evidence
‘We know little about the effect of diet on health. That’s why so much is written about it’. That is the title of a post in which I advocate the view put by John Ioannidis that remarkably little is known about the health effects if individual nutrients. That ignorance has given rise to a vast industry selling advice that has little evidence to support it.
The 2016 Conference of the so-called "College of Medicine" had the title "Food, the Forgotten Medicine". This post gives some background information about some of the speakers at this event. I’m sorry it appears to be too ad hominem, but the only way to judge the meeting is via the track record of the speakers.


Quite a lot has been written here about the "College of Medicine". It is the direct successor of the Prince of Wales’ late, unlamented, Foundation for Integrated Health. But unlike the latter, its name is disguises its promotion of quackery. Originally it was going to be called the “College of Integrated Health”, but that wasn’t sufficently deceptive so the name was dropped.
For the history of the organisation, see
Don’t be deceived. The new “College of Medicine” is a fraud and delusion
The College of Medicine is in the pocket of Crapita Capita. Is Graeme Catto selling out?
The conference programme (download pdf) is a masterpiece of bait and switch. It is a mixture of very respectable people, and outright quacks. The former are invited to give legitimacy to the latter. The names may not be familiar to those who don’t follow the antics of the magic medicine community, so here is a bit of information about some of them.
The introduction to the meeting was by Michael Dixon and Catherine Zollman, both veterans of the Prince of Wales Foundation, and both devoted enthusiasts for magic medicne. Zollman even believes in the battiest of all forms of magic medicine, homeopathy (download pdf), for which she totally misrepresents the evidence. Zollman works now at the Penny Brohn centre in Bristol. She’s also linked to the "Portland Centre for integrative medicine" which is run by Elizabeth Thompson, another advocate of homeopathy. It came into being after NHS Bristol shut down the Bristol Homeopathic Hospital, on the very good grounds that it doesn’t work.
Now, like most magic medicine it is privatised. The Penny Brohn shop will sell you a wide range of expensive and useless "supplements". For example, Biocare Antioxidant capsules at £37 for 90. Biocare make several unjustified claims for their benefits. Among other unnecessary ingredients, they contain a very small amount of green tea. That’s a favourite of "health food addicts", and it was the subject of a recent paper that contains one of the daftest statistical solecisms I’ve ever encountered
"To protect against type II errors, no corrections were applied for multiple comparisons".
If you don’t understand that, try this paper.
The results are almost certainly false positives, despite the fact that it appeared in Lancet Neurology. It’s yet another example of broken peer review.
It’s been know for decades now that “antioxidant” is no more than a marketing term, There is no evidence of benefit and large doses can be harmful. This obviously doesn’t worry the College of Medicine.
Margaret Rayman was the next speaker. She’s a real nutritionist. Mixing the real with the crackpots is a standard bait and switch tactic.
Eleni Tsiompanou, came next. She runs yet another private "wellness" clinic, which makes all the usual exaggerated claims. She seems to have an obsession with Hippocrates (hint: medicine has moved on since then). Dr Eleni’s Joy Biscuits may or may not taste good, but their health-giving properties are make-believe.
Andrew Weil, from the University of Arizona
gave the keynote address. He’s described as "one of the world’s leading authorities on Nutrition and Health". That description alone is sufficient to show the fantasy land in which the College of Medicine exists. He’s a typical supplement salesman, presumably very rich. There is no excuse for not knowing about him. It was 1988 when Arnold Relman (who was editor of the New England Journal of Medicine) wrote A Trip to Stonesville: Some Notes on Andrew Weil, M.D..
“Like so many of the other gurus of alternative medicine, Weil is not bothered by logical contradictions in his argument, or encumbered by a need to search for objective evidence.”
This blog has mentioned his more recent activities, many times.
Alex Richardson, of Oxford Food and Behaviour Research (a charity, not part of the university) is an enthusiast for omega-3, a favourite of the supplement industry, She has published several papers that show little evidence of effectiveness. That looks entirely honest. On the other hand, their News section contains many links to the notorious supplement industry lobby site, Nutraingredients, one of the least reliable sources of information on the web (I get their newsletter, a constant source of hilarity and raised eyebrows). I find this worrying for someone who claims to be evidence-based. I’m told that her charity is funded largely by the supplement industry (though I can’t find any mention of that on the web site).
Stephen Devries was a new name to me. You can infer what he’s like from the fact that he has been endorsed byt Andrew Weil, and that his address is "Institute for Integrative Cardiology" ("Integrative" is the latest euphemism for quackery). Never trust any talk with a title that contains "The truth about". His was called "The scientific truth about fats and sugars," In a video, he claims that diet has been shown to reduce heart disease by 70%. which gives you a good idea of his ability to assess evidence. But the claim doubtless helps to sell his books.
Prof Tim Spector, of Kings College London, was next. As far as I know he’s a perfectly respectable scientist, albeit one with books to sell, But his talk is now online, and it was a bit like a born-again microbiome enthusiast. He seemed to be too impressed by the PREDIMED study, despite it’s statistical unsoundness, which was pointed out by Ioannidis. Little evidence was presented, though at least he was more sensible than the audience about the uselessness of multivitamin tablets.
Simon Mills talked on “Herbs and spices. Using Mother Nature’s pharmacy to maintain health and cure illness”. He’s a herbalist who has featured here many times. I can recommend especially his video about Hot and Cold herbs as a superb example of fantasy science.
Annie Anderson, is Professor of Public Health Nutrition and
Founder of the Scottish Cancer Prevention Network. She’s a respectable nutritionist and public health person, albeit with their customary disregard of problems of causality.
Patrick Holden is chair of the Sustainable Food Trust. He promotes "organic farming". Much though I dislike the cruelty of factory farms, the "organic" industry is largely a way of making food more expensive with no health benefits.
The Michael Pittilo 2016 Student Essay Prize was awarded after lunch. Pittilo has featured frequently on this blog as a result of his execrable promotion of quackery -see, in particular, A very bad report: gamma minus for the vice-chancellor.
Nutritional advice for patients with cancer. This discussion involved three people.
Professor Robert Thomas, Consultant Oncologist, Addenbrookes and Bedford Hospitals, Dr Clare Shaw, Consultant Dietitian, Royal Marsden Hospital and Dr Catherine Zollman, GP and Clinical Lead, Penny Brohn UK.
Robert Thomas came to my attention when I noticed that he, as a regular cancer consultant had spoken at a meeting of the quack charity, “YestoLife”. When I saw he was scheduled tp speak at another quack conference. After I’d written to him to point out the track records of some of the people at the meeting, he withdrew from one of them. See The exploitation of cancer patients is wicked. Carrot juice for lunch, then die destitute. The influence seems to have been temporary though. He continues to lend respectability to many dodgy meetings. He edits the Cancernet web site. This site lends credence to bizarre treatments like homeopathy and crystal healing. It used to sell hair mineral analysis, a well-known phony diagnostic method the main purpose of which is to sell you expensive “supplements”. They still sell the “Cancer Risk Nutritional Profile”. for £295.00, despite the fact that it provides no proven benefits.
Robert Thomas designed a food "supplement", Pomi-T: capsules that contain Pomegranate, Green tea, Broccoli and Curcumin. Oddly, he seems still to subscribe to the antioxidant myth. Even the supplement industry admits that that’s a lost cause, but that doesn’t stop its use in marketing. The one randomised trial of these pills for prostate cancer was inconclusive. Prostate Cancer UK says "We would not encourage any man with prostate cancer to start taking Pomi-T food supplements on the basis of this research". Nevertheless it’s promoted on Cancernet.co.uk and widely sold. The Pomi-T site boasts about the (inconclusive) trial, but says "Pomi-T® is not a medicinal product".
There was a cookery demonstration by Dale Pinnock "The medicinal chef" The programme does not tell us whether he made is signature dish "the Famous Flu Fighting Soup". Needless to say, there isn’t the slightest reason to believe that his soup has the slightest effect on flu.
In summary, the whole meeting was devoted to exaggerating vastly the effect of particular foods. It also acted as advertising for people with something to sell. Much of it was outright quackery, with a leavening of more respectable people, a standard part of the bait-and-switch methods used by all quacks in their attempts to make themselves sound respectable. I find it impossible to tell how much the participants actually believe what they say, and how much it’s a simple commercial drive.
The thing that really worries me is why someone like Phil Hammond supports this sort of thing by chairing their meetings (as he did for the "College of Medicine’s" direct predecessor, the Prince’s Foundation for Integrated Health. His defence of the NHS has made him something of a hero to me. He assured me that he’d asked people to stick to evidence. In that he clearly failed. I guess they must pay well.
Follow-up
A constant theme of this blog is that the NHS should not pay for useless treatments. By and large, NICE does a good job of preventing that. But NICE has not been allowed by the Department of Health to look at quackery.
I have the impression that privatisation of many NHS services will lead to an increase in the provision of myth-based therapies. That is part of the "bait and switch" tactic that quacks use in the hope of gaining respectability. A prime example is the "College of Medicine", financed by Capita and replete with quacks, as one would expect since it is the reincarnation of the Prince’s Foundation for Integrated Health.
One such treatment is acupuncture. Having very recently reviewed the evidence, we concluded that "Acupuncture is a theatrical placebo: the end of a myth". Any effects it may have are too small to be useful to patients. That’s the background for an interesting case study.
A colleague got a very painful frozen shoulder. His GP referred him to the Camden & Islington NHS Trust physiotherapy service. That service is now provided by a private company, Connect Physical Health.
That proved to be a big mistake. The first two appointments were not too bad, though they resulted in little improvement. But at the third appointment he was offered acupuncture. He hesitated, but agreed, in desperation to try it. It did no good. At the next appointment the condition was worse. After some very painful manipulation, the physiotherapist offered acupuncture again. This time he refused on the grounds that "I hadn’t noticed any effect the first time, because there is no evidence that it works and that I was concerned by her standards of hygiene". The physiotherapist then became "quite rude" and said that she would put down that the patient had refused treatment.
The lack of response was hardly surprising. NHS Evidence says
"There is no clinical evidence to show that other treatments, such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), Shiatsu massage or acupuncture are effective in treating frozen shoulder."
In fact it now seems beyond reasonable doubt that acupuncture is no more than a theatrical placebo.
According to Connect’s own web site “Our services are evidence-based”. That is evidently untrue in this case, so I asked them for the evidence that acupuncture was effective.
I’d noticed that in other places, Connect Physical Health also offers the obviously fraudulent craniosacral therapy (for example, here) and discredited chiropractic quackery. So I asked them about the evidence for their effectiveness too.
This is what they said.
|
Many thanks for your comments via our web site. In response, we thought you might like to access the sources for some of the evidence which underpins our MSK services: Integrating Evidence-Based Acupuncture into Physiotherapy for the Benefit of the Patient – you can obtain the information you require from www.aacp.org.uk The General Chiropractic Council www.gcc-uk.org/page.cfm We have also attached a copy of the NICE Guidelines. |
So, no Cochrane reviews, no NHS Evidence. Instead I was referred to the very quack organisations that promote the treatments in question, the Acupuncture Association of Chartered Physiotherapists, and the totally discredited General Chiropractic Council.
The NICE guidelines that they sent were nothing to do with frozen shoulder. They were the guidelines for low back pain which caused such a furore when they were first issued (and which, in any case, don’t recommend chiropractic explicitly).
When I pointed out these deficiencies I got this.
|
Your email below has been forwarded to me. I am sorry if you feel that that that information we pointed you towards to enable you to make your own investigations into the evidence base for the services provided by Connect Physical Health and your hospital did not meet with your expectations. ‘ ‘ ‘ Please understand that our NHS services in Camden were commissioned by the Primary Care Trust. The fully integrated MSK service model included provision for acupuncture and other manual therapy provided by our experienced Chartered Physiotherapists. If you have any problems with the evidence base for the use of acupuncture or manual therapy within the service, which has been commissioned on behalf of the GPs in Camden Borough, then I would politely recommend that you direct your observations to the clinical commissioning authorities and other professional bodies who do spend time evidencing best practice and representing the academic arguments. I am sure they will be pleased to pick up discussions with you about the relative merits of the interventions being procured by the NHS. Yours sincerely, Mark Mark Philpott BSc BSc MSc MMACP MCSP
Head of Operations, Community MSK Services Connect Physical Health 35 Apex Business Village Cramlington Northumberland NE23 7BF |
So, "don’t blame us, blame the PCT". A second letter asked why they were shirking the little matter of evidence.
|
In response to your last email, I would like to say that Connect does not wish to be drawn into a debate over two therapeutic options (acupuncture and craniosacral therapy) that are widely practiced [sic] within and outside the NHS by very respectable practitioners. You will be as aware, as Connect is, that there are lots of treatments that don’t have a huge evidence base that are practiced in mainstream medicine. Connect has seen many carefully selected patients helped by acupuncture and manual therapy (craniosacral therapy / chiropractic) over many years. Lack of evidence doesn’t mean they don’t work, just that benefit is not proven. Furthermore, nowhere on our website do we state that ALL treatments / services / modalities that Connect offer are ‘Evidence Based’. We do however offer many services that are evidence based, where the evidence exists. We aim to offer ‘choice’ to patients, from a range of services that are safe and delivered by suitably trained professionals and practitioners in line with Codes of Practice and Guidelines from the relevant governing bodies. Connect’s service provision in Camden is meticulously assessed and of a high standard and we are proud of the services provided. |
This response is so wrong, on so many levels, that I gave up on Mr Philpott at this point. At least he admitted implicitly that all of their treatments are not evidence-based. In that case their web site needs to change that claim.
If, by "governing bodies" he means jokes like the GCC or the CNHC then I suppose the behaviour of their employees is not surprising. Mr Philpott is evidently not aware that "craniosacral therapy" has been censured by the Advertising Standards Authority. Well he is now, but evidently doesn’t seem to give a damn.
Next I wrote to the PCT and it took several mails to find out who was responsible for the service. Three mails produced no response so I sent a Freedom of Information Act request. In the end I got some
"Connect PHC provide the Community musculoskeletal service for Camden. The specification for the service specifically asks for the provision of evidence based management and treatments see paragraph on Governance page 14 of attached.. Patients are treated with acupuncture as per the NICE Guidelines (May 2009) for the management of low back pain … . .. Chiropractors are not employed in the service and craniosacral therapy is not provided as part of the service either."
Another letter, pointing out that they were using acupuncture for things other than low back pain got no more information. They did send a copy of the contract with Connect. It makes no mention whatsoever of alternative treatments. It should have done, so part of the responsibility for the failure must lie with the PCT.
The contract does, however, say (page 18)
The service to be led by a lead clinician/manager who can effectively demonstrate ongoing and evidence-based development of clinical guidelines, policies and protocols for effective working practices within the service
In my opinion, Connect Physical Health are in breach of contract
Another example of Connect ignoring evidence
The Connect Physical Health web site has an article about osteoarthritis of the knee
Physiotherapy can be extremely beneficial to help to reduce the symptoms of OA. Treatments such as mobilizations, rehab exercises, acupuncture and taping can help to reduce pain, increase range of movement, increase muscle strength and aid return to functional activities and sports.
There is little enough evidence that physiotherapy does any of these things, but at least it is free of mystical mumbo-jumbo. Although at one time the claim for acupuncture was thought to have some truth, the 2010 Cochrane review concludes otherwise
Sham-controlled trials show statistically significant benefits; however, these benefits are small, do not meet our pre-defined thresholds for clinical relevance, and are probably due at least partially to placebo effects from incomplete blinding.
This conclusion is much the same as has been reached for acupuncture treatments of almost everything. Two major meta-analyses come to similar conclusions. Madsen Gøtzsche & Hróbjartsson (2009) and Vickers et al (2012) both conclude that if there is an effect at all (dubious) then it is too small to be noticeable to the patient. (Be warned that in the case of Vickers et al. you need to read the paper itself because of the spin placed on the results in the abstract.). These papers are discussed in detail in our recent paper.
Why is Connect Physical Health not aware of this?
Their head of operations told me (see above) that
"Connect does not wish to be drawn into a debate [about acupuncture and craniosacral therapy]".
That outlook was confirmed when I left a comment on their osteoarthritis post. This is what it looked like almost a month later.

Guess what? The comment has never appeared..
The attitude of Connect Physical Health to evidence is simply to ignore it if it gets in the way of making money, and to censor any criticism.
What have Camden NHS done about it?
The patient and I both complained to Camden NHS in August 2012. At first, they simply forwarded the complaints to Connect Physical Health with the unsatisfactory results shown above. It took until May 2013 to get any sort of reasonable response. That seems a very long time. In fact by the time the response arrived the PCT had been renamed a Clinical Commissioning Group (CCG) because of the vast top-down reorganisation inposed by Lansley’s Health and Social Care Act.
On 8 May 2013, this response was sent to the patient, Here is part of it.
|
I have received your email of complaint from the NHSNCL complaints department regarding your care. You raise some very clear concerns and I will attempt to address these in order. 1) The fact that you felt pressurised into having acupuncture is a concern as everybody should be given a choice. As part of the informed consent relating to acupuncture you should have been told about the treatment, it’s [sic] benefits and risks and then you sign to confirm you are happy to proceed. I understand that this was the case in your situation but I have reinforced that the consent is important and must be adhered to by the provider Connect Physical Health. There are clear standards of clinical practice that all Chartered Physiotherapists must follow which I will discuss further with the Connect Camden team Manager Nick Downing. I do disagree with you around acupuncture; there is no conclusive evidence for acupuncture in frozen shoulder but I have referenced a systematic review which concludes the studies were too small to draw any conclusions although shoulder function was significantly improved at 4 weeks (Green S et al. Acupuncture for shoulder pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005; 18: CD005319). There is a growing body of evidence supporting the use of acupuncture and until such time as there is specific evidence against it I don’t think we would be absolutely against the practice of this modality alongside other treatments. .Best wishes Strategy and Planning Directorate |
This response raises more questions than it answers.
For example, what is "informed consent" worth if the therapist is his/herself misinformed about the treatment? It is the eternal dilemma of alternative medicine that it is no use referring to well-trained practitioners, when their training has inculcated myths and untruths.
There is not a "growing body of evidence supporting the use of acupuncture". Precisely the opposite is true.
And the statement "until such time as there is specific evidence against it I don’t think we would be absolutely against the practice of this modality alongside" betrays a basic misunderstanding of the scientific process.
So I sent the writer of this letter a reprint of our paper, "Acupuncture is a theatrical placebo: the end of a myth" (the blog version alone has had over 12,000 page views). A few days later we had an amiable lunch together and we had a constructive discussion about the problems of deciding what should be commissioned and what shouldn’t.
It seems to me to be clear that CCGs should take better advice before boasting that they commission evidence-based treatments.
Postscript
Stories like this are worrying to the majority of physiotherapists who don’t go in for mystical mumbo-jumbo of acupuncture. One of the best is Neil O’Connell who blogs at BodyInMind. He tweeted
Physio fail, sigh RT@david_colquhoun: Yet more #acupuncture. Sold to the NHS by private contractor @ConnectPHC http://t.co/HylkwMCVTh
— Neil O'Connell (@NeilOConnell) June 10, 2013
It isn’t clear how many physiotherapists embrace nonsense, but the Acupuncture Association of Chartered Physiotherapists has around 6000 members, compared with 47,000 chartered physiotherapists (AACP), so it’s a smallish minority. The AACP claims that it is “Integrating Evidence-Based Acupuncture into Physiotherapy”. Like most politicians, the term “evidence-based” is thrown around with gay abandon. Clearly they don’t understand evidence.
Follow-up
12 June 2013
The Advertising Standards Authority has, one again, upheld complaints against the UCLH Trust, for making false claims in its advertising. This time, appropriately, it’s about acupuncture. Just about everything in their advertising leaflets was held to be unjustifiable. They’ve been in trouble before about false claims for homeopathy, hypnosis and craniosacral "therapy".
Of course all of these embarrassments come from one very small corner of the UCLH Trust, the Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine (previously known as the Royal London Homeopathic Hospital).
Why is it tolerated in an otherwise excellent NHS Trust? Well, the patron is the Queen herself (not Charles, aka the Quacktitioner Royal), She seems to exert more power behind the scenes than is desirable in In a constitutional monarchy
29 June 2013
I wrote to Dr Gill Gaskin about the latest ASA judgement against RLHIM. She is the person at the UCLH Trust who has responsibility for the quack hospital. She previously refused to do anything about the craniosacral nonsense that is promoted there. This time the ASA seems to have stung them into action at long last. I was told
|
In response to your question about proposed action: All written information for patients relating to the services offered by the Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine are being withdrawn for review in the light of the ASA’s rulings (and the patient leaflets have already been withdrawn). It will be reviewed and modified where necessary item by item, and only reintroduced after sign-off through the Queen Square divisional clinical governance processes and the Trust’s patient information leaflet team. With best wishes Gill Gaskin Dr Gill Gaskin |
It remains to be seen whether the re-written information is accurate or not.
The rules for advertising
The Advertising Standards Authority gives advice for advertisers about what’s permitted and what isn’t.
Acupuncture The CAP advice
Craniosacral therapy The CAP advice
Homeopathy The CAP advice and 2013 update
Chiropractic The CAP advice.
This article has been re-posted on The Winnower, so it now has a digital object identifier: DOI: 10.15200/winn.142935.50603
The latest news: eating red meat doesn’t do any harm. But why isn’t that said clearly? Alarmism makes better news, not only for journalists but for authors and university PR people too.
I’ve already written twice about red meat.
In May 2009 Diet and health. What can you believe: or does bacon kill you? based on the WCRF report (2007).
In March 2012 How big is the risk from eating red meat now? An update.
In the first of these I argued that the evidence produced by the World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF) for a causal relationship was very thin indeed. An update by WCRF in 2010 showed a slightly smaller risk, and weakened yet further the evidence for causality, though that wasn’t reflected in their press announcement.
The 2012 update added observations from two very large cohort studies. The result was that the estimates of risk were less than half as big as in 2009. The relative risk of dying from colorectal cancer was 1.21 (95% Confidence interval 1.04–1.42) with 50 g of red or processed meat per day, whereas in the new study the relative risk for cancer was only 1.10 (1.06-1.14) for a larger ‘dose’, 85 g of red meat. Again this good news was ignored and dire warnings were issued.
This reduction in size of the effect as samples get bigger is exactly what’s expected for spurious correlations, as described by Ioannidis and others. And it seems to have come true. The estimate of the harm done by red meat has vanished entirely in the latest study.
The EPIC study
This is the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition, another prospective cohort study, so it isn’t randomised [read the original paper]. And it was big, 448,568 people from ten different European countries. These people were followed for a median time of 12.7 years, and during follow-up 26,344 of them died.
The thing that was different about this paper was that red meat was found to pose no detectable risk, as judged by all-cause mortality. But this wasn’t even mentioned in the headline conclusions.
Conclusions: The results of our analysis support a moderate positive association between processed meat consumption and mortality, in particular due to cardiovascular diseases, but also to cancer.
To find the result you have to dig into Table 3.
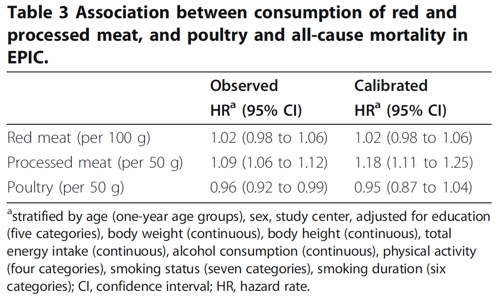
So, by both methods of calculation, the relative risk from eating red meat is negligible (except possibly in the top group, eating more than 160 g (7 oz) per day).
There is still an association between intake of processed meat and all-cause mortality, as in previous studies, though the association of processed meat with all-cause mortality, 1.09, or 1.18 depending on assumptions, is, if anything, smaller than was observed in the 2012 study, in which the relative risk was 1.20 (Table 2).
Assumptions, confounders and corrections.
The lowest meat eaters had only 13% of current smokers, but for the biggest red meat eaters it was 40%, for males. The alcohol consumption was 8.2 g/day for the lowest meat eaters but 23.4 g/day for the highest-meat group (the correlations were a bit smaller for women and also for processed meat eaters).
These two observations necessitate huge corrections to remove the (much bigger) effects of smoking and drinking if we want find the association for meat-eating alone. The main method for doing the correction is to fit the Cox proportional hazards model. This model assumes that there are straight-line relationships between the logarithm of the risk and the amount of each of the risk factors, e.g smoking, drinking, meat-eating and other risk factors. It may also include interactions that are designed to detect whether, for example, the effect of smoking on risk is or isn’t the same for people who drink different amounts.
Usually the straight-line assumption isn’t tested, and the results will depend on which risk factors (and which interactions between them) are included in the calculations. Different assumptions will give different answers. It simply isn’t known how accurate the corrections are when trying to eliminate the big effect of smoking in order to isolate the small effect of meat-eating. And that is before we get to other sorts of correction. For example, the relative risk from processed meat in Table 3, above, was 9% or 18% (1.09, or 1.18) depending on the outcome of a calculation that was intended to increase the accuracy of food intake records ("calibration").
The Conclusions of the new study don’t even mention the new result with red meat. All they mention is the risk from processed meat.
In this population, reduction of processed meat consumption to less than 20 g/day would prevent more than 3% of all deaths. As processed meat consumption is a modifiable risk factor, health promotion activities should include specific advice on lowering processed meat consumption.
Well, you would save that number of lives if, and only if, the processed meat was the cause of death. Too many epidemiologists, the authors pay lip service to the problem of causality in the introduction, but then go on to assume it in the conclusions. In fact the problem of causality isn’t even metnioned anywhere in either the 2012 study, or the new 2013 EPIC trial.
So is the risk of processed meat still real? Of course I can’t answer that. All that can be said is that it’s quite small, and as sample sizes get bigger, estimates of the risk are getting smaller. It wouldn’t be surprising if the risk from processed meat were eventually found not to exist, just as has happened for red (unprocessed) meat
The Japanese study
Last year there was another cohort study, with 51,683 Japanese. The results were even more (non-) dramatic [Nagao et al, 2012] than in the EPIC trial. This is how they summarise the results for the relative risks (with 95% confidence intervals).
"…for the highest versus lowest quintiles of meat consumption (77.6 versus 10.4 g/day) among men were 0.66 (0.45 — 0.97) for ischemic heart disease, 1.10 (0.84 — 1.43) for stroke and 1.00 (0.84 — 1.20) for total cardiovascular disease. The corresponding HRs (59.9 versus 7.5 g/day) among women were 1.22 (0.81 — 1.83), 0.91 (0.70 — 1.19) and 1.07 (0.90 — 1.28). The associations were similar when the consumptions of red meat, poultry, processed meat and liver were examined separately.
CONCLUSION: Moderate meat consumption, up to about 100 g/day, was not associated with increased mortality from ischemic heart disease, stroke or total cardiovascular disease among either gender."
In this study, the more meat (red or processed) you eat, the lower your risk of ischaemic heart disease (with the possible exception of overweight women). The risk of dying from any cardiovascular disease was unrelated to the amount of meat eaten (relative risk 1.0) whether processed meat or not.
Of course it’s possible that things which risky for Japanese people differ from those that are risky for Europeans. It’s also possible that even processed meat isn’t bad for you.
The carnitine study
The latest meat study to hit the headlines didn’t actually look at the effects of meat at all, though you wouldn’t guess that from the pictures of sausages in the headlines (not just in newspapers, but also in NHS Choices). The paper [reprint] was about carnitine, a substance that occurs particularly in beef, with lower amounts in pork and bacon, and in many other foods. The paper showed that bacteria in the gut can convert carnitine to a potentially toxic substance, trimethylamine oxide (TMAO). That harms blood vessels (at least in mice). But to show an effect in human subjects they were given an amount of carnitine equivalent to over 1 lb of steak, hardly normal, even in the USA.
The summary of the paper says it is an attempt to explain "the well-established link between high levels of red meat consumption and CVD [cardiovascular disease] risk". As we have just seen, it seems likely that this risk is far from being “well-established”. There is little or no such risk to explain.
It would be useful to have a diagnostic marker for heart disease, but this paper doesn’t show that carnitine or TMAO) is useful for that. It might also be noted that the authors have a maze of financial interests.
Competing financial interests Z.W. and B.S.L. are named as co-inventors on pending patents held by the Cleveland Clinic relating to cardiovascular diagnostics and have the right to receive royalty payments for inventions or discoveries related to cardiovascular diagnostics from Liposciences. W.H.W.T. received research grant support from Abbott Laboratories and served as a consultant for Medtronic and St. Jude Medical. S.L.H. and J.D.S. are named as co-inventors on pending and issued patents held by the Cleveland Clinic relating to cardiovascular diagnostics and therapeutics patents. S.L.H. has been paid as a consultant or speaker by the following companies: Cleveland Heart Lab., Esperion, Liposciences, Merck & Co. and Pfizer. He has received research funds from Abbott, Cleveland Heart Lab., Esperion and Liposciences and has the right to receive royalty payments for inventions or discoveries related to cardiovascular diagnostics from Abbott Laboratories, Cleveland Heart Lab., Frantz Biomarkers, Liposciences and Siemens.
The practical significance of this work was summed up the dietitian par excellence, Catherine Collins, on the BBC’s Inside Health programme.
Listen to Catherine Collins on carnitine.
She points out that the paper didn’t mean that we should change what we already think is a sensible diet.
At most, it suggests that it’s not a good idea to eat 1 lb steaks very day.
And the paper does suggest that it’s not sensible to take the carnitine supplements that are pushed by every gym. According to NIH
"twenty years of research finds no consistent evidence that carnitine supplements can improve exercise or physical performance in healthy subjects".
Carnitine supplements are a scam. And they could be dangerous.
Follow-up
Another blog on this topic, one from Cancer Research UK also fails to discuss the problem of causality. Neither does it go into the nature (and fallibility) of the corrections for counfounders like smoking and alcohol,. Nevertheless that, and an earlier post on Food and cancer: why media reports are often misleading, are a good deal more realistic than most newspaper reports.
The Scottish Universities Medical Journal asked me to write about the regulation of alternative medicine. It’s an interesting topic and not easy to follow because of the veritable maze of more than twenty overlapping regulators and quangos which fail utterly to protect the public against health fraud. In fact they mostly promote health fraud. The paper is now published, and here is a version with embedded links (and some small updates).
We are witnessing an increasing commercialisation of medicine. It’s really taken off since the passage of the Health and Social Security Bill into law. Not only does that mean having NHS hospitals run by private companies, but it means that “any qualified provider” can bid for just about any service. The problem lies, of course, in what you consider “qualified” to mean. Any qualified homeopath or herbalist will, no doubt, be eligible. University College London Hospital advertised for a spiritual healer. The "person specification" specified a "quallfication", but only HR people think that a paper qualification means that spiritual healing is anything but a delusion.
The vocabulary of bait and switch
First, a bit of vocabulary. Alternative medicine is a term that is used for medical treatments that don’t work (or at least haven’t been shown to work). If they worked, they’d be called “medicine”. The anti-malarial, artemesinin, came originally from a Chinese herb, but once it had been purified and properly tested, it was no longer alternative. But the word alternative is not favoured by quacks. They prefer their nostrums to be described as “complementary” –it sounds more respectable. So CAM (complementary and alternative medicine became the politically-correct euphemism. Now it has gone a stage further, and the euphemism in vogue with quacks at the moment is “integrated” or “integrative” medicine. That means, very often, integrating things that don’t work with things that do. But it sounds fashionable. In reality it is designed to confuse politicians who ask for, say, integrated services for old people.
Put another way, the salespeople of quackery have become rather good at bait and switch. The wikepedia definition is as good as any.
Bait-and-switch is a form of fraud, most commonly used in retail sales but also applicable to other contexts. First, customers are “baited” by advertising for a product or service at a low price; second, the customers discover that the advertised good is not available and are “switched” to a costlier product.
As applied to the alternative medicine industry, the bait is usually in the form of some nice touchy-feely stuff which barely mentions the mystical nonsense. But when you’ve bought into it you get the whole panoply of nonsense. Steven Novella has written eloquently about the use of bait and switch in the USA to sell chiropractic, acupuncture, homeopathy and herbal medicine: "The bait is that CAM offers legitimate alternatives, the switch is that it primarily promotes treatments that don’t work or are at best untested and highly implausible.".
The "College of Medicine" provides a near-perfect example of bait and switch. It is the direct successor of the Prince of Wales’ Foundation for Integrated Health. The Prince’s Foundation was a consistent purveyor of dangerous medical myths. When it collapsed in 2010 because of a financial scandal, a company was formed called "The College for Integrated Health". A slide show, not meant for public consumption, said "The College represents a new strategy to take forward the vision of HRH Prince Charles". But it seems that too many people have now tumbled to the idea that "integrated", in this context, means barmpottery. Within less than a month, the new institution was renamed "The College of Medicine". That might be a deceptive name, but it’s a much better bait. That’s why I described the College as a fraud and delusion.
Not only did the directors, all of them quacks, devise a respectable sounding name, but they also succeeded in recruiting some respectable-sounding people to act as figureheads for the new organisation. The president of the College is Professor Sir Graham Catto, emeritus professor of medicine at the University of Aberdeen. Names like his make the bait sound even more plausible. He claims not to believe that homeopathy works, but seems quite happy to have a homeopathic pharmacist, Christine Glover, on the governing council of his college. At least half of the governing Council can safely be classified as quacks.
So the bait is clear. What about the switch? The first thing to notice is that the whole outfit is skewed towards private medicine: see The College of Medicine is in the pocket of Crapita Capita. The founder, and presumably the main provider of funds (they won’t say how much) is the huge outsourcing company, Capita. This is company known in Private Eye as Crapita. Their inefficiency is legendary. They are the folks who messed up the NHS computer system and the courts computer system. After swallowing large amounts of taxpayers’ money, they failed to deliver anything that worked. Their latest failure is the court translation service.. The president (Catto), the vice president (Harry Brunjes) and the CEO (Mark Ratnarajah) are all employees of Capita.
The second thing to notice is that their conferences and courses are a bizarre mixture of real medicine and pure quackery. Their 2012 conference had some very good speakers, but then it had a "herbal workshop" with Simon Mills (see a video) and David Peters (the man who tolerates dowsing as a way to diagnose which herb to give you). The other speaker was Dick Middleton, who represents the huge herbal company, Schwabe (I debated with him on BBC Breakfast), In fact the College’s Faculty of Self-care appears to resemble a marketing device for Schwabe.
Why regulation isn’t working, and can’t work
There are various levels of regulation. The "highest" level is the statutory regulation of osteopathy and chiropractic. The General Chiropractic Council (GCC) has exactly the same legal status as the General Medical Council (GMC). This ludicrous state of affairs arose because nobody in John Major’s government had enough scientific knowledge to realise that chiropractic, and some parts of osteopathy, are pure quackery,
The problem is that organisations like the GCC function more to promote chiropractic than to regulate them. This became very obvious when the British Chiropractic Association (BCA) decided to sue Simon Singh for defamation, after he described some of their treatments as “bogus”, “without a jot of evidence”.
In order to support Singh, several bloggers assessed the "plethora of evidence" which the BCA said could be used to justify their claims. When, 15 months later, the BCA produced its "plethora" it was shown within 24 hours that the evidence was pathetic. The demolition was summarised by lawyer, David Allen Green, in The BCA’s Worst Day.
In the wake of this, over 600 complaints were made to the GCC about unjustified claims made by chiropractors, thanks in large part to heroic work by two people, Simon Perry and Allan Henness. Simon Perry’s Fishbarrel (browser plugin) allows complaints to be made quickly and easily -try it). The majority of these complaints were rejected by the GCC, apparently on the grounds that chiropractors could not be blamed because the false claims had been endorsed by the GCC itself.
My own complaint was based on phone calls to two chiropractors, I was told such nonsense as "colic is down to, er um, faulty movement patterns in the spine". But my complaint never reached the Conduct and Competence committee because it had been judged by a preliminary investigating committee that there was no case to answer. The impression one got from this (very costly) exercise was that the GCC was there to protect chiropractors, not to protect the public.
The outcome was a disaster for chiropractors, wno emerged totally discredited. It was also a disaster for the GCC which was forced to admit that it hadn’t properly advised chiropractors about what they could and couldn’t claim. The recantation culminated in the GCC declaring, in August 2010, that the mythical "subluxation" is a "historical concept " "It is not supported by any clinical research evidence that would allow claims to be made that it is the cause of disease.". Subluxation was a product of the fevered imagination of the founder of the chiropractic cult, D.D. Palmer. It referred to an imaginary spinal lesion that he claimed to be the cause of most diseases. .Since ‘subluxation’ is the only thing that’s distinguished chiropractic from any other sort of manipulation, the admission by the GCC that it does not exist, after a century of pretending that it does, is quite an admission.
The President of the BCA himself admitted in November 2011
“The BCA sued Simon Singh personally for libel. In doing so, the BCA began one of the darkest periods in its history; one that was ultimately to cost it financially,”
As a result of all this, the deficiencies of chiropractic, and the deficiencies of its regulator were revealed, and advertisements for chiropractic are somewhat less misleading. But this change for the better was brought about entirely by the unpaid efforts of bloggers and a few journalists, and not at all by the official regulator, the GCC. which was part of the problem. not the solution. And it was certainly not helped by the organisation that is meant to regulate the GCC, the Council for Health Regulatory Excellence (CHRE) which did nothing whatsoever to stop the farce.
At the other end of the regulatory spectrum, voluntary self-regulation, is an even worse farce than the GCC. They all have grand sounding "Codes of Practice" which, in practice, the ignore totally.
The Society of Homeopaths is just a joke. When homeopaths were caught out recommending sugar pills for prevention of malaria, they did nothing (arguably such homicidal advice deserves a jail sentence).
The Complementary and Natural Healthcare Council (CNHC) is widely know in the blogosphere as Ofquack. I know about them from the inside, having been a member of their Conduct and Competence Committee, It was set up with the help of a £900,000 grant from the Department of Health to the Prince of Wales, to oversee voluntary self-regulation. It fails utterly to do anything useful.. The CNHC code of practice, paragraph 15 , states
“Any advertising you undertake in relation to your professional activities must be accurate. Advertisements must not be misleading, false, unfair or exaggerated”.
When Simon Perry made a complaint to the CNHC about claims being made by a CNHC-registered reflexologist, the Investigating Committee upheld all 15 complaints. But it then went on to say that there was no case to answer because the unjustified claims were what the person had been taught, and were made in good faith.
This is precisely the ludicrous situation which will occur again and again if reflexologists (and many other alternative therapies) are “accredited”. The CNHC said, correctly, that the reflexologist had been taught things that were not true, but then did nothing whatsoever about it apart from toning down the advertisements a bit. They still register reflexologists who make outrageously false claims.
Once again we see that no sensible regulation is possible for subjects that are pure make-believe.
The first two examples deal (or rather, fail to deal) with regulation of outright quackery. But there are dozens of other quangos that sound a lot more respectable.
European Food Standards Agency (EFSA). One of the common scams is to have have your favourite quack treatment classified as a food not as a medicine. The laws about what you can claim have been a lot laxer for foods. But the EFSA has done a pretty good job in stopping unjustified claims for health benefits from foods. Dozens of claims made by makers of probiotics have been banned. The food industry, needless to say, objects very strongly to be being forced to tell the truth. In my view, the ESFA has not gone far enough. They recently issued a directive about claims that could legally be made. Some of these betray the previously high standards of the EFSA. For example you are allowed to say that "Vitamin C contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigue" (as long as the product contains above a specified amount of Vitamin C. I’m not aware of any trials that show vitamin C has the slightest effect on tiredness or fatigue, Although these laws do not come into effect until December 2012, they have already been invoked by the ASA has a reason not to uphold a complaint about a multivitamin pill which claimed that it “Includes 8 nutrients that can contribute to the reduction in tiredness and fatigue”
The Advertising Standards Authority (ASA). This is almost the only organisation that has done a good job on false health claims. Their Guidance on Health Therapies & Evidence says
"Whether you use the words ‘treatment’, ‘treat’ or ‘cure’, all are likely to be seen by members of the public as claims to alleviate effectively a condition or symptom. We would advise that they are not used"
"Before and after’ studies with little or no control, studies without human subjects, self-assessment studies and anecdotal evidence are unlikely to be considered acceptable"
"Before and after’ studies with little or no control, studies without human subjects, self-assessment studies and anecdotal evidence are unlikely to be considered acceptable"
They are spot on.
The ASA’s Guidance for Advertisers of Homeopathic Services is wonderful.
"In the simplest terms, you should avoid using efficacy claims, whether implied or direct,"
"To date, the ASA has have not seen persuasive evidence to support claims that homeopathy can treat, cure or relieve specific conditions or symptoms."
That seems to condemn the (mis)labelling allowed by the MHRA as breaking the rules.. Sadly, though, the ASA has no powers to enforce its decisions and only too often they are ignored. The Nightingale collaboration has produced an excellent letter that you can hand to any pharmacist who breaks the rules
The ASA has also judged against claims made by "Craniosacral therapists" (that’s the lunatic fringe of osteopathy). They will presumably uphold complaints about similar claims made (I’m ashamed to say) by UCLH Hospitals.
The private examination company Edexcel sets exams in antiscientific subjects, so miseducating children. The teaching of quackery to 16 year-olds has been approved by a maze of quangos, none of which will take responsibility, or justify their actions. So far I’ve located no fewer than eight of them. The Office of the Qualifications and Examinations Regulator (OfQual), Edexcel, the Qualifications and Curriculum Authority (QCA), Skills for Health, Skills for Care, National Occupational Standards (NOS), private exam company VTCT and the schools inspectorate, Ofsted.. Asking any of these people why they approve of examinations in imaginary subjects meets with blank incomprehension. They fail totally to protect tha public from utter nonsense.
The Department of Education has failed to do anything about the miseducation of children in quackery. In fact it has encouraged it by, for the first time, giving taxpayers’ money to a Steiner (Waldorf) school (at Frome, in Somerset). Steiner schools are run by a secretive and cult-like body of people (read about it). They teach about reincarnation, karma, gnomes, and all manner of nonsense, sometimes with unpleasant racial overtones. The teachers are trained in Steiner’s Anthroposophy, so if your child gets ill at school they’ll probably get homeopathic sugar pills. They might well get measles or mumps too, since Steiner people don’t believe in vaccination.
Incredibly, the University of Aberdeen came perilously close to appointing a chair in anthroposophical medicine. This disaster was aborted by bloggers, and a last minute intervention from journalists. Neither the university’s regulatory mechanisms. nor any others, seemed to realise that a chair in mystical barmpottery was a bad idea.
Trading Standards offices and the Office of Fair Trading.
It is the statutory duty of Trading Standards to enforce the Consumer Protection Regulations (2008) This European legislation is pretty good. it caused a lawyer to write " Has The UK Quietly Outlawed “Alternative” Medicine?". Unfortunately Trading Standards people have consistently refused to enforce these laws. The whole organisation is a mess. Its local office arrangement fails totally to deal with the age of the internet. The situation is so bad that a group of us decided to put them to the test. The results were published in the Medico-Legal Journal, Rose et al., 2012. "Spurious Claims for Health-care Products: An Experimental Approach to Evaluating Current UK Legislation and its Implementation". They concluded "EU directive 2005/29/EC is
largely ineffective in preventing misleading health claims for consumer products in
the UK"
Skills for Health is an enormous quango which produces HR style "competences" for everything under the son. They are mostly quite useless. But those concerned with alternative medicine are not just useless. They are positively harmful. Totally barmy. There are competences and National Occupational Standards for every lunatic made-up therapy under the sun. When I phoned them to discover who’d written them, I learned that the had been drafted by the Prince of Wales’ Foundation for Magic Medicine. And when I joked by asking if they had a competence for talking to trees, I was told, perfectly seriously, “You’d have to talk to LANTRA, the land-based organisation for that.”
That was in January 2008. A lot of correspondence with the head of Skills for Health got nowhere at all. She understood nothing and it hasn’t improved a jot.
This organisation costs a lot of taxpayers’ money and it should have been consigned to the "bonfire of the quangos" (but of course there was no such bonfire in reality). It is a disgrace.
The Quality Assurance Agency (QAA) is supposed to ensure the quality of university courses. In fact it endorses courses in nonsense alternative medicine and so does more harm than good. The worst recent failure of the QAA was in the case of the University of Wales: see Scandal of the University of Wales and the Quality Assurance Agency. The university was making money by validating thousands of external degrees in everything from fundamentalist theology to Chinese Medicine. These validations were revealed as utterly incompetent by bloggers, and later by BBC Wales journalist Ciaran Jenkins (now working for Channel 4).
The mainstream media eventually caught up with bloggers. In 2010, BBC1 TV (Wales) produced an excellent TV programme that exposed the enormous degree validation scam run by the University of Wales. The programme can be seen on YouTube (Part 1, and Part 2). The programme also exposed, incidentally, the uselessness of the Quality Assurance Agency (QAA) which did nothing until the scam was exposed by TV and blogs. Eventually the QAA sent nine people to Malaysia to investigate a dodgy college that had been revealed by the BBC. The trip cost £91,000. It could have been done for nothing if anyone at the QAA knew how to use Google.
The outcome was that the University of Wales stopped endorsing external courses, and it was soon shut down altogether (though bafflingly, its vice-chancellor, Marc Clement was promoted). The credit for this lies entirely with bloggers and the BBC. The QAA did nothing to help until the very last moment.
Throughout this saga Universities UK (UUK), has maintained its usual total passivity. They have done nothing whatsoever about their members who give BSc degrees in anti-scientific subjects. (UUK used to known as the Committee of Vice-Chancellors and Principals).
Council for Health Regulatory Excellence (CHRE), soon to become the PSAHSC,
Back now to the CHRE, the people who failed so signally to sort out the GCC. They are being reorganised. Their consultation document says
"The Health and Social Care Act 20122 confers a new function on the Professional Standards Authority for Health and Social Care (the renamed Council for Healthcare Regulatory Excellence). From November 2012 we will set standards for organisations that hold voluntary registers for people working in health and social care occupations and we will accredit the register if they meet those standards. It will then be known as an ‘Accredited Register’. "
They are trying to decide what the criteria should be for "accreditation" of a regulatory body. The list of those interested has some perfectly respectable organisations, like the British Psychological Society. It also contains a large number of crackpot organisations, like Crystal and Healing International, as well as joke regulators like the CNHC.
They already oversee the Health Professions Council (HPC) which is due to take over Herbal medicine and Traditional Chinese Medicine, with predictably disastrous consequences.
Two of the proposed criteria for "accreditation" appear to be directly contradictory.
Para 2.5 makes the whole accreditation pointless from the point of view of patients
2.5 It will not be an endorsement of the therapeutic validity or effectiveness of any particular discipline or treatment.
Since the only thing that matters to the patient is whether the therapy works (and is safe), accrediting of organisations that ignore this will merely give the appearance of official approval of crystal healing etc etc. This appears to contradict directly
A.7 The organisation can demonstrate that there either is a sound knowledge base underpinning the profession or it is developing one and makes that explicit to the public.
A "sound knowledge base", if it is to mean anything useful at all, means knowledge that the treatment is effective. If it doesn’t mean that, what does it mean?
It seems that the official mind has still not grasped the obvious fact that there can be no sensible regulation of subjects that are untrue nonsense. If it is nonsense, the only form of regulation that makes any sense is the law.
Please fill in the consultation. My completed return can be downloaded as an example, if you wish.
Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) should be a top level defender of truth. Its strapline is
"We enhance and safeguard the health of the public by ensuring that medicines and medical devices work and are acceptably safe."
The MHRA did something (they won’t tell me exactly what) about one of the most cruel scams that I’ve ever encountered, Esperanza Homeopathic Neuropeptide, peddled for multiple sclerosis, at an outrageous price ( £6,759 for 12 month’s supply). Needless to say there was not a jot of evidence that it worked (and it wasn’t actually homeopathic).
Astoundingly, Trading Standards officers refused to do anything about it.
The MHRA admit (when pushed really hard) that there is precious little evidence that any of the herbs work, and that homeopathy is nothing more than sugar pills. Their answer to that is to forget that bit about "ensuring that medicines … work"
Here’s the MHRA’s Traditional Herbal Registration Certificate for devils claw tablets.

The wording "based on traditional use only" has to be included because of European legislation. Shockingly, the MHRA have allowed them to relegate that to small print, with all the emphasis on the alleged indications. The pro-CAM agency NCCAM rates devil’s claw as "possibly effective" or "insufficient evidence" for all these indications, but that doesn’t matter because the MHRA requires no evidence whatsoever that the tablets do anything. They should, of course, added a statement to this effect to the label. They have failed in their duty to protect and inform the public by allowing this labelling.
But it gets worse. Here is the MHRA’s homeopathic marketing authorisation for the homeopathic medicinal product Arnicare Arnica 30c pillules
It is nothing short of surreal.

|

|
Since the pills contain nothing at all, they don’t have the slightest effect on sprains, muscular aches or bruising. The wording on the label is exceedingly misleading.
If you "pregnant or breastfeeding" there is no need to waste you doctor’s time before swallowing a few sugar pills.
"Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one". Since the pills contain nothing, it doesn’t matter a damn.
"If you overdose . . " it won’t have the slightest effect because there is nothing in them
And it gets worse. The MHRA-approved label specifies ACTIVE INGREDIENT. Each pillule contains 30c Arnica Montana
No, they contain no arnica whatsoever.

|

|
It truly boggles the mind that men with dark suits and lots of letters after their names have sat for hours only to produce dishonest and misleading labels like these.
When this mislabeling was first allowed, it was condemned by just about every scientific society, but the MHRA did nothing.
The Nightingale Collaboration.
This is an excellent organisation, set up by two very smart skeptics, Alan Henness and Maria MacLachlan. Visit their site regularly, sign up for their newsletter Help with their campaigns. Make a difference.
Conclusions
The regulation of alternative medicine in the UK is a farce. It is utterly ineffective in preventing deception of patients.
Such improvements as have occurred have resulted from the activity of bloggers, and sometime the mainstream media. All the official regulators have, to varying extents, made things worse.
The CHRE proposals promise to make matters still worse by offering "accreditation" to organisations that promote nonsensical quackery. None of the official regulators seem to be able to grasp the obvious fact that is impossible to have any sensible regulation of people who promote nonsensical untruths. One gets the impression that politicians are more concerned to protect the homeopathic (etc, etc) industry than they are to protect patients.
Deception by advocates of alternative medicine harms patients. There are adequate laws that make such deception illegal, but they are not being enforced. The CHRE and its successor should restrict themselves to real medicine. The money that they spend on pseudo-regulation of quacks should be transferred to the MHRA or a reformed Trading Standards organisation so they can afford to investigate and prosecute breaches of the law. That is the only form of regulation that makes sense.
Follow-up
The shocking case of the continuing sale of “homeopathic vaccines” for meningitis, rubella, pertussis etc was highlighted in an excellent TV programme by BBC South West. The failure of the MHRA and the GPC do take any effective action is a yet another illustration of the failure of regulators to do their job. I have to agree with Andy Lewis when he concludes
“Children will die. And the fault must lie with Professor Sir Kent Woods, chairman of the regulator.”
Systems biology is all the rage, No surprise then, to see the University of Westminster advertising a job for a systems biologist in the The Department of Molecular and Applied Biosciences. Well, no surprise there -until you read the small print.
Much has been wriiten here about the University of Westminster, which remains the biggest provider of junk sciencne degrees in the UK, despite having closed two of them.
Senior Lecturer in Systems BiologyUniversity of Westminster – Department of Molecular and Applied Biosciences, School of Life SciencesCavendish Site Salary £37,886 – £50,751 (Inc. LWA) The Department of Molecular and Applied Biosciences wishes to appoint a Senior Lecturer in Systems Biology. The post-holder will teach on the undergraduate and postgraduate degree programmes within the School of Life Sciences, particularly in the areas of Molecular Biology, Bioinformatics and/or statistics, establish their own and participate in ongoing research programmes and undertake external income generation activities. The candidate should have an active interest in bridging the gap between western life sciences and Chinese medicine using emerging systems biology approaches, specifically in metabolomics and proteomics with a goal of developing novel diagnostic technologies facilitating the creation of a personalised approach to medical care. They should therefore be willing to work closely with colleagues in the life sciences as well as with clinicians and clinical researchers from within the East Asian medical tradition. The post is available from 1st October 2010 or as soon as possible thereafter. The closing date for applications, together with a short statement on why you believe you are suitable for the position and a description of your research plans, is Monday 6th September 2010. Interviews are expected to be held later in September. Administrative contact (for queries only): Tayjal Tailor (t.tailor1@wmin.ac.uk) Reference Number: 50000360 Closing Date: Friday 3 September 2010 |
A note about systems biology
Systems biology is about about how whole organs behave, as opposed to single cells or single molecules, It has to be the ultimate aim of biology. There is one case in which this has been done with some success, That is the modelling of the behaviour of the whole heart by Denis Noble and his colleagues in the Phyiology department (now gone) in Oxford. They adopted a bottom up approach. They measured the currents that flow though many sorts of ion channels in single cells from various parts of the heart, and how individual cells communicate with each other. Starting from this solid basis, together with a lot of computer power, they were able to model successfully a lot of phenomena that occur in the whole heart, but can’t be investigated in single cells. For example their work cast light on abnormal heart rhythms like ventricular fibrillation, and on the effect of drugs on heart rhythm.
This work was mostly done before the term ‘systems biology" thought of. It was called physiology. It is impressive work, and systems biology became a fashionable buzzword among research administrators and funding agencies. Despite the amount of money thrown at the problem, I’m not aware of any success that remotely approaches Noble’s.. One reason for that is that people have not been willing to put in the groundwork. In the case of the heart, the models were built on -many years of basic research on the electrophysiology of single heart cells. People have tried to model from the top down, without doing the spade work first. There has developed a perception that computing power can compensate for lack of basic knowledge about things work. It can’t. The usual aphorism applies: garbage in, garbage out.
Here’s an example, which eas noted in the diary pages for 29 June, 2008. While in Edinbuurgh, to give a talk to the European Conference on Mathematical and Theoretical Biology, I noticed a poster. It described an attempt to model on a computer the entire metabolic network of yeast.
“81 of the 662 intracellular concentrations were defined . . . The remainder were set to the median concentration of c. 0.2 mM.”
Ahem. We didn’t know the concentrations so we just made them up so we could run the program.
It’s interesting that even people in the business seem to realise that even that it isn’t living up to the hype. The Fixing proteomics web site shows why.
Put another way, if you try to run before you can walk, you risk falling falling on your face.
For these reasons, it seems to me that that most attempts at system biology have been disappointing (please correct me if I’m wrong)
Systems biology for Chinese medicine
If systems biology suffers from trying to run before it can walk in regular biology, where at least something is known about the functions of cells, how much more true that must be of Chinese medicine. In Chinese medicine almost all the treatments have never been tested properly in man. The odds are that most don’t work at all, and some are very poisonous (not to mention the cruelty and destruction of endangered species that is involved in making some of their more bizarre medicines). The idea that you can explain it with systems biology, is ludicrous in the extreme.
One can’t imagine any vaguely competent biologist who’d want to touch a project as bizarre as this with a bargepole.
Eastmedicine
This advertisement stems presumably from EASTmedicine is the University of Westminster’s research centre for East Asian Sciences and Traditions in Medicine. The proclaimed aims are to focus on “understanding, development and evaluation of East Asian medicines as living traditions”. The director of EASTmedicine, Volker Scheid, is a herbalist and acupuncturist and, as such, a firm believer in alternative medicine. When he isn’t at the University he has a private practice, the Traditional Acupuncture Centre, in London.
The website of his private practice makes some astonishing claims
"Acupuncture is effective in the treatment of numerous conditions including headache, migraine, digestive problems, menstrual disorders, indeterminate aches and pains, asthma, hayfever, stress, tiredness, depression and anxiety. Also commonly treated are chronic conditions such as arthritis, back pain, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, eczema, sinusitis, high blood pressure and repetitive strain injuries."
These claims simply cannot be justified by any worthwhile evidence. It will be interesting to see what Trading Standards make of them.
Dr Scheid describes himself as a "scholar physician". Physician seems a rather pretentious description for someone whose qualifications are stated to be PhD, MBAcC, FRCHM. But in similar vein he describes himself thus "I am one of the West’s leading experts on Chinese medical formulas and treatment strategies".
Although Scheid sells acupuncture treatments to patients, he seems ro be more anthropologist than medical. In a discussion of two acupuncture papers
"From the Perspective of the Anthropologist –
Volker Scheid, London, UK
From a perspective anchored in the cultural studies of science, technology and medicine my main interest in these papers is their status as cultural artifacts that provide access to the lifeworlds of a particular research community. If any, life-world debate and argument marks sites of contestation." Forsch Komplementärmed 2007;14:371–375
Scheid shows not the slightest interest in whether acupuncture works other than as a placebo. Since he is selling acupuncture, he presumably starts from the premise that it works.
Volker Scheid has had a £205,000 Wellcome Trust for the History of Medicine Project Grant: 2009 2012; Treating the Liver: Towards a Transnational History of East Asian Medicine; There’s nothing wrong with writing the history of long-outdated systems of medicine, though one could hardly imagine that the history would be very impartial, when it is written by a true believer. Another taste of his style can be found in his paper on Globalising Chinese Medical Understandings of Menopause. There is lots of rather pretentious stuff about culture, but very little about what actually works, Towards the end of the paper we come to the usual feeble excuse.
" . . once traditional medicines allow themselves to be evaluated by biomedical research methods, the odds against receiving fair treatment are heavily stacked against them."
The translation of that into plain English is something like ‘when we test our treatments properly we find they don’t work, so we blame the methods and carry on with selling them anyway’.
Judging from its web site, EASTmedicine does not to do any serious clinical trials to test whether the treaments work in man, They just know that they do. But they are hoping to add some spurious scientific background to their dubious claims by hiring someone to do compuations that will cast no light whatsoever on the question that really matters, Do they work or not?
The agenda is made clear by the statement
EASTmedicine seeks to describe and analyse the dynamics of these transformations with a specific view of managing their integration into contemporary health care.
So it is just yet another group of people pushing to have unproven and disproved treatments accepted by real medicine.
The University of Westminster appears to be determined to make itself the laughing stock by persisting in promoting junk science at a time when most other universities have realise that the harm done to their reputations is not worth the income it generates, Plenty of it has been revealed here.
The vice-chancellor of Westminster, Prof Geoffrey Petts, made into the pages of Private Eye (see Crystal balls. Professor Petts in Private Eye when he announced that he wouldn’t get rid of the junk, but would make it more ‘scientific’. Well, credit where it’s due, They have dropped homeopathy. see The last BSc (Hons) Homeopathy closes! But look at what they still teach at Westminster University For 2010 they still off ten different “BSc (Hons)” degrees in pre-scientific forms of medicine. It will take more than a bit od talk about systems biology to make anyone believe that these courses have anything to do with science.
For example, look at some slides from their lectures on “energy medicine”, Westminster University BSc: “amethysts emit high yin energy”
More make-believe from the University of Westminster. This time it’s Naturopathy , or
Why degrees in Chinese medicine are a danger to patients
The Dean of the School of the Life Sciences, Jane Lewis, is an entirely respectable marine biologist. She has had the thankless task of merging the real science with the alternative medicine in a single school. I phoned her to get a reaction
" outcome of merger of the school and trying to bring various parts of the school together" " "things are much more rigorous than they were".
DC: "Why don’t you just phase it out?"
"I’m not in a poition to do that. i move things forward as seems best -for the whole school I have to say". We’re retaining those bits thatI think have some good standing -I see NICE has approved the use of acupuncture for lower back pain and some other bits and pieces so I see acupuncture as something that does have some standing, andwe make sure it rigorously taught"
"DCHave you looked at the stuff on naturopathy?" "Are amethysts emit high Yin energy still taught?" " i don’t think so".
It seems, as so often in this case, that the senior people don’t really know what’s being taught under their noses. Prof
Lewis says she has not read about the background
to the (unusually) daft advice from NICE. Neither has she read Barker Bausell’s book on acupuncture research. If she had done any of these things,I suspect she would not have such a high opinion of it as appears to be the case.
Bait and switch. Astonishingly there is a now a whole organisation devoted to the respectabalisation of Traditional Chinese Medicine Good Practice in Traditional Chinese Medicine Research in the Post-genomic Era It sounds nice and sciencey but, as usual, they are trying to run before they can walk. The first thing has to be to do good clinical trials to find out if there is anything there to be investigated. If, and only if, this is the case, would there be any case for fancy talk about "proteomics"
and "the post-genomic era".
I do hope that no funding agency would be fooled into parting with money on the basis of the present vacuous rhetoric.
Professor Lewis said that I have I have quoted things like "amethysts emit high Yin energy" out of context. There is a simple solution to that. I have asked Westminster to make available the entire contents of the courses. Then we shall all be able to see the context of what their sudents are being taught.
Follow up
A brief report of this matter has appeared in Times Higher Education. In a statement, the University of Westminster says “its research into Chinese medicine is following the lead of “top research institutions”. I’m not aware of anyhting quite like this from anywhere else. In any case, Westminster should be able to think for themselves.
It seems very reasonable to suggest that taxpayers have an interest in knowing what is taught in universities. The recent Pittilo report suggested that degrees should be mandatory in Acupuncture, Herbal Medicine and Traditional Chinese Medicine. So it seems natural to ask to see what is actually taught in these degrees, so one can judge whether it protects the public or endangers them.
Since universities in the UK receive a great deal of public money, it’s easy. Just request the material under the Freedom of Information Act.
Well, uh, it isn’t as simple as that.
Every single application that I have made has been refused. After three years of trying, the Information Commissioner eventually supported my appeal to see teaching materials from the Homeopathy "BSc" at the University of Central Lancashire. He ruled that every single objection (apart from one trivial one) offered by the universities was invalid. In particular, it was ruled that univerities were not "commercial" organisations for the purposes of the Act.
So problem solved? Not a bit of it. I still haven’t seen any of the materials from the original request because the University of Central Lancashire appealed against the decision and the case of University of Central Lancashire v Information Commissioner is due to be heard on November 3rd, 4th and 5th in Manchester. I’m joined (as lawyers say) as a witness. Watch this space.
UCLan is not the exception. It is the rule. I have sought under the Freedom of Information Act, teaching materials from UClan (homeopathy), University of Salford (homeopathy, reflexology and nutritional therapy), University of Westminster (homeopathy, reflexology and nutritional therapy), University of West of England, University of Plymouth and University of East London, University of Wales (chiropractic and nutritional therapy), Robert Gordon University Aberdeen (homeopathy), Napier University Edinburgh (herbalism).
In every single case, the request for teaching materials has been refused. And that includes the last three, which were submitted after the decision of the Information Commissioner. They will send things like course validation documents, but these are utterly uninformative box-ticking documents. They say nothing whatsoever about what is actually taught.
The fact that I have been able to discover quite a lot about what’s being taught owes nothing whatsoever to the Freedom of Information Act. It is due entirely to the many honest individuals who have sent me teaching materials, often anonymously. We should be grateful to them. Their principles are rather more impressive than those of their principals.
Since this started about three years ago, two of the universities, UCLan and Salford, have shut down entry to all of their CAM courses. And Westminster has shut two of them, with more rumoured to be closing soon. They are to be congratulated for that, but is far from being the end of the matter. The Department of Health, and some of the Royal Colleges, have yet to catch up with the universities, The Pittolo report, which recommends making degrees compulsory, is being considered by the Department of Health. The consultation ends on November 2nd: if you haven’t yet responded, please do so now (see how here, and here).
A common excuse: the university does not possess teaching materials (yes, really)
Several of the universities claim that they cannot send teaching materials, because they have no access to them. This happens when the university has accredited a course that is run by another, privately run, institution. The place that does the actual teaching, being private, is exempt from the Freedom of Information Act.
The ludicrous corollary of this excuse is that the university has accredited the course without checking on what is taught, and in some cases without even having seen a timetable.
The University of Wales
In fact the University of Wales doesn’t run courses at all. Like the (near moribund) University of London, it acts as a degree-awarding authority for a lot of Welsh Universities. It also validates a lot of courses in non-university institutions, 34 or so of them in the UK, and others scattered round the world.
Many of them are theological colleges. It does seem a bit odd that St Petersburg Christian University, Russia, and International Baptist Theological Seminary, Prague, should be accredited by the University of Wales.
They also validate the International Academy of Osteopathy, Ghent (Belgium), Osteopathie Schule Deutschland, the Istituto Superiore Di Osteopatia, Milan, the Instituto Superior De Medicinas Tradicionales, Barcelona, the Skandinaviska Osteopathögskolan (SKOS) Gothenburg, Sweden and the College D’Etudes Osteopathiques, Canada.
The 34 UK institutions include the Scottish School of Herbal Medicine, the Northern College of Acupuncture and the Mctimoney College of Chiropractic.
The case of the Nutritional Therapy course has been described already in Another worthless validation: the University of Wales and nutritional therapy. It emerged that the course was run by a grade 1 new-age fantasist. It is worth recapitulating the follow up.
What does the University of Wales say? So far, nothing. Last week I sent brief and polite emails to Professor Palastanga and to
Professor Clement to try to discover whether it is true that the validation process had indeed missed the fact that the course organiser’s writings had been described as “preposterous, made-up, pseudoscientific nonsense” in the Guardian.
So far I have had no reply from the vice-chancellor, but on 26 October I did get an answer from Prof Palastanga.
As regards the two people you asked questions about – J.Young – I personally am not familiar with her book and nobody on the validation panel raised any concerns about it. As for P.Holford similarly there were no concerns expressed about him or his work. In both cases we would have considered their CV’s as presented in the documentation as part of the teaching team. In my experience of conducting degree validations at over 16 UK Universities this is the normal practice of a validation panel.
I have to say this reply confirms my worst fears. Validation committees such as this one simply don’t do their duty. They don’t show the curiosity that is needed to discover the facts about the things that they are meant to be judging. How could they not have looked at the book by the very person that they are validating? After all that has been written about Patrick Holford, it is simply mind-boggling that the committee seems to have been quite unaware of any of it.It is yet another example of the harm done to science by an unthinking, box-ticking approach.
Incidentally, Professor Nigel Palastanga has now been made Pro Vice-Chancellor (Quality) at the University of Wales and publishes bulletins on quality control. Well well.
The McTimoney College of Chiropractic was the subject of my next Freedom of Information request to the University of Wales. The reasons for that are, I guess, obvious. They sent me hundreds of pages of validation documents, Student Handbooks (approx 50 pages), BSc (Hons) Chiropractic Course Document. And so on. Reams of it. The documents mostly are in the range of 40 to 100 pages. Tons of paper, but none of it tells you anyhing whatsover of interest about what’s being taught. They are a testament to the ability of universities to produce endless vacuous prose with
very litlle content.
They did give me enough information to ask for a sample of the teaching materials on particular topics. But I gor blank refusal, on the grounds that they didn’t possess them. Only McTimoney had them. Their (unusually helpful) Freedom of Information officer replied thus.
“The University is entirely clear about the content of the course but the day to day timetabling of teaching sessions is a matter for the institution rather than the University and we do not require or possess timetable information. The Act does not oblige us to request the information but there is no reason you should not approach McTimoney directly on this.”
So the university doesn’t know the timetable. It doesn’t know what is taught in lectures, but it is " entirely clear about the content of the course".
This response can be described only as truly pathetic.
Either this is a laughably crude form of obstruction of my request, or perhaps, even more frighteningly, the university really believes that its endless box-ticking documents actually provide some useful control of quality. Perhaps the latter interpretation is more charitable. After all, the QAA, CHRE, UUK and every HR department share similar delusions about what constitutes quality.
Perhaps it is just yet another consequence of having science run largely by people who have never done it and don’t understand it.
Validation is a business. The University of Wales validates no fewer than 11,675 courses altogether. Many of these are perfectly ordinary courses in universities in Wales, but they validate 594 courses at non-Welsh accredited institutions, an activity that earned them £5,440,765 in the financial year 2007/8. There’s nothing wrong with that if they did the job properly. In the two cases I’ve looked at, they haven’t done the job properly. They have ticked boxes but they have not looked at what’s being taught or who is teaching it.
The University of Kingston
The University of Kingston offers a “BSc (Hons)” in acupuncture. In view of the fact that the Pittilo group has recommended degrees in acupuncture, there is enormous public interest in what is taught in such degrees, so I asked.
They sent the usual boring validation documents and a couple of sample exam papers . The questions were very clinical, and quite beyond the training of acupuncturists. The validation was done by a panel of three, Dr Larry Roberts (Chair, Director of Academic Development, Kingston University), Mr Roger Hill (Accreditation Officer, British Acupuncture Accreditation Board) and Ms Celia Tudor-Evans (Acupuncturist, College of Traditional Acupuncture, Leamington Spa). So nobody with any scientific expertise, and not a word of criticism.
|
Further to your recent request for information I am writing to advise that the University does not hold the following requested information: (1) Lecture handouts/notes and powerpoint presentations for the following sessions, mentioned in Template 3rd year weekend and weekday course v26Aug2009_LRE1.pdf (a) Skills 17: Representational systems + Colour & Sound ex. Tongue feedback 11 (b) Mental Disease + Epilepsy Pulse feedback 21 (c) 18 Auricular Acupuncture (d) Intro. to Guasha + practice Cupping, moxa practice Tongue feedback 14 (2) I cannot see where the students are taught about research methods and statistics. I would like to see Lecture handouts/notes and PowerPoint presentations for teaching in this area, but the ‘timetables’ that you sent don’t make clear when or if it is taught. The BSc Acupuncture is delivered by a partner college, the College of Integrated Chinese Medicine (CICM), with Kingston University providing validation only. As such, the University does not hold copies of the teaching materials used on this course. In order to obtain copies of the teaching materials required you may wish to contact the College of Integrated Chinese Medicine directly. This completes the University’s response to your information request. |
So again we see that Kingston has validated the course but has not seen a timetable, far less what is taught. My reply was thus
|
Yes I am exceedingly unhappy about it. The university attaches its name to the course so it must obviously be able to get the material simply by asking for it (I’m surprised that the university should endorse a course without knowing what is taught on it, but that’s another matter). I request formally that you obtain this material. If necessary please read this as a formal appeal. |
I await with interest. In every single case so far, the internal review has merely confirmed the initial refusal. It means a bit of a delay before the case goes to the Information Commisssioner’s Office.
Napier University Edinburgh
Napier University runs a "BSc (Hons) Herbal medicine". (brochure here). Since herbal medicine is a subject of the Pittilo recommendations, there is enormous public interest in what they teach. So I asked, under the Freedom of Information (Scotland) Act (2002). They sent quite quickly validation and accreditation documents, some examination papers, timetables and lecture lists.
The validation was the usual vacuous box-ticking stuff though it did reveal that the course “made extensive use of techniques such as tongue and pulse diagnosis”, which are well known phoney diagnosis methods, about as much use as a pendulum (as used at Westminster University).
As at Kingston University, the exam papers they chose to send were mostly "pretend doctor" stuff. One of them was
Discuss the herbal practitioner’s role in the management of IHD [ischaemic heart disease)
How one would like to see what the students said, and, even more one would like to see the model answer. Amateurs who try to treat potentially serious conditions are a danger to the public.
So then we got to the interesting bit, the request for actual teaching materials.
|
I have looked at the material that you sent and I’d now like to make the following supplementary request (A) Lecture notes/handouts and powerpoint slides for the following small smaple of lectures HRB09102 Materia Medica 4 Materia Medica 3 HRB08103 Clinical Medicine and Diagnosis 4 (HRB09104) HRB09100 Materia Medica & Herbal Practice BSc Herbal Medicine : Materia Medica HRB07102 Lastly, I can see nowhere in the timetable, lectures that deal with Research methods, clinical trial design and statistics. |
No prizes for guessing the result Total refusal to send any of them. To make matters worse, the main grounds for refusal were the very "commercial interests" which, after careful legal examination, the Information Commissioner (for England and Wales) had decided were invalid. They say too that "The public interest in withholding the information is greater than the public interest in its release".. It is hard to see how the public interest is served by concealing from the people who pay for the degrees what is taught on degrees that Pittilo wants to make compulsory. [Download the whole response]
The matter is now under internal appeal (read the appeal) and eventually we shall find out whether the Scottish Information Commissioner backs the judgement.
Robert Gordon University Aberdeen
This case has particular interest because the Vice-Chancellor of Robert Gordon University is Professor Michael Pittilo, chair of the highly contentious steering group that recommended degress in CAM. Robert Gordon University (RGU) does not teach herbal medicine or acupuncture. But they do run An Introduction to Homeopathy. All the degrees in homeopathy have closed. It is perhaps the daftest and most discredited of all the popular forms of Magic Medicine. But Professor Pittilo thinks it is an appropriate subject to teach in his university.
So again I asked for information under the Freedom of Information (Scotland) Act 2002. They sent me quite quckly a list of the powerpoint presentations used on the courses [download it]. I asked for a small sample of the powerpoints. And again the university did not possess them!
|
I should like to see only the following three powerpoint presentations in the first instance, please.
Please can you let me know also who produced the powerpoints. (1) Evidence for homeopathy I note that you will have to request them but since they are being offered as part of a course offered by RGU, so RGU is responsible for their quality, I presume that this should cause no problem. |
The request was refused on much the same grounds as used by Napier University. As usual, the internal review just confirmed the initial proposal (but dropped the obviously ludicrous public interest defence). The internal review said
“it is mainly the quality of our courses (including course material) and teaching which has given us the position of "the best modern university in Scotland"
I am bound to ask, if the university is so proud of its course material, why is it expending so much time and money to prevent anyone from seeing a small sample of it?
My appeal has been sent to the Scottish Information Commissioner [download the appeal].
What are vice-chancellors thinking about?
I find it very difficult to imagine what is going through the heads of vice-chancellors who run courses in mumbo-jumbo. Most of them don’t believe a word of it (though Michael Pittilo might be an exception) yet they foist it on their students. How do they sleep at night?
Recently the excellent Joe Collier wrote a nice BMJ blog which applauded the lack of respect for authority in today’s students, Joe Collier says good riddance to old-fashioned respect. I couldn’t resist leaving a comment.
|
I couldn’t agree more. There is nothing quite so unnerving as being addressed as “Sir”. It is an advantage of age that you realise what second-rate people come to occupy very grand positions. Still odder since, if occasionally they are removed for incompetence, they usually move to an even grander position. I guess that when I was an undergraduate, I found vice-chancellors somewhat imposing. That is, by and large, not a view that survives closer acquaintance. |
Should teaching materials be open to the public?
There is only one university in the world that has, as a matter of policy, made all of its teaching material open to the public, that is the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). I can recommend strongly course 18.06, a wonderful set of lectures on Linear Algebra by Gilbert Strang. (It is also a wonderful demonstration of why blackboards may be better than Powerpoint for subjects like this). Now they are on YouTube too.
A lot of other places have made small moves in the same direction, as discussed recently in Times Higher Education, Get it Out in the Open.
Now the OU is working with other British universities to help them develop and share open course materials. In June, at the celebrations for the 40th anniversary of the OU, Gordon Brown announced funding to establish the Support Centre for Open Resources in Education at the OU, as part of a £7.8 million grant designed to enhance the university’s national role.
The funding follows a separate grant of £5.7 million from the Higher Education Funding Council for England for universities across the sector to make thousands of hours of free learning materials available.
Much material is available on the web, when individual teachers choose to place it there, but at the same time there is a move in the other direction. In particular, the widespread adoption of Moodle has resulted in a big decrease in openness. Usually you have to be registered on a course to see the material. Even other people in the university can’t see it. I think that is a deplorable development (so, presumably, does HEFCE).
Conclusion
I was told by the Univerity of Kingston that
“The course is one which the University has validated and continues to be subject to the University’s quality assurance procedures, such as internal subject reviews, annual monitoring and external examining”
The only conclusion to be drawn from this is that “quality arrurance procedures” work about as well in universities as they did in the case of baby Peter. No doubt they were introduced with worthy aims. But in practice they occupy vast amounts of time for armies of bureaucrats, and because the brain does not need to be engaged they end up endorsing utter nonsenes. The system is broken.
Resistance is futile. You can see a lot of the stuff here
It is hard to keep secrets in the internet age. Thanks to many wonderful people who have sent me material. you can see plenty of what is taught, despite the desperate attempts of vice-chancellors to conceal it. Try these links.
What is actually taught
Chinese medicine -acupuncture gobbledygook revealed
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=1950
Consultation opens on the Pittilo report: help top stop the Department of Health making a fool of itself
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=2007
Why degrees in Chinese medicine are a danger to patients
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=2043
More make-believe from the University of Westminster. This time its Naturopathy
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=1812
The last BSc (Hons) Homeopathy closes! But look at what they still teach at Westminster University.
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=1329
The opposite of science
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=1191
Bad medicine. Barts sinks further into the endarkenment.
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=1143
A letter to the Times, and progress at Westminster
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=984
Nutritional Fairy Tales from Thames Valley University
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=260
Westminster University BSc: amethysts emit high yin energy
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=227
References for Pittilo report consultation
A very bad report: gamma minus for the vice-chancellor
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=235
The Times (blame subeditor for the horrid title)
http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/comment/columnists/guest_contributors/article4628938.ece
Some follow up on the Times piece
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=251
The Health Professions Council breaks its own rules: the result is nonsense
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=1284
One month to stop the Department of Health endorsing quackery. The Pittilo questionnaire,
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=2310
An excellent submission to the consultation on statutory regulation of alternative medicine (Pittilo report)
https://www.dcscience.net/?p=2329
Follow-up
On 17th June 2009, 15 months after Singh’s article was published, the British Chiropractic Association (BCA) has finally produced its evidence (though only after enormous pressure from bloggers [download as pdf]..
Jack of Kent has already made some comments from the legal point of view.
As expected, the list of references they give is truly pathetic, The list of 29 references has nine about infantile colic, four about asthma (two of which refer to osteopathy not chiropractic). three about the safety of chiropractic (a contentious matter but not the point here) and three about the safety of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (an important matter but utterly irrelevant here).
Let’s look at the papers about colic. Most are in obscure alternative medicine journals, not easily available, but the BCA’s own synopsis is sufficient for now.
-
Klougart N, Nilsson N and Jacobsen J (1989) Infantile Colic Treated by Chiropractors: A Prospective Study of 316 Cases, J Manip Physiol Ther,12:281-288. [ download thr reprint]. As evidence it is about as useless as the infamous Spence study so beloved of homeopaths. There was no control group at all. It simply follows 316 babies and found that most of them eventually got better. Well, they do, don’t they? It is a sign of the pathetic standard of research in chiropractic that anyone should think this paper worth mentioning at all.
-
Mercer, C. and Nook, B. in the Proceedings of the 5th Biennial Congress of the World Federation of Chiropractic (1999) (so no peer review, for what that is worth). “Resolution of symptoms [of infantile colic] in 93% of infants treated with spinal manipulation”.. This sounds as useless as Klougart et al. Why only 93% one wonders? Every parent knows that 100 percent of babies stop crying eventually.
-
Wiberg et al. J Manip Physiol Ther, 1999, 242 517 – 522. This one was randomised (but not blind) and showed that spinal manipulation was as effective as dimethicone for colic. [Download pdf]
I expect that all that means is that dimethicone doesn’t work either. -
Hayden & Mullinger (2006) Complementary Ther. clin. Prac. “This preliminary study suggested that cranial osteopathic treatment can benefit infants with colic”. So. (a) preliminary and (b) not chiropractic.
-
Hipperson AJ (2004) Clinical Chiropractic 11, 122 – 129. A report of two case studies, so essentially worthless as evidence The journal isn’t even listed in Pubmed.
-
Browning M. Miller, J. Clinical Chiropractic (2008) 11, 122—129 [download pdf] Comparison of the short-term effects of chiropractic spinal manipulation and occipito-sacral decompression in the treatment of infant colic: A single-blinded, randomised, comparison trial. This paper just compared two different chiropractic methods. It shows that both are equally effective, or equally plausibly, both are equally ineffective.
- Leach RA (2002) J Manip Physiol Ther, 25, 58 -62. Merely two case reports and they refer to usie of a mechanical device, not the usual chiropractic manipulation.
-
Miller J (2007) Clinical Chiropractic 10, 139—146 Cry babies: A framework for chiropractic care [download pdf]. No evidence at all here. It isn’t a research paper.
- Nilsson N. 1985 Eur J Chiropr 33, 264 – 255 Infantile colic and chiropractic. “Respondents to a questionnaire revealed that 91% of of infants improved after 2 – 3 manipulations”. Again, no controls. So, babies stop crying, eventually.
That seems to be the best they can do. What they don’t do is mention any of the papers that contradict their claims. They cite Sackett et al. (1996) as their criterion for what constitutes evidence, That paper says “Evidence based medicine is the conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of current best evidence”. That means all the evidence. So why, for example, is there no mention of Olafsdottir et al. (2001), “Randomised controlled trial of infantile colic treated with chiropractic spinal manipulation”. That is one of the few really good papers in the area. It compared chiropractic treatment of babies for colic with placebo treatment (the nurse just held the baby for 10 minutes (the time the chiropractor took). The conclusion was
Conclusion Chiropractic spinal manipulation is no more effective than placebo in the treatment of infantile colic. This study emphasises the need for placebo controlled and blinded studies when investigating alternative methods to treat unpredictable conditions such as infantile colic.
More on this dishonest selectivity can be found at Holfordwatch.
No doubt there will soon be more analyses of what passes, in the eyes of the BCA, for evidence, The nine papers they cite for colic are truly pathetic. Not a single one of them amounts to anything that would be recognised as evidence in the real world. And papers that do provide real evidence are not mentioned.
Follow-up
As always, the blogs provided a very fast response to a document that appeared only late last night. And, as always, these unpaid people, working in their spare time, have done a far better job than the suits at the BCA (or NICE).
Here are some of them.
“A Review of The BCA’s Evidence for Chiropractic”. Martin on The Lay Scientist.
“The BCA have no evidence that chiropractic can help with ear infections” on Gimpy’s blog.
“Examining the BCA’S ‘Plethora’ of Evidence”. Unity, at Ministry of Truth.
“British Chiropractic Association and The Plethora of Evidence for Paediatric Asthma”. On Evidence Matters
“BCA Statement Baffles Blogger”. James Cole on jdc325’s Weblog
“Careful, BCA, you might slip a disk. The British Chiropractic Association may need to hire a chiropractor to work on themselves: they’re shoveling so hard they’re likely to hurt their backs.” In the US magazine, Discover.
“British Chiropractic Association (BCA) demonstrate what evidence-based medicine isn’t” at Holfordwatch. This one shows nicely how the BCA fail to apply their own standard of evidence, based on Sackett et al. (1996).
“The BCA’s worst day”. “Today has not been a good day for the British Chiropractic Association”. Jack of Kent summarises the demolition, in 24 hours, of the BCA’s ‘evidence’
Laurie Taylor says it all.
Could this bit (dated 18 June) in Laurie Taylor’s saga of the University of Poppleton possibly have been inspired by the Singh affair?
|
Sweet smell of success Our campus burst into colour last week as members of the Department of Aromatherapy, led by Professor Gwendolyn Frisson, paraded round the former administrative block happily waving bunches of wild carrot, devil’s claw, cinnamon leaf and lime blossom. What sparked the herbal celebration was the news of a full retraction from the journalist on the Poppleton Evening News who had described the department in print as “a hotchpotch of untestable propositions and unproven medical interventions”. The journalist in question, Simeon Rainbow, explained in his published retraction that he’d had time to reflect on the department’s reaction to his original article and now fully recognised that there was no better way of deciding upon the scientific validity of practices such as aromatherapy than by threatening anyone who denied such validity with an enormously costly libel action. Professor Frisson said that she welcomed the retraction. She would now be able to return with renewed enthusiasm to her research on the beneficial effects of grated angelica root on patients with advanced encephalitis. |
A flood of complaints against chiropractors has arrived at the General Chiropractic Council (GCC) in the wake of the British Chiropractic Association (BCA) v Singh affair. It is really rather beautiful that people have put some such enormous effort into writing complaints for no gain to themselves.
My own paltry two complaints to the GCC produced an interesting reaction. Yesterday I was told by the GCC
“Under the provisions of the General Chiropractic Council (Investigating Committee) Rules
2000 (“the Rules”), the Committee is required to invite you to make a statement of evidence in relation to your complaint by way of statutory declaration or affidavit. If you wish to, you can discuss your complaint with a solicitor who acts on behalf of the Committee who could help you draft a statement of evidence that meets the requirements of the Rules. The General Chiropractic Council will pay for the Investigating Committee solicitor’s costs and will reimburse you for any fee you subsequently pay for having your witness statement sworn at a location convenient to you.”
Naturally I shall take up this offer. If the same offer is made to everyone who complained (must be approaching 600), the legal fees incurred by the GCC would presumably be enough to bankrupt them. No wonder they are wriggling.
Here is a letter sent by the GCC’s Chief Executive and Registrar, Margaret Coats, a couple of days ago. It reached me by more than one route, but it is already on the web anyway, on Richard Lanigan’s site, Told you the General Chiropractic Council would find a way to dismiss the complaints. “Protecting the public” my arse! Protecting themselves more like it.. (The GCC has been under attack from within for some time, though mainly because some chiropractors think it regulates too much, not too little)

The bit that is especially interesting is para 2

In quangos like the GCC, complaints don’t necessarily get considered at all. First they go to an investigating committee (IC) which has to decide if there is a ‘case to answer’. Now the GCC wants that criterion to be changed to ‘realistic prospect of success’. Given the GCC’s attitude to evidence it is hard to imagine that any complaint will have a ‘realistic prospect of success’.
The second idea is even more grotesque. The GCC want to be able to dismiss without consideration rafts of complaints where in their opinion, referral to the Professional Conduct Committee (PCC) ‘is not required in the public interest. Or, more likely, not required in the interests of the GCC.
Will the Privy Council acquiesce in this disgraceful attempt to evade complaints? Wel, until January 2008, Graham Donald was a senior civil Servant at the Privy Council bit he now works for the GCC. That must help.
The GCC has been contacted by several Trading Standards Offices too, after complaints made to them about chiropractors. . A response was sent by the GCC on 5 June [download the whole response]. It includes
“It is important to emphasise that the GCC doesn’t claim that chiropractors ‘treat’ asthma, headaches (including migraine) and infant colic. It is possible that chiropractic care may help to alleviate the symptoms of some of these conditions.”
What on earth is that meant to mean?
One hopes that Trading Standards officers are too smart to be taken in by weasel words like that.
The attitude of the GCC to evidence is amply illustrated by the fact that they have said that the rather crude myths known as craniosacral therapy and applied kinesiology fall within their definition of evidence-based care.
Any organisation that can say that is clearly incompetent.
Follow-up
Peter Dixon is a chiropractor. He is chair of the General Chiropractic Council (GCC). He was also a member of the hotly-disputed NICE low back pain guidance group that endorsed (you guessed it) the use of chiropractic, a decision that has led to enormous criticism of the standards of the National Institute of health and Clinical Excellence (NICE).
As a consequence largely of the decision of the British Chiropractic Association (BCA) to sue Simon Singh for defamation, there has been an unprecedented interest taken in the claims made by chiropractors in general.
Peter Dixon has a problem because something like 600 individual complaints about unjustified health claims have been sent to the GCC. Even when a web site does not claim to be able to benefit things like asthma and colic, a phone call may reveal that claims are made in private (one of the many complaints to the GCC concerns such behaviour by two practices belonging to, ahem, Peter Dixon Associates).
The crucial question is, as always, one of evidence. The BCA claim to have a plethora of evidence for their claims, but they have been strangely reluctant to produce it. In fact evidence is cited on the “Your first visit” page on Dixon’s site.

At the bottom we see “How effective is Chiropractic?”.

That sounds very impressive indeed: . ” . . . patients who received chiropractic treatment improved by 70% more than those given hospital out-patient.”
But hang on. If we look at the paper, Meade et al., 1990 [download reprint], we see that Figure 2 looks like this.
Several things jump out. First, the Oswestry disability index scale runs for 0 to 100, but scores are plotted only from 0 to 35, so the size of the effects are exaggerated. Second, there are no error bars on the points. Third there is essentially no advantage for chiropractic at all when all patients are taken together (top graph). Fourth, and most important, the patients who were followed up for two years (bottom graph) seem to show a slight advantage for chiropractic but on average, the effect is 7 percent (on the 100 point scale, NOT 70 percent as claimed on the web site of Peter Dixon Associates.
What sort of mistake was made?
The abstract of the paper itself says “A benefit of about 7% points on the Oswestry scale was seen at two years.” How did this become “improved by 70% more”?
It could have been simple a typographical error, but that seems unlikely, Who’d boast about a 7% improvement?
Perhaps it is a question of relative versus absolute change. The Figure does not show the actual scores on the 100 point scale, but rather the change in score, relative to a questionnaire given just before starting treatment. If we look at the lower part of the Figure, restricted to those patients who stayed with the trail for 2 years (by this time 28% of the patients had dropped out), we see that there is a reduction in score (improvement) of about 10 points on the 100 point scale with hospital treatment (not a very impressive response). The improvement with those sent to private chiropractic clinics was about seven points bigger. So a change from 10 to 17 is a 70 percent change. What’s wrong with that?
What’s wrong is that it is highly misleading, as relative changes often are. Imagine that the hospital number had been 7 points and the chiropractic number had been 14 (both out of 100). That would mean that both treatments had provided very modest benefits to the patients. Would it then be fair to describe the chiropractic patients as have improved by 100 percent more than the hospital patients, when in fact neither got much benefit? Of course it would not. To present the results in this way would be highly deceptive.
Put another way, a 70% increase in a trivial effect is still pretty trivial.
That isn’t all either. The paper has been analysed in some detail on the ebm-first site. The seven point difference on a 100 point scale, though it may be real, is too small to be ‘clinically significant’ In other words the patient would scarcely notice such a small change. Another problem lies in the nature of the comparison. Patients were, quite properly, allocated at random to chiropractic or to to hospital treatment. BUT the comparion was very from blind. one group was treated in hospital. The other group was sent to private chiropractic clinics. The trivial 7 point difference could easily be as much to do with the thickness of the carpets rather than any effect of spinal manipulation.
What this paper really tells you is that neither treatment is very effective and that there is little to choose between them.
It is really most unfortunate that the chairman of the GCC should show himself to be so careless about evidence at a time when the evidence for the claims of chiropractors is under inspection as never before. It does not add to their case for criticising Simon Singh and it does not add to one’s confidence in the judgement of the NICE guidance group.
Follow-up
The Pain Society revolt. A letter has been sent from several distinguished members of the British Pain Society to its President and Council.
“We, the undersigned, call upon the President of the British Pain Society to issue a statement to NICE and to the press condemning outright the conclusions of the recent UK National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidelines . . .”
The sigificance of this letter is that the present president of the British Pain Society is Professor Paul Watson who was a member of the NICE guidance group that produced the recommendations which have engendered such criticism. He was clinical advisor to the guidance group. There is a video of Paul Watson talking about back pain, that seems to me to illustrate very well the problem with the guidance. He says it is a huge problem (everyone knows that) and that something must be done, but he doesn’t say what. There is no admission that, in very many cases, nobody knows what to do. It is exactly this sort of hubris that that makes the NICE report so bad,
One caustic comment on the letter says
“We are led by a physiotherapist! A Professor who cannot even interpret straight forward evidence when it is presented to him on a plate.
Who’s going to be the next BPS President? A Hospital Porter?”
The publication of Gilbey’s paper and my editorial in the New Zealand Medical Journal (NZMJ) led to a threat of legal action by the NZ Chiropractors’ Association Inc for alleged defamation. After publishing a defiant editorial, the editor of the NZMJ offered chiropractors the chance to put their case.
In the last issue of NZMJ (22 Aug 2008) three letters appeared. One was from Brian Kelly, (President, New Zealand College of Chiropractic) [download letter]. One was from Karl Bale (CEO/Registrar, Chiropractic Board New Zealand) [download letter], and one was from Simon Roughan (Registered Chiropractor and Acting President of the New Zealand Chiropractors’ Association) [download letter].
In the current issue (5 September 2008) Gilbey, Ernst and I responded.{download Gilbey response] [download Ernst response].
Here’s mine. The printed version differs in minor ways [download pdf]
| I’m grateful for the opportunity to reply to the defences of chiropractic from Kelly1, Roughan2 and Bale3 in your last issue.
I’d like first to deal with the minor matter of titles, before getting on to the more important question of vidence. I notice that Brian Kelly signs his letter “Dr Brian Kelly B App Sci (Chiro)” in his letter to NZMJ. He seems to be a bit less careful in his use of titles on his own school’s web site where his president’s welcome4 is signed simply “Dr Brian Kelly”, a title he adopts in at least three other places. Karl Bale3 (CEO/Registrar, Chiropractic Board New Zealand) points out that “Failure to qualify the use of the title ‘Doctor’ may contravene the provisions of the Medical Practitioners Act 1995”. One wonders whether Bale has done anything to stop Kelly’s apparent breaches of this rule? This example makes on wonder whether the Chiropractic Board take its responsibilities seriously? It seems often to be the case that ‘voluntary self-regulation’ doesn’t work, because there are too many vested interests. Karl Bale points out that some ruthless sales methods characteristic of chiropractic are also contrary to the Chiropractic Board’s code of ethics. One would hope their well-known antipathy to vaccination and to medicine as a whole were also considered unethical. These practices seem to continue so the the code of ethics It seems to me quite remarkable that none of the letters mentions the ‘subluxation’ that lies at the heart of their subject6. Could that be because they are reluctant to admit openly that it is a mere metaphysical concept, that no one can see or define? It is sad that so many patients are subjected to X-rays in search of this phantom idea. It is this metaphysical nature of chiropractic that separates it quite clearly from science. Brian Kelly says “How can any reader take seriously, anything suggested by a writer who opines that a 19th Century journalist possessed superior “intellectual standards” to “the UK’s Department of Health” and “several university vice chancellors”. The views of the Davenport Leader on chiropractic were mild compared with those of the great H.L. Mencken (1924)7 who wrote “This preposterous quackery flourishes lushly in the back reaches of the Republic, and begins to conquer the less civilized folk of the big cities….” The problem is that the Department of Health is full of arts graduates who may be very good at classics but can’t understand the nature of evidence. And the UK has one vice-chancellor, a geomorphologist, who defends a course in his university that teaches that “amethysts emit high yin energy”8 I’ll admit, though, that perhaps ‘intellect’ is not what’s deficient in this case, but rather honesty. Your correspondents seem to confuse the duration of a course with its intellectual content. You can study homeopathy for years too, but after all that they are still treating sick people with medicines that contain no medicine. Anyone who works in a university knows that you can easily get accreditation for anything whatsoever if you choose the right people to sit on the committee. I have seen only too many of these worthless pieces of paper. “Amethysts emit high yin energy”8 was part of an accredited course (at the University of Westminster) too. Need I say more? Now to the real heart of the problem, namely the question of evidence. Brian Kelly says that the book by Singh and Ernst9 shows “extreme bias”, but what that book actually shows is an extremely scrupulous regard for evidence, Ernst is in a better position to do this than just about anyone else. He has qualified and practised both regular and alternative medicine, and he was appointed to his present position, as professor of complementary and alternative medicine to assess the evidence. Perhaps most importantly of all, his position allows him to do that assessment with complete lack of bias because, unlike Kelly, his livelihood does not depend on any particular outcome of the assessment. I’m afraid that what Kelly describes as “extreme bias” is simply a display of pique because it has turned out that when all the evidence is examined dispassionately, the outcome is not what chiropractors hoped. The fact of the matter is that when you look at all of the evidence, as Singh & Ernst do, it is perfectly clear that chiropractic is at best no better than conventional treatments even for back pain. For all other conditions its benefits fail to outweigh its risks – contrary to the many claims by chiropractors. Both the New Zealand and the UK governments have got themselves into an impossible position by giving official recognition to chiropractic before the evidence was in. Since the conventional manipulative treatments are cheaper, and may be well be safer, and because they involve no quasi-religious ideas like “subluxation” or “innate intelligence”, the only reasonable conclusion is that there is no need for chiropractic to exist at all. They do nothing they do that could not be done as well by medical practitioners and physiotherapists. What will governments do about that, I wonder? David Colquhoun 1. Kelly, B. New Zealand College of Chiropractic response to 2. Roughan, S. Setting the record straight: New Zealand Chiropractors’ Association response letter. NZMJ 22 3. Bale, 4. http://www.nzchiro.co.nz/about_president.php 6. http://www.chirobase.org/01General/chirosub.html 7. http://www.geocities.com/healthbase/mencken_chiro.html 8. http://dcscience.net/?p=227 9. Singh S, Ernst E. Trick or Treatment. Bantam Press; 2008 |
The wars within chiropractic
Although the chiropractors seem to be rather upset by the criticisms that have been levelled against them, the most interesting war is not between chiropractors and people who think that medicine should not be based on metaphysics. It’s the war within chiropractic itself.
The internecine wars within chiropractic have been going almost from the day it was invented. The (ex-)insider’s view gives us a rare insight into what chiropractic schools actually do. Now support has come from a rather unexpected quarter. An article by five chiropractors has just appeared by Murphy et al. (Chiropractic & Osteopathy, 2008, 16:10).
Although the authors declare that they have “a financial interest in the success” of chiropractic, the changes that they propose are so drastic that, if implemented, tthey would leave little left to distinguish chiropractic from, say, physiotherapy. The authors ask the very pertinent question, ‘why is it that podiatry (chiropody in the UK) is well accepted and chiropractic remains on the controversial fringe of medicine?.. Here are some quotations.
“It is also vital that those chiropractors who dogmatically oppose common public health practices, such as immunization [15] and public water fluoridation, cease such unfounded activity.”
“We are concerned that the common perception (which is well supported, in our experience) that chiropractors are only interested in “selling” a lifetime of chiropractic visits may be one of the primary factors behind our low standing in the minds of members of the public [2].”
“One of the problems that we encounter frequently in our interaction with chiropractic educational institutions is the perpetuation of dogma and unfounded claims. Examples include the concept of spinal subluxation as the cause of a variety of internal diseases and the metaphysical, pseudo-religious idea of “innate intelligence” flowing through spinal nerves, with spinal subluxations impeding this flow. These concepts are lacking in a scientific foundation [27] [28] [29] and should not be permitted to be taught at our chiropractic institutions as part of the standard curriculum. Much of what is passed off as “chiropractic philosophy” is simply dogma [30], or untested (and, in some cases, untestable) theories [27] which have no place in an institution of higher learning, except perhaps in an historical context.”
“The Council on Chiropractic Education requirement of 250 adjustments forces interns to use manipulation on patients whether they need it or not, and the radiographic requirement forces interns to take radiographs on patients whether they need them or not.”
“They [podiatrists] did not invent a “lesion” and a “philosophy” and try to force it on the public. They certainly did not claim that all disease arose from the foot, without any evidence to support this notion. The podiatric medical profession simply did what credible and authoritative professions do [32] – they provided society with services that people actually wanted and needed.”
“In the beginning, DD Palmer invented a lesion, and a theory behind this lesion, and developed a profession of individuals who would become champions of that lesion. This is not what credible professions do.”
“In the interim it [chiropractic] has seen its market share dwindle from 10% of the population [4] to 7.5% [3] [42]. Even amongst patients with back pain, the proportion of patients seeing chiropractors dropped significantly between 1987 and 1997, a period of time in which the proportion seeing both medical doctors and physical therapists increased [43].”
“When an individual consults a member of any of the medical professions, it is reasonably expected that the advice and treatment that he or she receives is based in science, not metaphysics or pseudoscience.”
“The chiropractic profession has an obligation to actively divorce itself from metaphysical explanations of health and disease as well as to actively regulate itself in refusing to tolerate fraud, abuse and quackery, which are more rampant in our profession than in other healthcare professions [46].”
“Podiatric medicine is a science-based profession dedicated to the diagnosis and treatment of foot disorders. Foot reflexology is a metaphysically-based group consisting of non-physicians who believe that many physical disorders arise from the foot. Podiatrists have rejected foot reflexology as an unproven and unscientific practice, and do not consider it part of mainstream podiatric practice.”
“We must finally come to the painful realization that the chiropractic concept of spinal subluxation as the cause of “dis-ease” within the human body is an untested hypothesis [27]. It is an albatross around our collective necks that impedes progress.”
All this, remember, comes from five chiropractors. That looks like all out war between their view of chiropractic and that taught in New Zealand College of Chiropractic, and, in the UK by the three chiropractic colleges in the UK.
Follow-up
A report in the New Zealand Herald (18 September 2008) is rather relevant to all this.
Chiropractor to apologise after patient has stroke
A chiropractor has been recommended to apologise to a woman patient who suffered a stroke after he treated her.
The case report is here.
The Advertising Standards Authority has had a bit to say about chiropractors too.