it. The revelation that the University of Westminster teaches first year undergraduates the “amethysts emit high yin energy” didn’t help their academic reputation much either.
Much credit for this decision must go also to the pressure from the many good academics at UCLAN. When it was revealed recently that UCLAN intended to open yet more courses in forms of medicine that are disproved or unproven, they naturally felt that their university was being brought into disrepute. Opposition to plans to introduce new “degrees” in acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine were exposed in Times Higher Education recently. It particular, great credit must go to Dr Michael Eslea from UCLAN’s Psychology department. His open letter to his vice-chancellor is an example of scientific integrity in action.
The abandonment of this degree in medicines that contain no medicine is a small victory for common sense, for science and for the integrity of universities. Sadly, there is still a long way to go.
It is my understanding that ‘bringing the university into disrepute’ is a serious offence. Please note, vice-chancellor.
A few more judgments like that to suspend your homeopathy degree could work wonders for your reputation.
The follow-up
Watch this space.
The Guardian was quick off the mark -this story appeared on their education web site within 3 hours of my posting it “Homeopathy degrees suspended after criticism” by Anthea Lipsett. My comment there disappeared for a while because the Guardian legal people misunderstood the meaning of the last sentence. It’s back now, with blame allocated unambiguously to the vice-chancellors of the 16 or so universities who run this sort of course.
UCLAN’s web site seems to need some updating. The “BSc” in homeopathic medicine is still advertised there. as of 28 August.
UCLAN’s best ally. Dr Michael Eslea, has had some publicity for his attempts to rescue his university’s reputation. The story appeared in the “High Principals” column of Private Eye (Issue 1217, Aug 22, 2008). It also appeared in his local paper, the Lancashire Evening Post.
The Lancashire Evening Post catches up with homeopathy suspension story, two days after you read it here. But the UCLAN web site still advertises it.
The article below is an editorial that I was asked to write for the New Zealand Medical Journal, as a comment on article in today’s edition about the misuse of the title ‘doctor’ by chiropractors [download pdf]. Titles are not the only form of deception used by chiropractors, so the article looks at some of the others too. For a good collection of articles that reveal chiropractic for what it is, look at Chirobase
THE NEW ZEALAND
MEDICAL JOURNAL
Journal of the New Zealand Medical Association
NZMJ 25 July 2008, Vol 121 No 1278; ISSN 1175 8716

URL: http://www.nzma.org.nz/journal/121-1278/3158/ ©NZMA
Doctor Who?
Inappropriate use of titles by some alternative “medicine” practitioners
David Colquhoun
Who should use the title ‘doctor’? The title is widely abused as shown by Gilbey1 in this issue of the NZMJ in an article entitled Use of inappropriate titles by New Zealand practitioners of acupuncture, chiropractic, and osteopathy. Meanwhile, Evans and colleagues 2, also in this issue, discuss usage and attitudes to alternative treatments.
Gilbey finds that the abuse of the title doctor is widespread and that chiropractors are the main culprits. An amazing 82% of 146 chiropractics used the title Doctor, andL most of them used the title to imply falsely that they were registered medical practitioners.
Although it is illegal in New Zealand to do that, it seems clear that the law is not being enforced and it is widely flouted. This is perhaps not surprising given the history of chiropractic. It has had a strong element of ruthless salesmanship since it was started in Davenport, Iowa by D.D. Palmer (1845–1913). His son, B.J. Palmer, said that their chiropractic school was founded on “a business, not a professional basis. We manufacture chiropractors. We teach them the idea and then we show them how to sell” (Shapiro 2008)3 It is the same now. You can buy advice on how to build “build high-volume, subluxation-based, cash-driven, lifetime family wellness practices”
In her recent book3 , Rose Shapiro comments on the founder of chiropractic as follows.
“By the 1890s Palmer had established a magnetic healing practice in Davenport, Iowa, and was styling himself “doctor”. Not everyone was convinced, as a piece about him in an 1894 edition of the local paper, the Davenport Leader, shows.
A crank on magnetism has a crazy notion hat he can cure the sick and crippled with his magnetic hands. His victims are the weak-minded, ignorant and superstitious,those foolish people who have been sick for years and have become tired of the regular physician and want health by the short-cut method he has certainly profited by the ignorance of his victim. His increase in business shows what can be done in Davenport, even by a quack.”
D.D. Palmer was a curious mixture: grocer, spiritual healer, magnetic therapist, fairground huckster, religious cult leader—and above all, a salesman. He finally found a way to get rich by removing entirely imaginary “subluxations”.
Over 100 years later, it seems that the “weak-minded, ignorant, and superstitious” include the UK’s Department of Health, who have given chiropractics a similar status to the General Medical Council.
The intellectual standards of a 19th Century Mid-Western provincial newspaper journalist are rather better than the intellectual standards of the UK’s Department of Health, and of several university vice-chancellors in 2007.
Do the treatments work?
Neither Gilbey nor Evans et al. really grasp the nettle of judging efficacy. The first thing one wants to know about any treatment —alternative or otherwise — is whether it works. Until that is decided, all talk of qualifications, regulation, and so on is just vacuous bureaucratese. No policy can be framed sensibly until the question of efficacy has been addressed honestly.
It is one good effect of the upsurge of interest in alternative treatments that there are now quite a lot of good trials of the most popular forms of treatments (as well as many more bad trials). Some good summaries of the results are now available too. Cochrane reviews set the standard for good assessment of evidence. New Zealand’s Ministry of Health commissioned the Complementary and Alternative Medicine
website to assess the evidence, and that seems to have done a good job too. Their assessment of chiropractic treatment of low back pain is as follows:
There appears to be some evidence from one systematic review and four other studies, although not conclusive, that chiropractic treatment is as effective as other therapies but this may be due to chance. There is very little evidence that chiropractic is more effective than other therapies.
And two excellent summaries have been published as books this year. Both are by people who have had direct experience of alternative treatments, but who have no financial interest in the outcome of their assessment of evidence. The book by Singh and Ernst4 summarises the evidence on all the major alternative treatments, and the book by Bausell5 concentrates particularly on acupuncture, because the author was for 5 years involved in research in that area, Both of these books come to much the same conclusion about chiropractic. It is now really very well-established that chiropractic is (at best) no more effective than conventional treatment. But it has the disadvantage of being surrounded by gobbledygook about “subluxations” and, more importantly, it kills the occasional patient.
Long (2004)7 said “the public should be informed that chiropractic manipulation is the number one reason for people suffering stroke under the age of 45.”
The chiropractors of Alberta (Canada) and the Alberta Government are now facing a class-action lawsuit8. The lead plaintiff is Sandra Nette. Formerly she was a fit 41 year old. Now she is tetraplegic. Immediately
after neck manipulation by a chiropractor she had a massive stroke as a result of a torn vertebral artery.
Acupuncture comes out of the assessments equally badly. Bausell (2007) concludes that it is no more than a theatrical placebo.
Are the qualifications even real?
It is a curious aspect of the alternative medicine industry that they often are keen to reject conventional science, yet they long for academic respectability. One aspect of this is claiming academic titles on the flimsiest of grounds. You can still be held to have misled the public into thinking you are a medical
practitioner, even if you have a real doctorate. But often pays to look into where the qualifications come from.
A celebrated case in the UK concerned the ‘lifestyle nutritionist’, TV celebrity and multi-millionaire, Dr Gillian McKeith, PhD. A reader of Ben Goldacre’s excellent blog, badscience.net did a little investigation. The results appeared in Goldacre’s Bad Science column in the Guardian9.
She claimed that her PhD came from the American College of Nutrition, but it turned out to come from a correspondence course from a non-accredited US ‘college’. McKeith also boasted of having “professional membership” of the American Association of Nutritional Consultants, for which she provided proof of her degree and three professional references.
The value of this qualification can be judged by the fact that Goldacre sent an application and $60 and as a result “My dead cat Hettie is also a “certified professional member” of the AANC. I have the certificate hanging in my loo”.
Is the solution government regulation?
In New Zealand the law about misleading the public into believing you are a medical practitioner already exists. The immediate problem would be solved if that law were taken seriously, but it seems that it is not.
It is common in both the UK and in New Zealand to suggest that some sort of official government regulation is the answer. That solution is proposed in this issue of NZMJ by Evans et al2. A similar thing has been proposed recently in the UK by a committee headed by Michael Pittilo, vice-chancellor of Robert Gordon’s University, Aberdeen.
I have written about the latter under the heading A very bad report. The Pittilo report recommends both government regulation and more degrees in alternative medicine. Given that we now know that most alternative medicine doesn’t work, the idea of giving degrees in such subjects must be quite ludicrous to any thinking person.
The magazine Nature7 recently investigated the 16 UK universities who run such degrees. In the UK, first-year students at the University of Westminster are taught that “amethysts emit high yin energy” . Their vice chancellor, Professor Geoffrey Petts, describes himself a s a geomorphologist, but he cannot be tempted to express an opinion about the curative power of amethysts.
There has been a tendency to a form of grade inflation in universities—higher degrees for less work gets bums on seats. For most of us, getting a doctorate involves at least 3 years of hard experimental research in a university. But in the USA and Canada you can get a ‘doctor of chiropractic’ degree and most chiropractic (mis)education is not even in a university but in separate colleges.
Florida State University famously turned down a large donation to start a chiropractic school because they saw, quite rightly, that to do so would damage their intellectual reputation. This map, now widely distributed on the Internet, was produced by one of their chemistry professors, and it did the trick.

Other universities have been less principled. The New Zealand College of Chiropractic [whose President styles himself “Dr Brian Kelly”,though his only qualification is B. App Sci (chiro)] is accredited by the New Zealand Qualifications Authority (NZQA). Presumably they, like their UK equivalent (the QAA), are not allowed to take into account whether what is being taught is nonsense or not. Nonsense courses are accredited by experts in nonsense. That is why much accreditation is not worth the paper it’s written on.
Of course the public needs some protection from dangerous or fraudulent practices, but that can be done better (and more cheaply) by simply enforcing existing legislation on unfair trade practices, and on false advertising. Recent changes in the law on unfair trading in the UK have made it easier to take legal action against people who make health claims that cannot be justified by evidence, and that seems the best
way to regulate medical charlatans.
Conclusion
For most forms of alternative medicine—including chiropractic and acupuncture—the evidence is now in. There is now better reason than ever before to believe that they are mostly elaborate placebos and, at best, no better than conventional treatments. It is about time that universities and governments recognised the evidence and stopped talking about regulation and accreditation.
Indeed, “falsely claiming that a product is able to cure illnesses, dysfunction, or malformations” is illegal in Europe10.
Making unjustified health claims is a particularly cruel form of unfair trading practice. It calls for prosecutions, not accreditation.
Competing interests: None.
NZMJ 25 July 2008, Vol 121 No 1278; ISSN 1175 8716
URL: http://www.nzma.org.nz/journal/121-1278/3158/ ©NZMA
Author information: David Colquhoun, Research Fellow, Dept of Pharmacology, University College London, United Kingdom (http://www.ucl.ac.uk/Pharmacology/dc.html)
Correspondence: Professor D Colquhoun, Dept of Pharmacology, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, United Kingdom. Fax: +44(0)20 76797298; email: d.colquhoun@ucl.ac.uk
References:
1. Gilbey A. Use of inappropriate titles by New Zealand practitioners of acupuncture, chiropractic, and osteopathy. N Z Med J. 2008;121(1278). [pdf]
2. Evans A, Duncan B, McHugh P, et al. Inpatients’ use, understanding, and attitudes towards traditional, complementary and alternative therapies at a provincial New Zealand hospital. N Z Med J. 2008;121(1278).
3 Shapiro. Rose. Suckers. How Alternative Medicine Makes Fools of Us All Random House, London 2008. (reviewed here)
4. Singh S, Ernst E. Trick or Treatment. Bantam Press; 2008 (reviewed here)
5. Bausell RB. Snake Oil Science. The Truth about Complementary and Alternative Medicine. (reviewed here)
Oxford University Press; 2007
6. Colquhoun D. Science degrees without the Science, Nature 2007;446:373–4. See also here.
7. Long PH. Stroke and spinal manipulation. J Quality Health Care. 2004;3:8–10.
8. Libin K. Chiropractors called to court. Canadian National Post; June21, 2008.
9. Goldacre B. A menace to science. London: Guardian; February 12, 2007/
10. Department for Business Enterprise & Regulatory Reform (BERR). Consumer Protection from Unfair Trading Regulations 2008. UK: Office of Fair Trading.
| A report has appeared on Regulation of Practitioners of Acupuncture, Herbal Medicine, Traditional Chinese Medicine. The report is written by people all of whom have vested interests in spreading quackery. It shows an execrable ability to assess evidence, and it advocates degrees in antiscience It would fail any examination. Sorry, Prof Pittilo, but it’s gamma minus.[Download the report] |  |
Alice Miles put it well in The Times, today.
“This week came the publication of the “Report to Ministers from the Department of Health Steering Group on the Statutory Regulation of Practitioners of Acupuncture, Herbal Medicine, Traditional Chinese Medicine and Other Traditional Medicine Systems Practised in the UK”. Otherwise known as twaddle.” . . .
“Regulate the practitioners – for safety, note, not for efficacy, as that is impossible to prove – and you give them official recognition. From recognition it is but a short hop to demand and then prescription: packet of Prozac, bit of yoga and a bag of dodgy herbs for you, sir.” . . .
“The Government responded on Monday – with a three-month consultation. So join in. Write to the Health Minister Ben Bradshaw at Richmond House, 79 Whitehall, SW1A 2NS. Write, on behalf of the NHS: “What I want for my 60th birthday is… the chance to provide medical, dental, and nursing care to all. And absolutely nothing else.”
Judging by Ben Bradshaw’s speech to the Prince’s Foundation, there may be a problem in conveying to him the evidence, but one can and must try.
Why is it that a health joutnalist can do so much better than a university head? Yes, the chair of the steering group is Professor R. Michael Pittilo BSc PhD CBiol FIBiol FIBMS FRSH FLS FRSA, Principal and Vice-Chancellor of The Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen. Despite all those impressive-lookin initials after his name, I believe that this is a very bad report.
Here is something about Prof Pittilo from his university’s web site (the emphasis is mine).
Professor Michael Pittilo joined The Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen, as Principal and Vice-Chancellor on 5th September, 2005.
After postdoctoral research on arterial disease at the University of London, he was appointed to Kingston University where he became Head of Life Sciences. In 1995 he became Foundation Dean of the Faculty of Health and Social Care Sciences at Kingston University and St George’s Medical School (University of London). He was appointed Pro Vice Chancellor at the University of Hertfordshire in 2001.
Professor Pittilo has held a number of additional roles, including chairing Department of Health working groups, and as a trustee for the Prince of Wales’s Foundation for Integrated Health. “
Notice that Prof Pittilo is a Trustee of the Prince’s Foundation for Integrated Health, source of some of the least reliable information about alternative medicine to be found anywhere.
This steering group is, as so often, a nest of vested interests. It does not seem to have on it any regular medical or clinical scientist whatsoever. Why not? They just might produce some embarrassing facts perhaps? Like most government committees its members seem to have been chosen to produce the desired outcome.
For a start, the university run by Prof Pittilo, Robert Gordon’s University, is itself involved in a few antiscientific courses. Since his report recommends that degrees in quackery should become mandatory, I expect he’d welcome the chance to run more. Amazingly, Robert Gordon’s University runs an Introduction to Homeopathy, just about the daftest of all the common sorts of magic medicine.
Most of the the members of the steering group represent vested interests, though strangely this is not made clear in the list of members. An earlier report, in 2006, from the steering group was more open about this. Twelve of the members of the group represent Herbal Medicine, Chinese Medicine and Acupuncture (four from each). Most of the rest are lay members or bureaucrats. With membership like that it is, I suppose, not surprising that the assessment of evidence is, to put it kindly, grossly distorted and woefully inadequate.
The report starts badly by failing to mention that the House of Lords report (2000), and the government’s response to it, set the following priorities. Both state clearly
“… we recommend that three important questions should be addressed in the following order . .
- (1) does the treatment offer therapeutic benefits greater than placebo?
- (2) is the treatment safe?
- (3) how does it compare, in medical outcome and cost-effectiveness, with other forms of treatment?
The word ‘placebo’ does not occur a single time in the main report (and only twice in the text of the seven appendices). But they do say (page 11):
“We recommend that public funding from the NHS should be used to fund CAM therapies where there is evidence of efficacy, safety and quality assurance.”
The evidence
The problem is that the assessment of the evidence for efficacy in the report is pathetically poor. The report, sad to say, consists essentially of 161 pages of special pleading by the alternative medicine industry, served up with the usual large dose of HR gobbledygook.
There is really no excuse for this utterly incompetent assessment. There have been plenty of books this year alone that make excellent summaries of the evidence, mostly written for the lay public. They should, therefore, be understandable by any university vice-chancellor (president). The one benefit of the upsurge in public interest in magic medicine is that there are now quite a lot of good clinical trials, and when the trials are done properly, they mostly confirm what we thought before: in most cases the effects are no more than placebo.
Here is one example. Annexe1 concerns “Developing Research and Providing an Evidence Base for Acupuncture and Herbal/Traditional Medicine Treatment”. The wording of the title itself suggests, rightly, that this evidence base does not exist, in which case why on earth are we talking about them as “professions”? The discussion of the evidence in Annexe 1 is nothing if not partial. But what do you expect if you ask herbalists to assess herbal medicine? An honest assessment would put them out of business. The eternal mantra of the alternative industry appears as usual, “Absence of evidence is, of course, not evidence of absence”. True of course, but utterly irrelevant. Annexe 1 says
“Acupuncture is a complex intervention and lack of a suitable placebo control has hindered efforts to evaluate efficacy”
This is simply untrue, In recent years enormous efforts have been put into devising controls for assessment of acupuncture, but they are entirely ignored here. One thing that has been established quite clearly is that it makes no difference where you put the needles, so all the talk of Qi and meridians is obvious mumbo-jumbo.
Have the authors of Annexe 1, and Professor Pittilo, not read the relevant studies? Two books this year have dealt with the question of evidence with great care. They are both by people who have been involved personally with acupuncture research, Prof Edzard Ernst and Dr Barker Bausell. Edzard Ernst is the UK’s first Professor of Complementary Medicine. Barker Bausell was research director of an NIH-funded Complementary and Alternative Medicine Specialized Research Center at the University of Maryland.
 |
 |
Singh and Ernst discuss thoroughly the question of controls and assess all the evidence carefully. Their conclusions include the following.
- The traditional principles of acupuncture are deeply flawed, as there is no evidence at all to demonstrate the existence of Ch’i [Qi] or meridians.
- By focussing on the increasing number of high-quality research papers, reliable conclusions from systematic reviews make it clear that acupuncture does not work for a whole range of conditions, except as a placebo.
- In short, the evidence is neither consistent nor convincing. It is borderline.
Barker Bausell was himself involved in designing and analysing trialsof acupuncture. His conclusions are even less positive.
“There is no compelling, credible scientific evidence to suggest that any CAM therapy benefits any medical condition or reduces any medical symptom (pain or otherwise) better than a placebo”.
These are serious authors with direct experience in CAM research, which is more than can be said of anyone on the steering group. Why are their conclusions ignored entirely? That is sheer incompetence.
Degrees in anti-science
One conclusion of the report is that
“The threshold entry route to the register will normally be through a Bachelor degree with Honours”
This is utter nonsense. It is quite obvious surely that you can’t award honours degrees until after you have the evidence. You can read on page 55 of the report
“3a: Registrant acupuncturists must:
understand the following aspects and concepts for traditional East-Asian acupuncture:
– yin/yang, /5 elements/phases, eight principles, cyclical rhythms, qi ,blood and body fluids, different levels of qi, pathogenic factors, 12 zang fu and 6 extraordinary fu, jing luo/ meridians, the major acupuncture points, East-Asian medicine disease categorisation, the three burners, the 4 stages/levels and 6 divisions
– causes of disharmony/disease causation
– the four traditional diagnostic methods: questioning, palpation, listening and observing”
This is utter baloney. Anyone who advocates giving honours degrees in such nonsense deserves to be fired for bringing his university into disrepute (and, in the process, bringing all universities and science itself into disrepute).
That includes also degrees that teach that “amethysts emit high yin energy“.
So what should be done?
If making peole do degrees in mumbo-jumbo is not the answer, what is? Clearly it would be far too draconian to try to ban quackery (and it would only increase its popularity anyway).
The answer seems to me to be quite simple. All that needs to done is to enforce existing laws. It is already illegal to sell contaminated and poisonous goods to the public. It is already illegal to make fraudulent advertisemants and to sell goods that are not as described on the label.
The only problem is that the agencies that enforce these rules are toothless and that there are a lot of loopholes and exceptions that work in favour of quackery. I have tried myself to complain about mislabelling of homeopathic pills to the Office of Fair Trading on the grounds that are labelled Arnica 30C but contain no Arnica. They solemnly bought a bottle and sent it to an analyst and of course they found no arnica, But nothing happened, because an exception to the usual law applies to homeopathic pills.
The Advertising Standards Authority is good as far as it goes. They quickly told Boots Pharmacies to withdraw advertisements that claimed CoQ10 “increased vitality”. But they can exact no penalties and they can’t deal with lies that are told to you orally, or with anything at all on the web.
The Health Professions Council (HPC) says that one of the criteria for registering new professions is aspirant groups must “Practise based on evidence of efficacy”. If that were actually applied, none of this process would occur anyway. No doubt the HPC will fail to apply its own criteria. On past form, it can be expected to adopt a “fluid concept of evidence“.,
One more thing, New European legislation was described recently in the BMJ
“Consumers in the United Kingdom are to receive stronger legal safeguards against products that claim, without any identifiable scientific evidence, to provide physical and mental health benefits such as tackling obesity or depression.”
“The scope of the legislation is deliberately wide and is the biggest shake up in consumer law for decades. It targets any unfair selling to consumers by any business.”
Politicians seem to be immune to rational argument when it comes to quackery. But a few legal actions under these laws could bring the house of cards tumbling so fast that this gamma-minus report would become rapidly irrelevant. There will be no shortage of people to bring the actions. I can’t wait.
Follow up
Dominic Lawson, 24 June 2008. An excellent column appeared today in the Independent. Dominic Lawson writes about the Pittilo report: “So now we will have degrees in quackery. What, really, is the difference between acupuncture and psychic surgery?“. The reference to that well known conjuring trick, “psychic surgery” as a “profession”, revealed here, causes Lawson to say
“It makes it clear that the lunatics have taken over the asylum. For a start, how could Philip Hunt, previously director of the National Association of Health Authorities and Trusts, possibly have thought that “psychic healing” constituted a “profession” – let alone one which would “develop its own system of voluntary self-regulation?”
“One can see how this might fit in with the Government’s “never mind the quality, feel the width” approach to university education. One can also see how established practitioners of such therapies might see this as a future source of income – how pleasant it might be to become Visiting Professor of Vibrational Medicine at the University of Westminster.
Thus garlanded with the laurels of academic pseudo-science, the newly professionalised practitioners of “alternative medicine” can look down on such riff-raff as the “psychic surgeons”
Once again I have to ask, how is it that we have to rely on journalists to prevent vice-chancellors eroding academic standards; indeed eroding simple common sense? I guess it is just another sign of the delusional thinking engendered by the culture of managerialism that grips universities.
This is a follow-up of the poat on BBC2 and the Open University on Alternative Medicine.
Following the article by Simon Singh in the Guardian (25 March 2006), two letters appeared on April 1, 2006. The first, from Prof. Edzard Ernst, confirmed that he felt the BBC had ignored and misrepresented his advice.
|
In its response to our criticism of the Alternative Medicine series, the BBC says “it is extremely unusual that Professor Ernst should make these comments so long after the series was aired” (Report, March 25). I made my criticism in writing two months before the programme was broadcast. The reason why I reiterated them when I did was simply because Simon Singh interviewed me in my capacity as adviser to the BBC. Extremely unusual? Long after? I don’t think so.
Prof Edzard Ernst Peninsula Medical School, Exeter |
The second letter defended the BBC. It was unequivocal in its support of the entire series of programmes, and its appearence surprised me. In the light of all that has been written, one might have hoped that the BBC would listen and learn from its mistakes. The letter has ten signatories.
|
We are all scientists involved as consultants or contributors to the BBC2 series, Alternative Medicine. We do not in any way recognise the experience of working on the series as described in your article (Was this proof of acupuncture’s power … or a sensationalised TV stunt?, Science, March 25), nor do we share the views of those scientists you have quoted in it. In all its dealings with us, the BBC asked for advice and input where needed, took on board our feedback and incorporated our comments into the final edit of the programme as transmitted, where appropriate. Far from feeling dissatisfied with the final outcome, we feel the series seemed well balanced and informative, doing full justice to the subject matter it addressed. Dr Jack Tinker Prof Brian Berman Prof Liz Williamson Dr Andrew Vickers Dr James Warner Dr Mike Cummings Prof Gary Green Dr Carl Albrecht Dr Jen Cleland Professor Irving Kirsch |
But all is not what it seems. Contrary to appearances, this letter was actually written by the BBC who also compiled the signatories (it seems to have been the responsibility of Kim Creed, of BBC Factual Publicity).
- One of the signatories. Dr James Warner, had never seen the letter until after it was published, and tells me that “[I] substantially do not agree with the sentiments expressed therein. Indeed, we had to resist attempts by the programme makers to sensationalise our work”.
The Guardian has published a correction. - Six other signatories tell me that their approval was limited to the way their own contribution was treated, and was not intended as approval of the whole series. One commented ” I’ve obviously been naïve, and I am very fed up with this whole thing”. Another says ” I suppose I (foolishly by the sounds of things) extrapolated from my own programme and experience, without considering the wider implications of the concluding sentence”.
- Only one of the eight signatories whom I’ve asked has actually seen all three programmes, as they were transmitted. This makes it rather odd that they should appear to endorse so unequivocally the whole series.
- One of the signatories, Carl Albrecht, gives his address as “University of Johannesburg”, but oddly the BBC forgot to mention that Dr Albrecht is co-owner (at least until very recently) of the South African Company, Phyto Nova, that makes, promotes and sells the untested herb, Sutherlandia, for treatment of AIDS (see, for example, here).
He is, therefore, highly biassed. He is also exceedingly controversial. One of his strongest critics has been Stuart Thomson, Director of the Gaia Research Institute,
hardly an organisation that is biassed against “natural medicines”. Albrecht is indeed a very curious choice of advisor for a programme about science. - Three of the signatories (Berman, Cummings and Albrecht) are heavily committed to CAM, and so unlikely to be critical of anything that favours it, even apart from financial interests in the outcome. Brian Berman even has is own an entry in Quackwatch. So several of the signatories are pretty much committed in advance. Asking them if they endorse the programmes is about as informative as asking a group of priests if the endorse god.
- It gets worse. This morning, 6th April, I heard from Andrew Vickers, of the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York. This is what he says.
“I didn’t sign this letter ”
“I was shown the text of the letter but didn’t fully agree with it and told them so. I said something along the lines that the series didn’t do ‘full justice to the subject matter’ (how could it possibly?) but that what they did was fair and reasonable within the constraints set by the medium. You are also right to point out that my comments only go so far as the acupuncture episodes (which I saw) rather than the other two shows (which I did not). No doubt had I been shown a final version for signature I would have also pointed this out.”
The BBC brought us superb programmes like Life on Earth and Planet Earth. They bring us superb news (I’m listening to the incomparable John Humphrys on the Today Programme right now). They have suffered unjustly at the hands of spin-meisters like Alastair Campbell and the execrable Hutton Report (If the Hutton Report had been an undergraduate essay, it would have scored alpha-plus for collection of evidence and gamma-minus for ability to connect evidence to conclusions).
How ironic it is, then, to see the BBC behaving in this case like spin artists. Deny everything, and, if necessary, falsify the evidence.
Jump to Open University course K221
BBC2 TV showed a much-advertised series on alternative medicine, in February 2006. The programmes seem to be linked with a dubious Open University course.
| The programmes are presented by Kathy Sykes, who is professor of the public understanding of science at Bristol University. She has done some excellent work in that area, for example, in the Rough Science TV series. |  |
The first programme: acupuncture
The first programme, on acupuncture, was shown on 24th January, 2006. The programme did not start
in a very promising way. Just lots of testimonials from happy patients, the staple diet of all snake oil salesmen.
They are watchable, of course, but don’t do anything at all to promote public understanding of what constitutes evidence.
There is, of course, little doubt that sticking needles into your body can produce physiological responses. Two things remain uncertain.
- Just how useful are these responses in helping particular conditions?
- Is there anything at all in the mumbo jumbo of meridians and chi?.
With a big flourish we were shown “a 21-year-old Shanghai factory worker undergoing open-heart surgery with only the needles to control her pain”. It turns out that this was a sham. The patient was doped on opiates and local anaesthetics. The needles were merely cosmetic. Why were we not told?
The apparently contradictory trials suggested that, at least the alleged principles of acupuncture are nonsense. The programme concentrated on a trial by Berman (Ann Intern Med. 2004,
141, 901-10 ) which used ‘sham acupuncture’, with ‘stage dagger needles’, on osteoarthritis of the knees. In this sort of trial there is no actual penetration, and the sham needles are placed on the places dictated by the mumbo jumbo. This procedure was justly criticised by a subsequent letters in the same journal (Ann
Intern Med 2005, 142, 871).
Another large study was ignored by the TV programme altogether. This was by Linde et al. (Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005 293(17):2118-25). This study concluded
“Acupuncture was no more effective than sham acupuncture in reducing migraine headaches although both interventions were more effective than a waiting list control.”
As pointed out above, this study is, in many ways, much more interesting than Berman’s, because the control group did not have ‘sham acupuncture’. Needles were really inserted, but they were inserted in points that have nothing to do with the mumbo jumbo of meridians. The fact that the controls were much the same as the treated group suggests that, whatever effect the needles produce, it doesn’t matter much where they are inserted. The only obvious interpretation of this is that the ‘principles’ on which acupuncture is based are so much nonsense (and, therefore, it is not a subject that can possibly be taught in a university).
This crucial point was ignored by the TV programme. A big fuss was made of a functional magnetic resonance experiment, staged for TV, that showed that the effects on brain ‘activation’ are different for superficial needling and for real needling. There is nothing in the least surprising in the observation that have a needle pushed into you affects the brain, but it really does not help at all in answering the important questions. Incidentally that experiment had already been done anyway.
In summary, the first programme, failed to give a fair assessment of current knowledge about acupuncture, and failed to consider the important questions of what sort of controls are appropriate, and whether talk of meridians means anything whatsoever. Sadly, I can’t agree with the boast that “It’s the deepest investigation into the efficacy of alternative medicine ever attempted on TV”. Let’s hope the second programme is a bit more critical.
The second programme: healing
The second programme (31st January, 2006). I liked this programme much better than the first, even if it left the crucial questions unresolved.
| The programme started with a healing meeting by the notorious Benny Hinn. The meeting had all the mass hysteria of a Nuremburg rally, though no mention was made of the fact that this (very rich) man’s financial malpractice had been revealed by a CBC TV programme. |  |
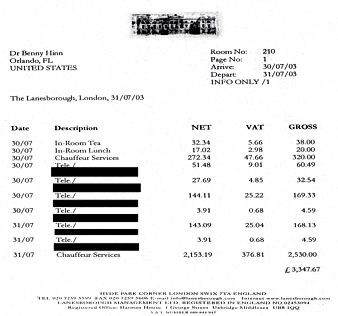 |
On the right is his receipt for £3347 for two nights at the Lanesborough hotel in London (that did not include $1700 he gave in tips).
The lovely Ghanaian lady who cleans my office and lab every morning gives gives money to this mega-rich man because “he needs it to preach the gospel”.
The National Institutes of Health provided $1.8 m of US taxpayers’ money for this project which seems not to do real research at all. After seeing a demonstration of the “Gas Discharge Visualization”, GDV, or Kirlian camera, given by a very gullible Dr Melinda Connor, Sykes comments that this ‘research’ “is not so much trying to find the evidence for ‘healing energy’, but is rather working on the basis that there is one”
Kathy Sykes did, though show a pretty healthy degree of scepticism about the people who pretend to photograph “auras” and other imaginary “force fields”. She visited the “Center for Frontier Medicine in Biofield Science” at the University of Arizona.
In other words, the ‘research’ is a con. Once again (see above) we see money given by well-intentioned governments diverted form the purpose for which it was given. For more first class boloney on ‘imaging’, see for example, Biofield Sciences in Exeter (UK) and ‘electro-crystal therapy’. The list is endless.
Kathy Sykes went on to show several interesting experiments on placebo effects. For example sham healers (played by actors) do at least as well as ‘real’ healers. And sham knee surgery may be as effective as real surgery, though the programme failed to mention the obvious possibility that this could mean nothing more than that real knee surgery is itself pretty ineffective. As so often in this series, the producers failed to talk to the right people.
She concludes “healing does not work beyond placebo”.
So I’m right with her, though it would have been better if there had been a more critical mention of the fact that not all placebo effects are real. Many probably depend on the natural fluctuations in the intensity of the patient’s condition. Anything can ‘cure a cold’, because you recover from a cold in a few days anyway,
Sykes concludes, speaking of the placebo effect, “I want to see that power properly harnessed -we’d be mad not to”. But that, disappointingly, was the end of the programme. That point is where the problems begin. How do you harness the placebo effect? How do you justify lying to the patient in order to maximize the effect? How do you train the ‘healers’? Are they themselves to believe the same lies, or are they to be trained in the art of deception? As pointed out in a recent review of the neurobiology of placebos (Colloca and Benedetti, 2005)
“For example, the assertion that placebos, fake therapies, fresh water and sugar pills could positively affect the brain biochemistry in the appropriate psychosocial context might lead to a dangerous justification for deception, lying and quackery”.
These are the central dilemmas of sCAM, as listed at the top of this page. The programme did nothing to solve them, or even to draw attention to them.
The link with Open University Course K221
The blurb on this programme on the Open University/BBC site concludes
“So, could the power of the mind explain the benefits people experience from healers? And have healers tapped into this power somehow? The conclusion throws new light on all healing processes, and has a surprising and inspirational message for every practitioner and patient.”
But what is to be done about this “inspiration”? Nothing is said about that. The TV programme was immediately followed by voice-over that advertised an Open University pamphlet, which is publicity for their course K221. That course, judging from what is posted on the web, is run by true believers who are a lot less sceptical than Sykes. She says that she did the voice-over but has not yet been shown the contents of the course.
The third programme: herbalism
Oooh dear. The third programme was, in my view, by far the worst. Hardly a single critical voice was heard. Despite the odd word of reservation, the programme left the impression of being an advertisement for the herbal medicine industry. Did the BBC not think of asking a pharmacologist? In my view, this programme was a disservice to human knowledge. Let’s look at some of the details.
The programme once again starts with dramatic testimonials from satisfied customers. No hint is given to the viewer of the total unreliability of such testimonials. References, in awed voice, are mad to “a vast body of ancient knowledge that herbalists draw on”. No mention of the superb track record that ‘ancient knowledge’ has for turning out to being dead wrong. It was 11 minutes into the programme before the question of evidence was even mentioned and then we had a herbalist wandering through a field. At 13 minutes, the herbalist, Simon Mills, was interviewed -he rattled on about dampness. marshy conditions. “There
are herbs for heating and drying”. Sheer gobbledygook. And still no discussion of evidence.
Sutherlandia At 18 minutes “To get another view I’m going to a country where herbs are claimed to have dramatic effects”. Off to Africa to spend a good 10 minutes on Sutherlandia, a totally unverified treatment for AIDS. Why spend all this time (and licence-payers money) to end up with the conclusion that clinical trials have
not been done yet, and we have no real idea whether it works or not? A search of Pubmed for Sutherlandia and AIDS produces a mere five papers. Mills et al. Nutrition Journal 2005, 4:19 write as follows.
“Despite the popularity of their use and the support of Ministries of Health and NGOs in some African countries, no clinical trials of efficacy exist, and low-level evidence of harm identifies the potential for drug interactions with antiretroviral drugs.”
(and one of the authors on that paper is from the Canadian College of Naturopathic Medicine: hardly likely to have a bias against herbs). The comments made in the programme about AIDS were irresponsible and potentially dangerous: they could kill people..
It took until almost half way through the programme, before we got round to the question of whether any of these claims are true. Very impressive to learn that the Nazis pushed herbal medicine, but totally uninformative (or does it mean that herbalism appeals to nutters?). We are shown the German herbal bible, but again it is pointed out that it contains no evidence about their efficacy. So no further forward yet. Then we are introduced to chromatography: very pretty, but still no evidence about whether herbs help people.
At 9.34 pm we are last get round to some evidence. Or do we? Not yet, just another personal testimonial about the the wonders of St John’s Wort. St John’s Wort (Hypericum) is an interesting case, because there is at least some evidence that it works, though certainly not enough for it to be described as a “superherb”, as Sykes did. Of course depression (like knee surgery -above) makes a pretty good case for herbalists, because conventional antidepressants are so very unsatisfactory themselves. It doesn’t take much to do better than Seroxat (Paxil, paroxetine). At 9.38 pm we get the first actual numbers. And very selective numbers they are
too. The view presented in the programme was desperately over-optimistic about the wondrous effects of St John’s wort. Consider the recent review by Linde et al. (2005 Brit J. Psychiatry, 186, 99-107) (read
it yourself –download pdf file). The conclusion was as follows.
“Current evidence regarding Hypericum extracts inconsistent and confusing. In patients who meet criteria for major depression, several recent placebo-controlled trials suggest that Hypericum has minimal beneficial effects while other trials suggest that Hypericum and standard antidepressants have similar beneficial effects. ”
And another trial, again not mentioned in the programme, was published in Journal of the American Medical Association, 2002, 287, 1807 – 1814) [download the pdf file]. This paper was interesting because it compared placebo, St John’s Wort and sertraline (Zoloft), a drug of the same class as Seroxat). All three were indistinguishable (on the two primary outcome measures). So St John’s Wort was as good as Zoloft, but only because Zoloft was no better than placebo either. The paper concluded thus.
“This study fails to support the efficacy the efficacy of H. perforatum [St John’s Wort] in moderately severe major depression. The result may be due to low assay sensitivity of the trial, but the complete absence of trends suggestive of efficacy for H. perforatum is noteworthy.”
Why were we not told about trials like these?
At 9.43 pm, almost three quarters of the way through the programme, we are eventually told that ginseng, echinacea and evening primrose oil do not work. What took so long?
9.46 pm. Off to South Africa to look at research in Johannesburg on Sutherlandia by Carl Albrecht (more of him below). Some impressive stuff about flavonoids but no results. Flavonoids can’t be absorbed, but, aha, it contains saponins too. Perhaps they allow the flavonoids into cells. Well perhaps.
But this is not information, it is idle speculation.
At 9.51, we get back to brain imaging, this time at Imperial College. Professor Sykes seems to be excessively impressed by brain imaging. We are then treated to more idle speculation about how ginko might help in Alzheimer’s disease. Dr Warner is running a clinical trial to find out whether ginko really helps. But there were no results yet. In that case why not wait until there is a result, before telling us all about it?
We are told that herbs now “have to go through rigorous quality standards”. It was NOT made clear that the standards don’t include anything about the herb actually doing anything useful. The standards may give some protection against your being poisoned. They do nothing at all to guarantee you’ll be helped.
The conclusions
“What’s really impressed me is the way that different ingredients from particular herb can combine together and have really powerful effects on us humans. So I believe that herbs are going to play a key role in medicines of the future”
“What started as an ancient wisdom may just might provide new medicines that will help us all live longer, fuller lives”
These statements are quite outrageous! The first statement has no basis whatsoever. It is sheer idle speculation. It could be true, but there is no reason to believe it is.
The second statement is content-free. Yes, it “may just” do that. On the other hand it may not.
The web site for the third programme. (7th February, 2006, 2100-2200) concludes thus.
“So, what’s their secret? Working with fellow scientists, Kathy discovers that plants contain much more than a single – or even two or three – active ingredients. They are enormously complex
Chemical cocktails that have medicinal properties modern pharmaceuticals simply can’t reproduce.”
Just one snag (apart from the misleading implication the Sykes was doing pharmacological experiments), There is not the slightest reason, thus far, to think there is any advantage in using an “enormously complex chemical cocktail”.
Stop press: on Saw palmetto (one of the “superherbs” of the TV series)
The New England Journal of Medicine, for February 9th 2006 (354, 557 – 566), reports a clinical trial of “Saw Palmetto for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia”. This is what they say.
“Saw palmetto is used by over 2 million men in the United States for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and is commonly recommended as an alternative to drugs approved by the Food and Drug Administration.”
“In this double-blind trial, we randomly assigned 225 men over the age of 49 years who had moderate-to-severe symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia to one year of treatment with saw palmetto extract (160 mg twice a day) or placebo.”
“Conclusions. In this study, saw palmetto did not improve symptoms or objective measures of benign prostatic hyperplasia.”
I hope that the BBC, the Open University and Prof Sykes now appreciate the folly of judging treatments before the results are in.
Postscript. Some reviews of the TV programmes
-
There has been some lively discussion of the BBC2 series on a forum of the James Randi Educational Foundation, on the BBC2/Open University site, on Ben Goldacres’s Badscience site, and at ebm-first.com.
- The Times TV critic was unenthusiastic.
“So having started out as a sceptic, Sykes ended the programme chirruping, like a born-again Christian, about how herbs contain complex combinations of chemicals that scientists cannot yet reproduce&”;
-
Simon Singh writes in the Daily Telegraph (14 Feb., 2006): "Did we really witness the ‘amazing power’ of acupuncture?
“A BBC series on unorthodox therapies was devoid of scepticism and rigour, says Simon Singh.”
“Although the second programme was indeed a rational look at the placebo effect, the other two episodes were little more than rose-tinted adverts for the alternative medicine industry.”
“For example, the scene showing a patient punctured with needles and undergoing open heart surgery left viewers with the strong impression that acupuncture was providing immense pain relief. In fact, in addition to acupuncture, the patient had a combination of three very powerful sedatives (midazolam, droperidol, fentanyl) and large volumes of local anaesthetic injected into the tissues on the front of the chest.
With such a cocktail of chemicals, the acupuncture needles were apparently cosmetic. In short, this memorable bit of telly was emotionally powerful, but scientifically meaningless in building a case for acupuncture. ”“This TV series pretended to be scientific and had the chance to set the record straight, but instead it chickened out of confronting the widespread failure of alternative medicine. ”
- Advertisers cash in. Sadly, but predictably, the programme on herbalism has
already been exploited by vendors of unproven treatments. While it is true that the programme did not actually assert that this herb cured AIDS, it certainly left the impression that it was good stuff. Here is an example: “As seen on BBC2”“In South Africa, BBC 2 TV presenter, Professor Kathy Sykes learnt of the herb Sutherlandia, which is being touted as a new weapon in the fight against HIV and ”
“It is with thanks to programmes such as Alternative Medicine shown on BBC 2 on Tuesday 7th February, and the work carried out by Professor Kathy Sykes that medicinal herbs can receive the acknowledgement they truly deserve, and this knowledge be passed on to the general public.”
“Bioharmony Sutherlandia is available from Revital Ltd in 60 x 300mg tablets for £19.99rrp. ”
- A groundbreaking experiment … or a sensationalised TV stunt?
Simon Singh, in The Guardian (25 March 2006) followed through with some more details on the BBC2 series. It’s not only pharmacologists who were unhappy about it. So were several of the people who advised the BBC and/or appeared on the programme.
“But this week scientists involved in the series have complained that elements of the programmes were misleading, the production team was uninformed, and scientists were used as “marionettes” ”
At the end of the first programme a “hugely ambitious” imaging experiment was shown with an enormous flourish. The outcome was, roughly speaking, that pushing needles into yourself produces a signal in the brain. Good heavens! Who’d have thought it? Even George Lewith, normally an apologist for CAM, was critical.
“The interpretation of the science in this particular programme was not good and was inappropriately sensationalised by the production team. I think all of us on the experiment felt like that.”
“The experiment was not groundbreaking, its results were sensationalised and there was insufficient time to analyse the data properly and so draw any sound conclusions. It was oversold and over-interpreted. We were encouraged to over-interpret, and proper scientific qualifications that might suggest alternative interpretations of the data appear to have been edited out of the programme.”
Edzard Ernst, professor of complementary medicine at Exeter University, and the main consultant for the series says:
“The BBC decided to do disturbingly simple storylines with disturbingly happy endings. But none of these stories is as simple as they presented, nor do they have such happy endings. Even when the evidence was outright negative, they somehow bent over backwards to create another happy ending.
“I feel that they abused me in a way. It was as if they had instructions from higher up that this had to be a happy story about complementary medicine without any complexity, and they used me to give a veneer of respectability.”The BBC, thus far, remain unapologetic
“We take these allegations very seriously and we strongly refute them.We used two scientific consultants for the series, Prof Ernst and Dr Jack Tinker, dean emeritus of the Royal Society of Medicine, both of whom signed off the programme scripts.”
This is the same Jack Tinker who, as Chairman of the Ethics Committee of the Dr Foster organisation, also approved their “COMPLEMENTARY therapists Guide 2004”, and the utterly uncritical complementary practioner directory. The ‘Dr Foster’ organisation is a commercial business that supplies "management information", "market research services", "marketing services" and "information for the public". Let’s hope their services in conventional health care are a bit more critical than their evaluation of CAM. Their “Guide to [CAM] therapies” repeats all the usual pseudo-scientific gobbledygook in a totally uncritical way.
Singh’s article ended with some quotations from this site, concerning Sutherlandia and AIDS, with the remark made above, highlighted: "Comments about Aids were irresponsible and potentially dangerous".
- Science accuses BBC of medical quackery
Lois Rogers, in the Sunday Times for 26th March, reports on the same topic.
“Ernst yesterday released the contents of a letter that he has written to Martin Wilson, the series producer, criticising him for promoting “US-style anti-science”.
He said he felt “abused” by the programme makers: “It was as if they had instructions from higher up that this had to be a happy story about complementary medicine without any complexity, and they used me to give a veneer of respectability.” “
“This is no longer a fringe game played by new age people,” said Colquhoun. “It is beginning to erode intellectual standards at real universities.”
Later a letter appeared in defence of the programmes. Investigation showed that this letter had actually been written by the BBC and not all of the ‘signatories’ had seen it.This is dealt with in a separate post, Alternative Medicine series: dirty tricks at the BBC?
