cancer
|
Maurice Nathan Saatchi, Baron Saatchi is an advertising man who, with his brother, Charles Saatchi ("‘why tell the truth when a good lie will do?), became very rich by advertising cigarettes and the Conservative party. After his second wife died of cancer he introduced a private members bill in the House of Lords in 2012. The Medical Innovation Bill came back to the Lords for its second reading on 24 October 2014. |
 |
The debate was deeply depressing: very pompous and mostly totally uninformed. You would never have guessed that the vast majority of those who understand the problem are against the bill. The Bill has failed to win the support of The British Medical Association, The Motor Neurone Disease Association, the Royal College of Physicians, the Royal College of Surgeons, the Medical Research Society, the Royal College of Radiologists, The Medical Defence Union, the Academy of Medical Sciences, the Royal College of Pathologists, the Royal College of General Practitioners, the Academy for Healthcare Science, the Wellcome Trust, Action Against Medical Accidents, and patient advocacy charities Health Watch and the Nightingale Collaboration, and others. Conservative MP Sarah Wollaston, a former GP, has “very serious concerns” about it.
Grief is not a good basis for legislation. In the Daily Telegraph, Lord Saatchi attributes the lack of a "cure for cancer" to fear of litigation.
“Any deviation by a doctor is likely to result in a verdict of guilt for medical negligence. The law defines medical negligence as deviation from that standard procedure. But as innovation is deviation, non-deviation is non-innovation. This is why there is no cure for cancer.”
This statement is utterly bizarre. Evidently Lord Saatchi knows much more about how to sell cigarettes than he does about how to discover new drugs. The reason there is no cure is that it’s a very difficult problem. It has nothing to do with litigation
Almost every medical organisation, and many lawyers, have pointed out the flaws in his ideas,. But slick, and often mendacious, advertising of his cure has deceived many of our scientifically-illiterate parliamentarians, and the bill is making progress
Lord Saatchi’s Bill would allow uncontrolled testing of treatments on any patient. It is not limited to cancer, nor to terminally ill patients (though some amendments, yet to be accepted, might change that). This sort of uncontrolled experimentation is likely to impede advances in treatment rather than to help them. And the vagueness of the wording of the bill could lead to an increase in litigation, rather than the intended decrease.
It is no coincidence that the legion of cancer quacks is in favour of the bill. It opens the door to their nonsense. Big pharma is likely to benefit too, because they will be able to sell improperly tested drugs with little or no effectiveness and immunity from prosecution if they do harm.
For more information about the Bill, see the excellent site, Stop the Saatchi Bill. There are sections on Dispelling Myths, on Professional Concerns, and on the many good articles and blogs that have pointed out the many problems with the bill.
Two recent articles are well worth reading
Saatchi’s ‘Medical Innovation Bill’ will benefit lawyers and charlatans, not patients, by neurologist David Nicholl. And it’s particularly interesting that the Telegraph’s arch-conservative, Peter Oborne has come out strongly against the bill, in The ‘Saatchi Bill’ is dangerous and will bring nothing but harm. I can’t agree with his opening words ("Lord Saatchi is rightly regarded as a national treasure. In his early days he was the advertising genius who played a fundamental role in selling the Thatcherite message"), but I agree entirely with
“The PR campaign distorts the facts, exploiting ignorance and desperation to plant false hope in the rich soil of multiple fallacies.”
“Quacks will be given free rein. No “treatment” is so loopy (or potentially dangerous) that the Saatchi Bill won’t protect doctors who prescribe or administer it from prosecution.”
“The propagation of falsehoods and fallacies surrounding and arising from this Bill will have a corrosive effect on medical ethics and society as a whole.”
Lord Saatchi, who proposed the bill said “To prevent more needless cancer deaths, doctors must be free to innovate”. This statement shows he has no idea of the efforts that go into cancer research. We are doing our best, but it is a very hard problem. In some areas (like breast cancer) there have been big advances. In others areas (e.g. pancreatic or ovarian cancer) there has not yet been any perceptible progress. It will take many more years of hard scientific work. Individual doctors tinkering with speculative untested treatments will not solve the problem.
- The only people who will benefit from the bill will be lawyers, quacks and big pharma.
- “Innovation” is undefined –the bill is based on the myth that there exists a miraculous cure waiting to be found. Sadly, the probability of this happening is vanishingly small.
- To some extent, medicine is victim of its own hype. The public feels it has a right to demand the latest miracle cure. Too often, they don’t exist.
- There is no need for the bill because doctors can already prescribe whatever they want. The Medical Defence Union says it has no reason to think that doctors are deterred from innovating by the fear of litigation.
- The bill won’t help to discover new cures –in fact it is more likely to hinder it, especially if it deters people from joining properly organised clinical trials. The bill will generate many separate anecdotes which may or may not be published. That’s the worst possible way to do research.
- The bill removes protections from patients and is more likely to increase litigation than reduce it.
- Anyone unlucky enough to get cancer is immediately a target for a legion of quacks trying to sell you crazy “treatments”. There is nothing to stop even the lunatic fringe of alternative medicine, homeopaths, promoting their sugar pills. There are, disgracefully, several hundred homeopaths with medical degrees –all a quack has to do is to ask another quack doctor to endorse their daft ideas.
- For untested treatments there is, by definition, no reason to think they’ll do more good than harm. The cancer surgeon, Michael Baum said, rightly, that in cases of terminal cancer "there will be many patients we can’t help. but none we can’t harm".
As a result of tweeting about the bill, I got a call on 21 October from RT TV (UK) asking me speak on the Saatchi Bill. That was a pleasure. Here it is (done from home, on Skype).
And on the day of the Lords debate (24 October 2014) I was asked to talk again about the Saatchi Bill, on the flagship Radio 4 morning news programme, Today. It was only a 3 minute interview with Mishal Husain, but it was unopposed so I managed to get in the main points.
![]() Click to play interview
Click to play interview
This is the Today Programme studio.

The BBC doesn’t pay you, but it’s good at driving you to/from the studio, though the cars are unnecessarily posh. On the way home, I had my first ever ride in an all-electric Tesla. It does 0 – 60 in 4.2 seconds but costs £50k -more than twice the price of a Prius.

|

|
Follow-up
25 October 2014 A summary of the misunderstandings in yesterday’s House of Lords debate: What the Lords Missed.
Here is a record of a couple of recent newspaper pieces. Who says the mainstream media don’t matter any longer? Blogs may be in the lead now when it comes to critical analysis. The best blogs have more expertise and more time to read the sources than journalists. But the mainstream media get the message to a different, and much larger, audience.
The Observer ran a whole page interview with me as part of their “Rational Heroes” series. I rather liked their subtitle [pdf of article]
“Professor of pharmacology David Colquhoun is the take-no-prisoners debunker of pseudoscience on his unmissable blog”
It was pretty accurate apart from the fact that the picture was labelled as “DC in his office”. Actually it was taken (at the insistence of the photographer) in Lucia Sivilotti’s lab.

Photo by Karen Robinson.
The astonishing result of this was that on Sunday the blog got a record 24,305 hits. Normally it gets 1,000-1,400 hits a day . between posts, fewer on Sunday, and the previous record was around 7000/day
A week later it was still twice normal. It remains to be seen whether the eventual plateau stays up.
I also gained around 1000 extra followers on twitter, though some dropped away quite soon, and 100 or so people signed for email updates. The dead tree media aren’t yet dead. I’m happy to say.
3 June 2013
Perhaps as a result of the foregoing piece, I got asked to write a column for The Observer, at barely 48 hours notice. This is the best I could manage in the time. The web version has links.
This attracted the usual "it worked for me" anecdotes in the comments, but I spent an afternoon answering them. It seems important to have a dialogue, not just to lecture the public. In fact when I read a regular scientific paper, I now find myself looking for the comment section. That may say something about the future of scientific publishing.
It is for others to judge how succesfully I engage with the public, but I was quite surprised to discover that UCL’s public engagement unit, @UCL_in_public, has blocked me on twitter. Hey ho. They have 1574 follower and I have 7597. I wish them the best of luck.
Follow-up
This article has been re-posted on The Winnower, so it now has a digital object identifier: DOI: 10.15200/winn.142935.50603
The latest news: eating red meat doesn’t do any harm. But why isn’t that said clearly? Alarmism makes better news, not only for journalists but for authors and university PR people too.
I’ve already written twice about red meat.
In May 2009 Diet and health. What can you believe: or does bacon kill you? based on the WCRF report (2007).
In March 2012 How big is the risk from eating red meat now? An update.
In the first of these I argued that the evidence produced by the World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF) for a causal relationship was very thin indeed. An update by WCRF in 2010 showed a slightly smaller risk, and weakened yet further the evidence for causality, though that wasn’t reflected in their press announcement.
The 2012 update added observations from two very large cohort studies. The result was that the estimates of risk were less than half as big as in 2009. The relative risk of dying from colorectal cancer was 1.21 (95% Confidence interval 1.04–1.42) with 50 g of red or processed meat per day, whereas in the new study the relative risk for cancer was only 1.10 (1.06-1.14) for a larger ‘dose’, 85 g of red meat. Again this good news was ignored and dire warnings were issued.
This reduction in size of the effect as samples get bigger is exactly what’s expected for spurious correlations, as described by Ioannidis and others. And it seems to have come true. The estimate of the harm done by red meat has vanished entirely in the latest study.
The EPIC study
This is the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition, another prospective cohort study, so it isn’t randomised [read the original paper]. And it was big, 448,568 people from ten different European countries. These people were followed for a median time of 12.7 years, and during follow-up 26,344 of them died.
The thing that was different about this paper was that red meat was found to pose no detectable risk, as judged by all-cause mortality. But this wasn’t even mentioned in the headline conclusions.
Conclusions: The results of our analysis support a moderate positive association between processed meat consumption and mortality, in particular due to cardiovascular diseases, but also to cancer.
To find the result you have to dig into Table 3.
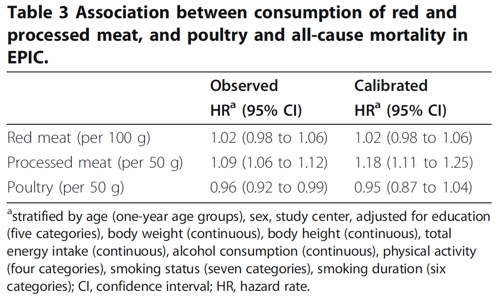
So, by both methods of calculation, the relative risk from eating red meat is negligible (except possibly in the top group, eating more than 160 g (7 oz) per day).
There is still an association between intake of processed meat and all-cause mortality, as in previous studies, though the association of processed meat with all-cause mortality, 1.09, or 1.18 depending on assumptions, is, if anything, smaller than was observed in the 2012 study, in which the relative risk was 1.20 (Table 2).
Assumptions, confounders and corrections.
The lowest meat eaters had only 13% of current smokers, but for the biggest red meat eaters it was 40%, for males. The alcohol consumption was 8.2 g/day for the lowest meat eaters but 23.4 g/day for the highest-meat group (the correlations were a bit smaller for women and also for processed meat eaters).
These two observations necessitate huge corrections to remove the (much bigger) effects of smoking and drinking if we want find the association for meat-eating alone. The main method for doing the correction is to fit the Cox proportional hazards model. This model assumes that there are straight-line relationships between the logarithm of the risk and the amount of each of the risk factors, e.g smoking, drinking, meat-eating and other risk factors. It may also include interactions that are designed to detect whether, for example, the effect of smoking on risk is or isn’t the same for people who drink different amounts.
Usually the straight-line assumption isn’t tested, and the results will depend on which risk factors (and which interactions between them) are included in the calculations. Different assumptions will give different answers. It simply isn’t known how accurate the corrections are when trying to eliminate the big effect of smoking in order to isolate the small effect of meat-eating. And that is before we get to other sorts of correction. For example, the relative risk from processed meat in Table 3, above, was 9% or 18% (1.09, or 1.18) depending on the outcome of a calculation that was intended to increase the accuracy of food intake records ("calibration").
The Conclusions of the new study don’t even mention the new result with red meat. All they mention is the risk from processed meat.
In this population, reduction of processed meat consumption to less than 20 g/day would prevent more than 3% of all deaths. As processed meat consumption is a modifiable risk factor, health promotion activities should include specific advice on lowering processed meat consumption.
Well, you would save that number of lives if, and only if, the processed meat was the cause of death. Too many epidemiologists, the authors pay lip service to the problem of causality in the introduction, but then go on to assume it in the conclusions. In fact the problem of causality isn’t even metnioned anywhere in either the 2012 study, or the new 2013 EPIC trial.
So is the risk of processed meat still real? Of course I can’t answer that. All that can be said is that it’s quite small, and as sample sizes get bigger, estimates of the risk are getting smaller. It wouldn’t be surprising if the risk from processed meat were eventually found not to exist, just as has happened for red (unprocessed) meat
The Japanese study
Last year there was another cohort study, with 51,683 Japanese. The results were even more (non-) dramatic [Nagao et al, 2012] than in the EPIC trial. This is how they summarise the results for the relative risks (with 95% confidence intervals).
"…for the highest versus lowest quintiles of meat consumption (77.6 versus 10.4 g/day) among men were 0.66 (0.45 — 0.97) for ischemic heart disease, 1.10 (0.84 — 1.43) for stroke and 1.00 (0.84 — 1.20) for total cardiovascular disease. The corresponding HRs (59.9 versus 7.5 g/day) among women were 1.22 (0.81 — 1.83), 0.91 (0.70 — 1.19) and 1.07 (0.90 — 1.28). The associations were similar when the consumptions of red meat, poultry, processed meat and liver were examined separately.
CONCLUSION: Moderate meat consumption, up to about 100 g/day, was not associated with increased mortality from ischemic heart disease, stroke or total cardiovascular disease among either gender."
In this study, the more meat (red or processed) you eat, the lower your risk of ischaemic heart disease (with the possible exception of overweight women). The risk of dying from any cardiovascular disease was unrelated to the amount of meat eaten (relative risk 1.0) whether processed meat or not.
Of course it’s possible that things which risky for Japanese people differ from those that are risky for Europeans. It’s also possible that even processed meat isn’t bad for you.
The carnitine study
The latest meat study to hit the headlines didn’t actually look at the effects of meat at all, though you wouldn’t guess that from the pictures of sausages in the headlines (not just in newspapers, but also in NHS Choices). The paper [reprint] was about carnitine, a substance that occurs particularly in beef, with lower amounts in pork and bacon, and in many other foods. The paper showed that bacteria in the gut can convert carnitine to a potentially toxic substance, trimethylamine oxide (TMAO). That harms blood vessels (at least in mice). But to show an effect in human subjects they were given an amount of carnitine equivalent to over 1 lb of steak, hardly normal, even in the USA.
The summary of the paper says it is an attempt to explain "the well-established link between high levels of red meat consumption and CVD [cardiovascular disease] risk". As we have just seen, it seems likely that this risk is far from being “well-established”. There is little or no such risk to explain.
It would be useful to have a diagnostic marker for heart disease, but this paper doesn’t show that carnitine or TMAO) is useful for that. It might also be noted that the authors have a maze of financial interests.
Competing financial interests Z.W. and B.S.L. are named as co-inventors on pending patents held by the Cleveland Clinic relating to cardiovascular diagnostics and have the right to receive royalty payments for inventions or discoveries related to cardiovascular diagnostics from Liposciences. W.H.W.T. received research grant support from Abbott Laboratories and served as a consultant for Medtronic and St. Jude Medical. S.L.H. and J.D.S. are named as co-inventors on pending and issued patents held by the Cleveland Clinic relating to cardiovascular diagnostics and therapeutics patents. S.L.H. has been paid as a consultant or speaker by the following companies: Cleveland Heart Lab., Esperion, Liposciences, Merck & Co. and Pfizer. He has received research funds from Abbott, Cleveland Heart Lab., Esperion and Liposciences and has the right to receive royalty payments for inventions or discoveries related to cardiovascular diagnostics from Abbott Laboratories, Cleveland Heart Lab., Frantz Biomarkers, Liposciences and Siemens.
The practical significance of this work was summed up the dietitian par excellence, Catherine Collins, on the BBC’s Inside Health programme.
Listen to Catherine Collins on carnitine.
She points out that the paper didn’t mean that we should change what we already think is a sensible diet.
At most, it suggests that it’s not a good idea to eat 1 lb steaks very day.
And the paper does suggest that it’s not sensible to take the carnitine supplements that are pushed by every gym. According to NIH
"twenty years of research finds no consistent evidence that carnitine supplements can improve exercise or physical performance in healthy subjects".
Carnitine supplements are a scam. And they could be dangerous.
Follow-up
Another blog on this topic, one from Cancer Research UK also fails to discuss the problem of causality. Neither does it go into the nature (and fallibility) of the corrections for counfounders like smoking and alcohol,. Nevertheless that, and an earlier post on Food and cancer: why media reports are often misleading, are a good deal more realistic than most newspaper reports.
The offering of quack cancer treatments at an exorbitant price is simple cruelty. The nature of the Burzynski clinic has been known for some time. But it has come to a head with some utterly vile threatening letters sent to the admirable Andrew Lewis, because he told a few truths about Stanislaw Burzynski’s despicable outfit. Please read his original post, The False Hope of the Burzynski Clinic.
I have to add by two-pennorth worth to the row that has blown up in the blogosphere at the outrageous behaviour of Burzynski. I hope other bloggers will do the same. There is safety in numbers. We need a Streisand effect to face down these pathetic bullies. It’s the "I am Spartacus" principle.
I won’t repeat all the details. They have spread like wildfire round the web. Briefly, it was sparked off by tragic case of a 4-year old girl, Billie Bainbridge who has a rare form of brain cancer. Well-intentioned pop stars have been trying to raise £200,000 to "enrol her into a clinical trial" at Burzynski clinic in Texas, despite the fact that Dr Stanislaw Burzynski has already been on trial for cancer fraud. In fact his clinic is not allowed to treat cancer patients, but it has evaded that ban, for many years, by pretending to run clinical trials. Normally patients volunteer for clinical trials. Sometimes they are paid a modest amount. Never, in the civilised world, are people asked to pay hundreds of thousands of pounds to be a guinea pig. Dorothy Bishop has written about The Weird World of US ethics regulation.
There is nothing new about this. The Cancerbusters site won the Anus Maximus Award for the year 2000. The award was announced in the following words:
The top award this year goes to the acolytes of Dr Stanislaw Burzynski who have created an advertising site at www.cancerbusters.com using a five-year-old boy named Thomas Navarro. Thomas is dying of cancer and this site exploits that tragedy to try and get the law changed so that quacks can have the untrammelled right to deceive desperate, sick people by promising them magic cures for cancer, AIDS and other diseases for which no cure is yet available. While this site is specifically a Burzynski promotion, his competitors support the site and mention it because if the campaign is successful it will dramatically increase the size of the market for quackery and therefore their opportunities to make money. [The boy died in November 2001]
The letters sent to Andrew Lewis are unspeakably nasty. They come from someone who calls himself "Marc Stephens" who claims to represent the company.
|
Le Canard Noir / Andy Lewis, I represent the Burzynski Clinic, Burzynski Research Institute, and Dr. Stanislaw Burzynski. It has been brought to our attention that you have content on your websites http://www.quackometer.net/blog/2011/11/the-false-hope-of-the-burzynski-clinic.html that is in violation of multiple laws. Please allow this correspondence to serve as notice to you that you published libelous and defamatory information. This correspondence constitutes a demand that you immediately cease and desist in your actions defaming and libeling my clients. Please be advised that my clients consider the content of your posting to be legally actionable under numerous legal causes of action, including but not limited to: defamation Libel, defamation per se, and tortious interference with business contracts and business relationships. The information you assert in your article is factually incorrect, and posted with either actual knowledge, or reckless disregard for its falsity. The various terms you use in your article connote dishonesty, untrustworthiness, illegality, and fraud. You, maliciously with the intent to harm my clients and to destroy his business, state information which is wholly without support, and which damages my clients’ reputations in the community. The purpose of your posting is to create in the public the belief that my clients are disreputable, are engaged in on-going criminal activity, and must be avoided by the public. You have a right to freedom of speech, and you have a right to voice your opinion, but you do not have the right to post libelous statements regardless if you think its your opinion or not. You are highly aware of defamation laws. You actually wrote an article about defamation on your site. In addition, I have information linking you to a network of individuals that disseminate false information. So the courts will apparently see the context of your article, and your act as Malicious. You have multiple third parties that viewed and commented on your article, which clearly makes this matter defamation libel. Once I obtain a subpoena for your personal information, I will not settle this case with you. Shut the article down IMMEDIATELY. GOVERN YOURSELF ACCORDINGLY. Regards, Marc Stephens |
Then later, at the end of another “foam-flecked angry rant”
|
. . . If you had no history of lying, and if you were not apart of a fraud network I would take the time to explain your article word for word, but you already know what defamation is. I’ve already recorded all of your articles from previous years as well as legal notice sent by other attorneys for different matters. As I mentioned, I am not playing games with you. You have a history of being stubborn which will play right into my hands. Be smart and considerate for your family and new child, and shut the article down..Immediately. FINAL WARNING. Regards, Marc Stephens |
Despite the attempt at legal style, "Marc Stephens" is not registered as an attorney in Texas.
Andy Lewis did not yield to this crude bullying. His post is still there for all to read. Before the days of the internet he would have been on his own. But now already dozens of blogs have drawn attention to what’s going on. Soon it will be hundreds. Burzynski can’t sue all of us. It’s the Streisand effect, or the "I am Spartacus" response.
Come on. Marc Stephens, make my day.
Some notes on the science
The Burzynski treatment is piss. Literally. A mixture of substances extracted from the patient’s own urine is dubbed with the preoposterous pseudoscientific name "antineoplastons". There are no such things as "neoplastons". And the chemicals are now made in the lab like any other drug.
|
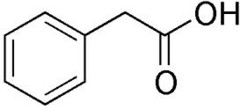
The main component seems to be a simple organic chemical, phenylacetic acid (PA). It is produced in normal metabolism but the liver copes with it by converting it to phenylacetyl glutamine (PAG), which is excreted in the urine.
|
|
Saul Green has summarised the evidence
Burzynski has never demonstrated that A-2.1 (PA) or “soluble A-10” (PA and PAG) are effective against cancer or that tumor cells from patients treated with these antineoplastons have been “normalized.” Tests of antineoplastons at the National Cancer Institute have never been positive. The drug company Sigma-Tau Pharmaceuticals could not duplicate Burzynski’s claims for AS-2.1 and A-10. The Japanese National Cancer Institute has reported that antineoplastons did not work in their studies. No Burzynski coauthors have endorsed his use of antineoplastons in cancer patients.
Cancer Research UK has a summary of the current evidence, Hope or false hope?
Despite it being illegal to advertise cancer cures in most country, the list of people who flout the law to make money from the desperate is enormous/ You can find a list of them at Quackwatch. Burzynski isn’t the only one but he could well be the most expensive.
Latest developments
You can follow the ever-growing list of publications by people who are determined to resist Burzynski at Josephine Jones "Stanislaw, Streisand and Spartacus". There is also a list at anarchic_teapot’s blog
Follow-up
Saturday 26 November Another frothy threat from Burzynski’s alleged representative. Lot’s of RED ARROWS.
Monday 28 November The Streisand effect is developing rapidly. The definitive lists of posts are here and here. But there are two that I must mention.
Today Rhys Morgan has published Threats from The Burzynski Clinic. The same “Marc Stephens” has made the same sort of threats against him as he made against Lewis. Rhys Morgan is still at school, and is now 17 years old. He was the hero of the MMS scandal.
David Gorski, a real oncologist, has gone into the evidence in excellent detall with Stanislaw Burzynski: Bad medicine, a bad movie, and bad P.R.
An email yesterday alerted me to YesToLife. This outfit seemed to me to be so dangerous that a word of warning is in the public interest.
Their own description says “YES TO LIFE is a new charitable initiative to open up a positive future for people with cancer in the UK by supporting an integrative* approach to cancer care”. That sounds sort of cuddly but lets look below the surface.
As so often, the funding seems to have been raised as the result of the death of an unfortunate 23 year old woman. Instead of putting the money into real research, yet another small charity was formed. My correspondent pointed out that “I came across them at St Pancras Station on Friday afternoon — they had a live DJ to draw in the crowd and were raising funds through bucket collections”. No doubt many people just see the word ‘cancer’ and put money in the bucket, without realising that their money will be spent on promoting nonsensical and ineffective treatments.
The supporters list.
The list of supporters tells you all you need to know, if you are familiar with the magic medicine business, though it might look quite convincing if you don’t know about the people. Sadly the list starts with some celebrities (I didn’t know before that Maureen Lipman was an enthusiast foir quackery -how very sad). But never mind the air-head celebrities. The more interesting supporters come later.
- Dr Rosy Daniel of Health Creation is an old friend. After I complained about her promotion of some herbal concoction called Carctol to “heal cancer”, she was reprimanded by Trading Standards for breaching the Cancer Act 1939, and forced to change the claims (in my view she should have neen prosecuted but, luckily of her, Trading Standards people are notoriously ineffective). There is, of course not the slightest reason to to think that Carctol works (download Carctol: Profits before Patients?). Read also what Cancer Research UK say about carctol.
Dr Daniel is also well known because ran a course that was, for one year, accredited by the University of Buckingham. But once the university became aware of the nonsense that was being taught on the course, they first removed her as the course director, and then removed accreditation from the course altogether. She then tried to run the course under the aegis of the Prince’s Foundation for Integrated Health, but even they turned her down. Now it is running as a private venture, and is being advertised by YesToLife. - Boo Armstrong, “Chief Executive of The Prince’s Foundation for Integrated Health and Founder and Executive Director GetWellUK”. The web site is out of date since the Prince’s Foundation shut its doors a year ago. She runs a private company, GetWellUK, that was responsible for a very poor study of alternative medicine in Northern Ireland. So she has a vested interest in promoting it. See Peter Hain and GetwellUK: pseudoscience and privatisation in Northern Ireland
- Professor George Lewith. This is beginning to look like the usual list of suspects. I’ve had cause to write twice about the curious activities of Dr Lewith. See Lewith’s private clinic has curious standards, in 2006, and this year George Lewith’s private practice. Another case study. The make up your own mind about whether you’d trust him.
- Dr Michael Dixon OBE, Chairman NHS Alliance and Medical Director The Prince’s Foundation for Integrated Health. Again the job description is a year out of date. You can read about Dr Dixon at Prince of Wales Foundation for magic medicine: spin on the meaning of ‘integrated’. He seems to be a well meaning man for whom no new-age idea is too barmy.
In fact both Dixon and Lewith have moved to a reincarnation of the Prince’s Foundation known as the “College of Medicine” (actually it’s a couple of offices in Buckingham Street). See Don’t be deceived. The new “College of Medicine” is a fraud and delusion.
It seems to me incomprehensible that people such as Sir Graeme Catto, Sir Cyril Chantler and Sir Muir Grey are willing to be associated with people who behave like this. - Charlotte Grobien, Managing Director, Give it Away. This seems to be a fund-raising organisation that has supported YesToLife. The lesson seems to be, never give money to fundraisers unless you know exactly where your money is going.
The Help Centre
YesToLife has a help centre. But beware, There is no medical person there. Just Traditional Chinese medicine (rather dangerous), acupuncture, osteopath and naturopathy (which means, roughly, do nothing and hope for the best).
Patrick Holford,
There can be no better indication of the standard of advice to be expected from YesToLife than the fact they are advertising a lecture by Holford, with the enticing title "Say no to cancer"."Through learning about the effects of diet and nutrition, people with cancer or at risk of developing cancer can be empowered to say Yes to Life and No to Cancer". Would that it were so easy. It will cost you £15.00.
Just in case there is still nobody who has heard of Holford, he is the media nutritionist who has an entire chapter devoted to him in Ben Goldacre’s Bad Science book, He has a whole website that has exposed his dubious advice, the excellent HolfordWatch. And you can find quite a lot about him on this blog. Try, for example, Patrick Holford’s CV: the strange case of Dr John Marks, and Response to a threatening letter from Mr Holford, or Holford’s untruthful and unsubstantiated advertisement
The treatments directory
Now we get to the truly scary bit of YesToLife, their treatment directory. Try searching for ‘cancer type’ and then "breast (metastatic)".. We find no mention of the advances in understanding of the genetics of breast cancer, nor ot real therapies like tamoxifen. What we find are four "alternative treatments".
- Neuroimmunomodulation Therapy It sounds impressive until you learn that its only proponent is a an 82 year old Venezuelan doctor with a clinic in Caracas. Even YesToLife doesn’t pretend that there is any evidence that it works
- Vitamin C Therapy The old chestnut cure-all Vitamin C Again even YesToLife don’t pretend there is any good evidence but it is still offered; treatment cost £3140.00 (what? Vitamin C is very cheap indeed)
- Dendritic Cell Therapy Said by YesToLife to be "well-researched", though that isn’t so for breast cancer (metastatic). Although possibly not as barmy as the other things that are recommended, it is nevertheless not shown to be effective for any sort of cancer,
- Gerson Therapy It is a sign of the extreme unreliability of advice given by YesToLife that they should still recommend anything as totally discredited as Gerson Therapy.Although YesToLife describes it as "well-researched" that is simply not true: there are no proper clinical trials. Cancer Research UK say
"Overall, there is no evidence to show that Gerson therapy works as a cure for cancer. "
"Available scientific evidence does not support claims that Gerson therapy can treat cancer. It is not approved for use in the United States. Gerson therapy can be very harmful to your health. Coffee enemas have been linked to serious infections, dehydration, constipation, colitis (inflammation of the colon), and electrolyte imbalances. In some people, particular aspects of the diet such as coffee enemas have been thought to be responsible for their death."Recommended reading: The (Not-So-)Beautiful (Un)Truth about the Gerson protocol and cancer quackery, by David Gorski (breast cancer surgeon, writing in Science-based Medicine.
Conclusion
The information supplied by YesToLife is more likely to kill you than to cure you.
The next time you see somebody collecting for a "cancer charity" be very careful before you give them money.
Follow-up
November 2012. It gets worse.
I had an email from someone who was distressed because a friend was trying to raise £15,000 to cover the cost of treatments recommended by YesToLife. The treatment is high-dose intravenous Vitamin C infusion. This is pure quackery. There isn’t the slightest reason to think it will affect the course of cancer, or the wellbeing of the patient. It is exploitation of the desperate. My heart sinks at the thought that a “charity” can be quite so wicked.
The purpose of this post is to reveal a few samples of things that are taught on a homeopathy ‘degree’ course. The course in question was the "BSc Hons homeopathy course at the University of Central Lancashire (UCLAN). Entry to this course was closed in 2008 and, after an internal review, UCLAN closed almost all of the rest of its courses in alternative medicine too. The university is to be commended for this .
The purpose of making public some of what used to be taught is not to embarrass UCLAN, which has already done the sensible thing, but to make it clear that the sort of thing taught on such courses is both absurd and dangerous, in the hope of discouraging other courses
|
.Three years after I first asked for teaching materials, the Information Commisioner ruled that all the reasons given for refusal were invalid, and they must be handed over. However UCLAN then appealed against the decision, so the appeal went to an Information Tribunal. That appeal was lost decisively and UCLAN was.obliged to provide the whole of the course material. On Christmas Eve I got five large box files, 13.7 kg of documents, or 30 pounds, in old money. |

|
Because these documents are copyright, I rely on the twin defences of fair quotation (only a tiny proportion is being quoted) and public interest. The Information Tribunal decided very firmly that it was in the public interest that it should be known what is taught on such courses, and that can be achieved if some of it is made public. Here are a few extracts.
Code of ethics
The students are given a copy of the code of ethics of the Society of Homeopaths. This is 25 pages long, but paragraph 48 is especially interesting.
48 Advertisements, stationery and name plates maintain a high standard of propriety and
integrity to enhance the reputation of homeopathy.
- Advertising shall not contain claims of superiority.
- No advertising may be used which expressly or implicitly claims to cure named diseases.
- Advertising shall not be false, fraudulent, misleading, deceptive, extravagant or sensational.
No mention though, of the fact that this code of ethics has been repeatedly breached by the Society of Homeopaths itself, on its own website. See, for example, here in 2007 and again in 2009. as well as Ernst’s article on this topic.
Anyone who has followed dialogues among homeopaths knows that "claims to cure named diseases" is the norm not the exception. The code of ethics is just a bad joke. And the (late) course at UCLAN was no exception. Take, for example, course HP3002, Therapeutic Homeopathy, module leader Jean Duckworth.
Homeopathic treatment of cancer
There was a lecture on HP3002 called "A Homeopathic Approach to Cancer (Ramakrishnan methodology [sic])".. Here are 10 slides from that lecture. It is illegal to claim to be able to cure cancer under the Cancer Act 1939. If a homeopath were to make claims like these in public they’d be open to prosecution, not to mention in breach of the SoH’s code of ethics. If cancer is not a "named disease", what is?



Specific treatments for a named disease are recommended.

What happened to treating the whole person? Now specific organs are being treated. The term "affinity", as used here, is of course sheer hocus pocus.


It is easy to forget when reading this that none of the “medicines” contain any medicine whatsoeever.
Notice that the term "remedy" is used throughout. Any reasonable person would interpret "remedy" to imply "cure", though no doubt a homeopath, if challenged, would claim that "remedy" carried no such implication. The last slide is typical of junk medicine: the personal testimonial, supplied with no detail whatsoever. Just an anecdote which is useless as evidence.
This lecture alone strikes me as a cruel (and possibly illegal) hoax perpetrated on desperate patients. Of course a true believer might get some solace from taking the sugar pills, but that is not sufficient justification.
The same course dealt with quite a lot of other "named diseases", autism, ADHD and coping with a heart attack. And, you are asked, did you think arnica is just a first aid remedy?


If that isn’t a list of "named diseases", what is? The code of ethics appears to be a total sham.
And of course never forget that the “arnica” doesn’t contain any arnica anyway. And if you don’t believe that you can read the words of Kate Chatfield, module leader on thie very course, as recorded in the minutes of evidence to the Select Committee on Science and Technology .
Q538 Lord Broers: I have a simple, technical question about homeopathy and drugs. Is it possible to distinguish between homeopathic drugs after they have been diluted? Is there any means of distinguishing one from the other?
Ms Chatfield: Only by the label.
You can read a lovely analysis of the views of Kate Chatfield by physicist A.P. Gaylard here.
Follow-up
The Daily Telegraph. January 8th 2009 Ian Douglas reported on this post: The workings of a BSc in homeopathy
The Lancashire Evening Post carried a big spread on January 15th, Professor seeks out the truth about ‘quackery’.
River’s Edge. News and thoughts from Preston, Lancashire reviewed the Lancashire Evening Post article on Saturday January 16th: Homeopathy at UCLAN, a degree in quackery.
The cost of trying to stop this material being revealed. UCLAN told me on 5 February 2010 that the legal costs alone were £80,307.94 (inc. VAT). That doesn’t include staff time and photocopying. I’m not convinced that this was a good way to spend taxpayers’ money.
This post has been translated into Belorussian..
Chinese medicine and herbal medicine are in the news at the moment. There is a real risk that the government could endorse them by accepting the Pittilo report.
In my view traditional Chinese medicine endangers people. The proposed ‘regulation’ would do nothing to protect the public. Quite on the contrary, it would add to the dangers, by giving an official stamp of approval while doing nothing for safety.
The government’s idea of improving safety is to make sure that practitioners are ‘properly trained’. But it is the qualifications that cause the danger in the first place. The courses teach ideas that are plain wrong and often really dangerous.
Why have government (and some universities) not noticed this? That’s easy to see. Governments, quangos and university validation committees simply don’t look. They tick boxes but never ask what actually goes on. Here’s some examples of what goes on for them to think about. They show clearly the sort of dangerous rubbish that is taught on some of these ‘degrees’.
These particular slides are from the University of Westminster, but similar courses exist in only too many other places. Watch this space for more details on courses at Edinburgh Napier University, Middlesex University and the University of East London

Just a lot of old myths. Sheer gobbledygook,

SO much for a couple of centuries of physiology,

It gets worse.

Plain wrong.

Curious indeed. The fantasy gobbledygook gets worse.

Now it is getting utterly silly. Teaching students that the brain is made of marrow is not just absurd, but desperately dangerous for anyone unlucky (or stupid) enough to go to such a person when they are ill.
Here’s another herbal lecture., and this time the topic is serious. Cancer.
Herbal approaches for patients with cancer.
I’ve removed the name of the teacher to spare her the acute embarrassment of having these dangerous fantasies revealed. The fact that she probably believes them is not a sufficient excuse for endangering the public. There is certainly no excuse for the university allowing this stuff to be taught as part of a BSc (Hons).

First get them scared with some bad statistics.
No fuss there about distinguishing incidence, age-standardisation and death rates. And no reference. Perhaps a reference to the simple explanation of statistics at Cancer Research UK might help? Perhaps this slide would have been better (from CDC). Seems there is some mistake in slide 2.
Straight on to a truly disgraceful statement in slide 3

The is outrageous and very possibly illegal under the Cancer Act (1939). It certainly poses a huge danger to patients. It is a direct incentive to make illegal, and untrue claims by using weasel words in an attempt to stay just on the right side of the law. But that, of course, is standard practice in alternative medicine,

Slide 11 is mostly meaningless. “Strengthen vitality” sounds good but means nothing. And “enhancing the immune system” is what alternative medicine folks always say when they can think of nothing else. Its meaning is ill-defined and there is no reason to think that any herbs do it.
The idea of a ‘tonic’ was actually quite common in real medicine in the 1950s. The term slowly vanished as it was realised that it was a figment of the imagination. In the fantasy world of alternative medicine, it lives on.
Detoxification, a marketing term not a medical one, has been extensively debunked quite recently. The use of the word by The Prince of Wales’ company, Duchy Originals recently fell foul of the Advertising Standards Authority, and his herbal ‘remedies’ were zapped by the MHRA (Medicines and Health Regulatory Authority).
And of course the antioxidant myth is a long-disproved hypothesis that has become a mere marketing term.

“Inhibits the recurrence of cancer”! That sounds terrific. But if it is so good why is it not even mentioned in the two main resources for information about herbs?
In the UK we have the National Library for Health Complementary and Alternative Medicine Specialist Library (NeLCAM), now a part of NHS Evidence. It was launched in 2006. The clinical lead was none other than Peter Fisher, clinical director of the Royal London Homeopathic Hospital, and the Queen’s homeopathic physician. The library was developed with the School of Integrated Health at the University of Westminster (where this particular slide was shown to undergraduates). Nobody could accuse these people of being hostile to magic medicine,
It seems odd, then, that NeLCAM does not seem to thnk to think that Centella asiatica, is even worth mentioning.
In the USA we have the National Center for Alternative and Complementary Medicine (NCCAM), an organisation that is so friendly to alternative medicine that it has spent a billion dollars on research in the area, though it has produced not a single good treatment for that vast expenditure. But NCCAM too does not even mention Centella asiatica in its herb list. It does get a mention in Cochrane reviews but only as a cosmetic cream and as an unproven treatment for poor venous circulation in the legs.

What on earth is a “lymph remedy”. Just another marketing term?
“especially valuable in the treatment of breast, throat and uterus cancer.“
That is a very dramatic claim. It as as though the hapless students were being tutored in doublespeak. What is meant by “especially valuable in the treatment of”? Clearly a desperate patient would interpret those words as meaning that there was at least a chance of a cure. That would be a wicked deception because there isn’t the slightest reason to think it works. Once again there this wondrous cure is not even mentioned in either NELCAM or NCCAM. Phytolacca is mentioned, as Pokeweed, in Wikipedia but no claims are mentioned even there. And it isn’t mentioned in Cochrane reviews either. The dramatic claims are utterly unfounded.

Ah the mistletoe story, again.
NHS Evidence (NeLCAM) lists three completed assessments. One concludes that more research is needed. Another concludes that “Rigorous trials of mistletoe extracts fail to demonstrate efficacy of this therapy”, and the third says “The evidence from RCTs to support the view that the application of mistletoe extracts has impact on survival or leads to an improved ability to fight cancer or to withstand anticancer treatments is weak”.
NCCAM says of mistletoe
- More than 30 human studies using mistletoe to treat cancer have been done since the early 1960s, but major weaknesses in many of these have raised doubts about their findings (see Question 6).
- Very few bad side effects have been reported from the use of mistletoe extract, though mistletoe plants and berries are poisonous to humans (see Question 7).
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved mistletoe as a treatment for cancer or any other medical condition (see Question 8).
- The FDA does not allow injectable mistletoe to be imported, sold, or used except for clinical research (see Question 8).
Cochrane reviews lists several reviews of mistletoe with similar conclusions. For example “The evidence from RCTs to support the view that the application of mistletoe extracts has impact on survival or leads to an improved ability to fight cancer or to withstand anticancer treatments is weak”.
Anthroposophy is one of the highest grades of fantasy you can find. A post on that topic is in the works.

“Indicated for cancers . . . colon/rectal, uterine, breast, lung“. A cure for lung cancer? That, of course, depends on how you interpret the weasel words “indicated for”. Even Wikipedia makes no mention of any claims that Thuja benefits cancer. NHS Evidence (NeLCAM) doesn’t mention Thuja for any indication. Neither does NCCAM. Nor Cochrane reviews. That is not the impression the hapless students of this BSc lecture were given. In my view suggestions that you can cure lung cancer with this tree are just plain wicked.

Pure snake oil, and not even spelled correctly, Harry Hoxsey’s treatment centres in the USA were closed by court order in the 1950s.

At least this time it is stated that there is no hard evidence to support this brand of snake oil.

More unfounded claims when it says “treated successfully many cancer patients”. No references and no data to support the claim. It is utterly unfounded and claims to the contrary endanger the public.

Gerson therapy is one of the most notorious and unpleasant of the quack cancer treatments. The Gerson Institute is on San Diego, but their clinics are in Mexico and Hungary. It is illegal in the USA. According to the American Cancer Society you get “a strict low-salt, low-fat, vegetarian diet and drinking juice from about twenty pounds of fresh fruits and vegetables each day. One glass of juice is consumed each hour, thirteen times a day. In addition, patients are given several coffee enemas each day. Various supplements, such as potassium, vitamin B12, pancreatic enzymes, thyroid hormone, and liver extracts, are used to stimulate organ function, particularly of the liver and thyroid.”. At one time you also got several glasses of raw calf liver every day but after infections killed several people] carrot juice was given instead.
Cancer Research UK says “there is no evidence to show that Gerson therapy works as a cure for cancer”, and “The Gerson diet can cause some very serious side effects.” Nobody (except perhaps the Price of Wales) has any belief in this unpleasant, toxic and expensive folk-lore.
Again patients are endangered by teaching this sort of stuff.

And finally, the usual swipe at vaccines. It’s nothing to do with herbalism. but just about every alternative medicine advocate seems to subscribe to the anti-vaccination lobby.. It is almost as though they have an active preference for things that are known to be wrong. They seem to believe that medicine and science are part of an enormous conspiracy to kill everyone.
Perhaps this dangerous propaganda might have been ameliorated if the students had been shown this slide (from a talk by Melinda Wharton).
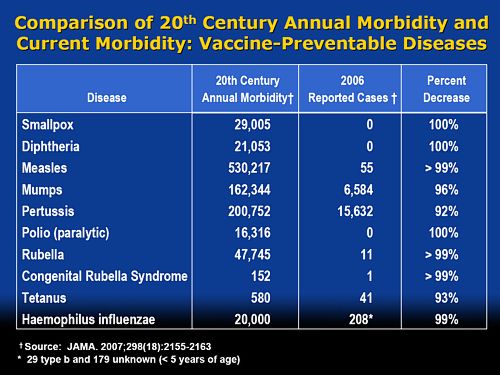
Left to people like this, we would still have smallpox, diphtheria. tetanus and rabies, Take a look at Vaccine-preventable diseases.
This is the sort of ‘education’ which the Pittilo report wants to make compulsory.
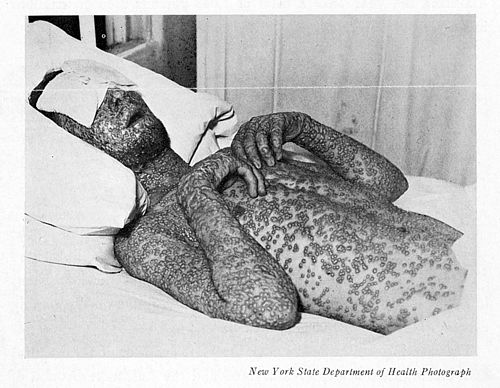
Smallpox in Baltimore, USA, 1939. This man was not vaccinated.
Conclusion
This selection of slides shows that much of the stuff taught in degrees in herbal medicine poses a real danger to public safety and to public health.
Pittilo’s idea that imposing this sort of miseducation will help safety is obviously and dangerously wrong. The Department of Health must reject the Pittilo recommendations on those grounds.
Follow-up
The much-delayed public consultation on the Pittilo report has just opened.
It is very important that as many people as possible respond to it. It’s easy to say that the consultation is sham. It will be if it is left only to acupuncturists and Chinese medicine people to respond to it. Please write to them before the closing date, November 2nd 2009. The way to send your evidence is here.
There is a questionnaire that you can complete, with the usual leading questions. Best do it anyway, but I’d suggest also sending written evidence as attachment too. I just got from DoH the email address where you can send it. They said
| if you have material you wish to send which you can’t easily “shoehorn” into the questionnaire, please send it to the following mailbox:
HRDListening@dh.gsi.gov.uk |
Here are three documents that I propose to submit in response to the consultation.I ‘d welcome criticisms that might make it more convincing. Use any parts of them you want in your own response.
- Submission to the Department of Health, for the consultation on the Pittilo report [download pdf].
- What is taught in degrees in herbal and traditional Chinese medicine? [download pdf]
- $2.5B Spent, No Alternative Med Cures [download pdf]
|
I’ve written quite a lot about the Pittilo report already, in particular A very bad report: gamma minus for the vice-chancellor, and in The Times (see also the blog version).
Intriguingly, these posts are at number 2 in a Google search for “Michael Pittilo”. |
 |
Briefly, the back story is this.
It is now over a year since the Report to Ministers from “The Department of Health Steering Group on the Statutory Regulation of Practitioners of Acupuncture, Herbal Medicine, Traditional Chinese Medicine and Other Traditional Medicine Systems Practised in the UK” [download the report].
The chair of the steering group was Professor R. Michael Pittilo, Principal and Vice-Chancellor of The Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen. The reason thet the report is so disastrously bad in its assessment of evidence is that it was written entirely by people with vested interests.
The committee consisted of five acupuncturists, five herbalists and five representatives of traditional Chinese medicine (plus eleven observers). There was not a single scientist or statistician to help in the assessment of evidence. And it shows: The assessment of the evidence in the report was execrable. Every one of the committee members would have found themselves out of work if they had come to any conclusion other than that their treatment works, Disgracefully, these interests were not declared in the report, though they are not hard to find. The university of which the chair is vice-chancellor runs a course in homeopathy, the most discredited of the popular forms of alternative medicine. That tells you all you need to know about the critical faculties of Michael Pittilo.
The two main recommendations of this Pittilo report are that
- Practitioners of Acupuncture, Herbal Medicine, Traditional Chinese Medicine should be subject to statutory regulation by the Health Professions Council
- Entry to the register normally be through a Bachelor degree with Honours
Let’s consider the virtue of these two recommendations.
Regulation by the Health Professions Council (HPC) breaks their own rules
For a start, this should be ruled out by the HPC’s own rules, which require “Practise based on evidence of efficacy” as a condition for registration. Since there is practically no “evidence of efficacy”, it follows that the HPC can’t regulate acupuncture, herbal and Chinese medicine as Pittilo recommends. Or so you’d think. But the official mind seems to have an infinite capacity for doublespeak. The HPC published a report on 11 September 2008, Regulation of Medical Herbalists, Acupuncturists and Traditional Chinese Medicine Practitioners.
The report says
1. Medical herbalists, acupuncturists and traditional Chinese medicine practitioners should be statutorily regulated in the public interest and for public safety reasons.
2. The Health Professions Council is appropriate as the regulator for these professions.
3. The accepted evidence of efficacy overall for these professions is limited, but regulation should proceed because it is in the public interest.
In other words, the HPC simply decided to ignore its own rules, Its excuse for doing so is that regulation would protect “public safety” . But it simply would not do that. It is ell known that some Chinese herbs are adulterated with dangerous substances, but laws against that already exist. Trading Standards are much more likely to take appropriate action than the HPC. The Medicines and Health Regulatory Authority (MHRA) already deals with the licensing of herbal medicines. and, despite the fact that it recently betrayed its trust by allowing them to be labelled in a misleading way, they are the people to do it, not the HPC.
The Pittilo report (page 11) says
In future, it is hoped that more Government funding can be allocated to research into traditional/herbal medicines and acupuncture and that grants will become available to encourage practitioners to undertake postgraduate research work.
So they are asking for more government money.
In March 2007, the Chinese Government pledged to spend over $130 million over the next five years on research into the effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine. It is to be hoped that this money will be targeted effectively to evaluate TCM.
It seems to have escaped the notice of Pittilo that roughly 100 percent of trials of Chinese medicine done in China come out positive. Elsewhere, very few come out positive,(see Vickers et al., 1998, Controlled Clinical Trials, 19, 159-166: download reprint) The Department of Health would be unwise to rely on Chinese research. Remember that modern acupuncture was not so much a product of ancient wisdom, but rather it stems from nationalist propaganda by Mao Tse-Tung, who needed a cheap way to keep the peasants quiet, though he was too sensible to use it himself.
The HPC report (page 5) cites these with the words
” . . . a lack of evidence of efficacy should not prevent regulation but that the professions should be encouraged and funded to strengthen the evidence base.”
This sentence seems to assume that the outcomes of research will be to strengthen the evidence base. Thus far, precisely the opposite has been the case. The Pittilo group has apparently not noticed that the US National Institutes of Health has already spent a billion dollars on research in alternative medicine and failed to come up with a single effective treatment. There are better ways to spend money on health. See, for example $2.5B Spent, No Alternative Med Cures found. .An enornous amount of research has already been done and the outcomes have produced no good treatments,
The proposed regulation would endanger the public, not protect it.
The excuse given by the HPC for breaking its own rules is that it should do so to protect the public.
Likewise Ann Keen, Health Minister, said:
“Patient safety is paramount, whether people are accessing orthodox health service treatments or using alternative treatments”
So first we need to identify what dangers are posed by acupuncture, herbal medicine and traditional Chinese medicine.
- Acupuncture is fairly safe. Its biggest danger lies in the unjustified claims that are routinely made for what can be achieved by being impaled by needles. This poses a danger that people may use acupuncture in place of treatments that work
- Herbal medicines are unstandardised, so even the very few that may work are dangerous to patients because the dose of active principle is unknown and varies from one batch to another. Taking a herbal medicine is a bit like swallowing a random number of tablets, False health claims pose a danger to patients too, when they cause patients to avoid treatments that work.
- Traditional Chinese Medicine is probably the most dangerous. Like the other two, the medicines are unstandardised so the dose is never known. False health claims abound. And in addition to these dangers, many cases have been found of Chinese medicines being adulterated with poisonous substances or with conventional drugs.
The form of regulation proposed by Pittilo would do little or nothing to protect the public from any of these dangers.
The proposals accept the herbal and Chinese medicine as traditionally practised. Nothing would be done about one of the major dangers, the lack of standardisation. That is a problem that was solved by pharmacologists in the 1930s, when international standards were set for the biological activity of things like tincture of digitalis, and assays were devised so that different batches could be adjusted to the same potency. Now, 80 years later, it is being proposed by Pittilo that we should return to the standards of safety that existed at the beginning of the last century. That is a threat to public safety., but the proposed regulation would do nothing whatsoever to protect the public from this dangerous practice. On the contrary, it would give official government sanction to it.
The other major danger is that patients are deceived by false health claims. This is dangerous (as well as dishonest) because it can cause patients to avoid treatments that work better, The internet abounds with claims that herbs can cure anything from diabetes to cancer. Many are doubtless illegal, but regulators like the HPC have traditionally ignored such claims: they are left to Trading Standards, Advertising Standards and the Medicines and Health Regulatory Authority (MHRA) to deal with. The MHRA already also has responsibility for monitoring side effects. The HPC would not do this.
The analogy with chiropractic and the GCC
The foolishness of allowing statutory regulation for unproven treatments has recently been illustrated quite dramatically by the case of chiropractic. Chiropractors have had statutory regulation by the General Chiropractic Council, which was established by the Chiropractors Act of 1994. The British Chiropractic Association (BCA) recently decided to sue the science writer, Simon Singh, for defamation when he cast doubt on some of the claims made by chiropractors, in particular their claims to be able to cure colic and asthma in children. That led to close examination of the claims. In fact there is no reason to think that spinal manipulation works for asthma, or that it works for colic. In fact there is quite good evidence that the claims are false. The result was that about 600 well-justified complaints have been lodged with the GCC (enough to bankrupt the GCC if the complaints are dealt with properly).
The point of this story is that the statutory regulator had nothing whatsoever to prevent these false health claims being made. Two of the complaints concern practices run by the chair of the GCC. Worse, the GCC actually endorsed such claims. The statutory regulator saw its duty to defend chiropractic (apart from a handful of cases of sexual misdemeanours), not to protect the patient from false health claims. The respectability conferred by statutory regulation made false health claims easier and endangered the public. It would be a disaster if the same mistake were made again.
On 11th December 2008 I got a letter form the HPC which said
in our opinion a lack of evidence of efficacy would not impede our ability to set standards or deal with complaints we receive. The vast majority of cases we consider are related to conduct.
But perhaps that is because they haven’t tried “regulating” quacks before. Now that the public is far more conscious about health fraud than it used to be, one can predict confidently that the HPC would be similarly overwhelmed by a deluge of complaints about the unjustified health claims made by acupuncturists, herbal medicine and traditional Chinese medicine practitioners. There is no shortage of them to complain about.
The education problem
The Pittilo report recommends that the entry level for registration should be a bachelors degree with honours. At first sight it seems reasonable to ask that practitioners should be ‘properly qualified’, but when one looks at what is actually taught on these degrees it becomes clear that they endanger, rather than protect, the public,
There are two very big problems with this recommendation.
Firstly, you can’t have a bachelors degree with honours until after you have decided whether or not there is anything useful to teach. If and when any of the subjects under consideration and shown to work to a useful extent, then it would be quite reasonable to establish degrees in them. Even the report does not pretend seriously that that stage has been reached. The proposal to set up degrees in subjects, at least some of which are quite likely to have no more than placebo value, is self-evidently nonsense,
The time for degrees, and the time for government endorsement by statutory regulation, is after the therapies have been shown to work, not before.
The absurdity of thinking that the public will be protected because a practitioner has a degree in, say, acupuncture, is shown with startling clarity by a recently revealed examination paper in acupuncture’
You can download the entire exam paper. Here are a few highlights from it.

So students, in 2009, are being taught the crudest form of vitalism.

Teaching of traditional Chinese medicine is just as bad. Here are two slides from a course run by the University of Westminster.
The first ‘explains’ the mysterious and entirly mythical “Qi”.

So “Qi” means breath, air, vapour, gas, energy, vitalism. This is meaningless nonsense.
The second slide shows the real dangers posed by the way Chinese medicine is taught, The symptoms listed at the top could easily be a clue to serious illness, yat students are taught to treat them with ginger. Degrees like this endanger the public.

There are more mind-boggling slides from lectures on Chinese medicine and cancer: they show that what students are being taught is terrifyingly dangerous to patients.
It is entirely unacceptable that students are being taught these ancient myths as though they were true, and being encouraged to treat sick people on their basis. The effect of the Pittilo recommendations would be to force new generations of students to have this sort of thing forced on them. In fact the course for which this exam was set has already closed its doors. That is the right thing to do.
Here’s another example. The course leader for “BSc (Hons) Herbal Medicine” at the Univsrsity of Central Lancashire is Graeme Tobyn BA. But Tobyn is not only a herbalist but also an astrologer. In an interview he said
“At the end I asked her if I could cast her horoscope. She threw up her hands and said, ‘I knew this would happen if I came to an alternative practitioner.”
“I think the ruler of the ascendant was applying to Uranus in the ninth house, which was very pertinent.”
This would be preposterous even in the life style section of a downmarket women’s magazine, The Pittilo report wants to make degrees run my people like this compulsory. Luckily the Univerity of Central Lancashire is much more sensible and the course is being closed.
The matter is, in any case, being taken out of the hands of the government by the fact that universities are closing degrees in complementary medicine, including courses in some of those under discussion here, The University of Salford and the University of Central Lancashire have recently announced the closure of all the degree programmes in complementary and alternative medicine. The largest provider of such degrees, the University of Westminster has already shut down two of them, and the rest are being assessed at the moment. It is likely that the rest will be closed in the future.
The revelation that Westminster had been teaching its first year students that “amethysts emit high yin energy” and that students had been taught to diagnose disease and choose treatments by means of a dowsing pendulum, showed very clearly the sort of utter nonsense that undergraduates were being forced to learn to get a ‘bachelors degree with honours’. It stretches credulity to its limits to imagine that the public is protected by degrees like this. Precisely the opposite is true. The universities have recognised this, and shut the degrees. One exception is Professor Pittilo’s own university which continues to run a course in homeopathy, the most discredited of all the popular types alternative medicine.
A simpler, more effective and cheaper way to protect the public
I must certainly agree with the minister that protection of the public is an important matter. Having established that the Pittllo recommendations are more likely to endanger the public than protect them, it is essential to suggest alternative proposals that would work better.
Luckily, that is easy, because mechanisms already exist for dealing with the dangers that were listed above. The matter of adulteration, which is serious in traditional Chinese medicine, is a matter that is already the responsibility of the Office of Trading Standards. The major problem of false claims being made for treatment is also the responsibility of the Office of Trading Standards, which has a statutory duty to enforce the Unfair Trading Consumer Protection Regulations of May 2008. These laws state, for example, that
“One of the 31 commercial practices which are in all circumstances considered unfair is “falsely claiming that a product is able to cure illnesses, dysfunction or malformations”
The monitoring of false claims, and of side effects of treatments, is also the responsibility of the Medicines and Health Regulatory Authority (MHRA).
Rather than setting up complicated, expensive and ineffective ‘regulation’ by the HPC, all that need to be done is to ensure that the MHRA and/or Trading Standards have the funds to enforce existing laws. At the moment, they are not being implemented effectively, so I’d recommend that responsibility for enforcing the law against false health claims be transferred entirely to the MHRA, which has much more expertise in such matters than Trading Standards This would be both cheaper and more effective than the present system in which the responsibility is divided between the two organisations in an unclear way.
This proposal would protect the public against unsafe and adulterated treatments, and it would protect the public against false and fraudulent claims. That is what matters. It would do so more effectively,
more cheaply and more honestly than the Pittilo recommendations. There would be no reduction in patient choice either, There is no proposal to ban acupuncture, herbal medicine or traditional Chinese medicine. All that is necessary is to ensure that they don’t endanger the public.
Since the root of the problem lies in the fact that the evidence for the effectiveness is very weak. the question of efficacy, and cost-benefit ratio, should be referred to NICE. This was recommended by the House of Lords Report (2000). It is recommended again by the Smallwood report (sponsored by the Prince of Wales Foundation). It is baffling that this has not been done already. It does not seem wise to spend large amounts of money on new research at the moment, in the light of the fact that the US National Institutes of Health has already spent over $1 billion on such research without finding a single useful treatment.
The results of all this research has been to show that hardly any alternative treatment are effective. That cannot be ignored.
Conclusion
Recent events show that the halcyon days for alternative medicine are over. When the Pittilo report first appeared, it was greeted with derision in the media. For example, in The Times Alice Miles wrote
“This week came the publication of the Report to Ministers from the Department of Health Steering Group on the Statutory Regulation of Practitioners of Acupuncture, Herbal Medicine, Traditional Chinese Medicine and Other Traditional Medicine Systems Practised in the UK. Otherwise known as twaddle.”
In the Independent, Dominic Lawson wrote
So now we will have degrees in quackery.
What, really, is the difference between acupuncture and psychic surgery?
People will no doubt continue to use it and that is their right and their responsibility. But if the government were to accept the recommendations of the Pittilo report it would be seen, quite rightly, as being anti-scientific and of posing a danger to the public.
Fortunately there is a better, and cheaper, way to protect the public.
Follow-up
Margaret McCartney’s blog in the Financial Times puts rhw view of a GP with her usual sense, humour and incisiveness.
“This report would, if implemented, create lots more nonsense exam papers funded by a lot more public money – and would produce practitioners without the absolutely crucial skill of how to assess evidence and reject or use it appropriately”
The Times has covered the story (with some interesting comments) Consultation on how to regulate complementary and alternative therapies
Times Higher Education UK-wide consultation on CAM regulation is launched Excellent response from Andy Lewis.
The Sun has by far the best coverage up to now, Jane Symons writes “Regulating quacks helps them prey on gullible patients“
| The Prince of Wales’ Foundation for Integrated Health (FiH) is a propaganda organisation that aims to persuade people, and politicians, that the Prince’s somewhat bizarre views about alternative medicine should form the basis of government health policy.
His attempts are often successful, but they are regarded by many people as being clearly unconstitutional. |
 |
The FiH’s 2009 AnnualConferen ce conference was held at The King’s Fund, London 13 – 14 May 2009. It was, as always, an almost totally one-sided affair devoted to misrepresentation of evidence and the promotion of magic medicine. But according to the FiH, at least, it was a great success. The opening speech by the Quacktitioner Royal can be read here. It has already been analysed by somebody who knows rather more about medicine than HRH. He concludes
“It is a shocking perversion of the real issues driven by one man; unelected, unqualified and utterly misguided”.
We are promised some movie clips of the meeting. They might even make a nice UK equivalent of “Integrative baloney @ Yale“.
This post is intended to provide some background information about the speakers at the symposium. But let’s start with what seems to me to be the real problem. The duplicitous use of the word “integrated” to mean two quite different things.
The problem of euphemisms: spin and obfuscation
One of the problems of meetings like this is the harm done by use of euphemisms. After looking at the programme, it becomes obvious that there is a rather ingenious bit of PR trickery going on. It confuses (purposely?) the many different definitions of the word “integrative” . One definition of “Integrative medicine” is this (my emphasis).
” . . . orienting the health care process to engage patients and caregivers in the full range of physical, psychological, social, preventive, and therapeutic factors known to be effective and necessary for the achievement of optimal health.”
That is a thoroughly admirable aim. And that, I imagine, is the sense in which several of the speakers (Marmot, Chantler etc) used the term. Of course the definition is rather too vague to be very helpful in practice, but nobody would dream of objecting to it.
But another definition of the same term ‘integrative medicine’ is as a PR-friendly synonym for ‘alternative medicine’, and that is clearly the sense in which it is used by the Prince of Wales’ Foundation for Integrated Health (FIH), as is immediately obvious from their web site.
The guide to the main therapies supports everything from homeopathy to chiropractic to naturopathy, in a totally uncritical way. Integrated service refers explicitly to integration of ‘complementary’ medicine, and that itself is largely a euphemism for alternative medicine. For example, the FIH’s guide to homeopathy says
“What is homeopathy commonly used for?
Homeopathy is most often used to treat chronic conditions such as asthma; eczema; arthritis; fatigue disorders like ME; headache and migraine; menstrual and menopausal problems; irritable bowel syndrome; Crohn’s disease; allergies; repeated ear, nose, throat and chest infections or urine infections; depression and anxiety.”
But there is not a word about the evidence, and perhaps that isn’t surprising because the evidence that it works in any of these conditions is essentially zero.
The FIH document Complementary Health Care: A Guide for Patients appears to have vanished from the web after its inaccuracy received a very bad press, e.g. in the Times, and also here. It is also interesting that the equally widely criticised Smallwood report (also sponsored by the Prince of Wales) seems to have vanished too).
The programme for the meeting can be seen here, for Day 1, and Day 2
Conference chair Dr Phil Hammond, GP, comedian and health service writer. Hammond asked the FIH if I could speak at the meeting to provide a bit of balance. Guess what? They didn’t want balance.
09:30 Opening session
Dr Michael Dixon OBE
09:30 Introduction: a new direction for The Prince’s Foundation for Integrated Health and new opportunities in integrated health and care. Dr Michael Dixon, Medical Director, FIH
Michael Dixon is devoted to just about every form of alternative medicine. As well as being medical director of the Prince’s Foundation he also runs the NHS Alliance. Despite its name, the NHS Alliance is nothing to do with the NHS and acts, among other things, as an advocate of alternative medicine on the NHS, about which it has published a lot.
Dr Dixon is also a GP at College Surgery, Cullompton, Devon, where his “integrated practice” includes dozens of alternative practitioners. They include not only disproven things like homeopathy and acupuncture, but also even more bizarre practitioners in ‘Thought Field Therapy‘ and ‘Frequencies of Brilliance‘.
To take only one of these, ‘Frequencies of Brilliance’ is bizarre beyond belief. One need only quote its founder and chief salesperson.
“Frequencies of Brilliance is a unique energy healing technique that involves the activation of energetic doorways on both the front and back of the body.”
“These doorways are opened through a series of light touches. This activation introduces high-level Frequencies into the emotional and physical bodies. It works within all the cells and with the entire nervous system which activates new areas of the brain.”
“Frequencies of Brilliance is a 4th /5th dimensional work. The process is that of activating doorways by lightly touching the body or working just above the body.”
“Each doorway holds the highest aspect of the human being and is complete in itself. This means that there is a perfect potential to be accessed and activated throughout the doorways in the body.”
Best of all, it can all be done at a distance (that must help sales a lot). One is reminded of the Skills for Health “competence” in distant healing (inserted on a government web site at the behest (you guessed it) of the Prince’s Foundation, as related here)
“The intent of a long distance Frequencies of Brilliance (FOB) session is to enable a practitioner to facilitate a session in one geographical location while the client is in another.
A practitioner of FOB that has successfully completed a Stage 5 Frequency workshop has the ability to create and hold a stable energetic space in order to work with a person that is not physically present in the same room.
The space that is consciously created in the Frequencies of Brilliance work is known as the “Gap”. It is a space of nonlinear time. It contains ”no time and no space” or respectively “all time and all space”. Within this “Gap” a clear transfer of the energies takes place and is transmitted to an individual at a time and location consciously intended. Since this dimensional space is in non-linear time the work can be performed and sent backward or forward in time as well as to any location.
The Frequencies of Brilliance work cuts through the limitations of our physical existence and allows us to experience ourselves in other dimensional spaces. Therefore people living in other geographic locations than a practitioner have an opportunity to receive and experience the work.
The awareness of this dimensional space is spoken about in many indigenous traditions, meditation practices, and in the world of quantum physics. It is referred to by other names such as the void, or vacuum space, etc.”
This is, of course, preposterous gobbledygook. It, and other things in Dr Dixon’s treatment guide, seem to be very curious things to impose on patients in the 21st century.
Latest news. The Mid-Devon Star announces yet more homeopathy in Dr Dixon’s Cullompton practice. This time it comes in the form of a clinic run from the Bristol Homeopathic Hospital. I guess they must be suffering from reduced commissioning like all the other homeopathic hospitals, but Dr Dixon seems to have come to their rescue. The connection seems to be with Bristol’s homeopathic consultant, Dr Elizabeth A Thompson. On 11 December 2007 I wrote to Dr Thompson, thus
|
In March 2006, a press release http://www.ubht.nhs.uk/press/view.asp?257 announced a randomised trial for homeopathic treatment of asthma in children. This was reported also on the BBC http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/bristol/4971050.stm . I’d be very grateful if you could let me know when results from this trial will become available. Yours sincerely David Colquhoun |
The reply, dated 11 December 2007, was unsympathetic
|
I have just submitted the funders report today and we have set ourselves the deadline to publish two inter-related papers by March 1st 2007. Can I ask why you are asking and what authority you have to gain this information. I shall expect a reply to my questions, |
I answered this question politely on the same day but nevertheless my innocent enquiry drew forth a rather vitriolic complaint from Dr Thompson to the Provost of UCL (dated 14 December 2007). In this case, the Provost came up trumps. On 14 January 2008 he replied to Thompson: “I have looked at the email that you copied to me, and I must say that it seems an entirely proper and reasonable request. It is not clear to me why Professor Colquhoun should require some special authority to make such direct enquiries”. Dr Thompson seems to be very sensitive. We have yet to see the results of her trial in which I’m still interested.
Not surprisingly, Dr Dixon has had some severe criticism for his views, not least from the UK’s foremost expert on the evidence for efficacy, Prof Edzard Ernst. Accounts of this can be found in Pulse,
and on Andrew Lewis’s blog.
Dixon is now (in)famous in the USA too. The excellent Yale neurologist, Steven Novella, has written an analysis of his views on Science Based Medicine. He describes Dr. Michael Dixon as “A Pyromaniac In a Field of (Integrative) Straw Men”
Peter Hain
09:40 Politics and people: can integrated health and care take centre stage in 2009/2010? Rt Hon Peter Hain MP
It seems that Peter Hain was converted to alternative medicine when his first baby, Sam, was born with eczema. After (though possibly not because of) homeopathic treatment and a change in diet, the eczema got better. This caused Hain, while Northern Ireland Secretary to spend £200,000 of taxpayers’ money to set up a totally uninformative customer satisfaction survey, which is being touted elsewhere in this meeting as though it were evidence (see below). I have written about this episode before: see Peter Hain and Get Well UK: pseudoscience and privatisation in Northern Ireland.
I find it very sad that a hero of my youth (for his work in the anti-apartheid movement) should have sunk to promoting junk science, and even sadder that he does so at my expense.
There has been a report on Hain’s contribution in Wales Online.
09:55 Why does the Health Service need a new perspective on health and healing? Sir Cyril Chantler, Chair, King’s Fund, previous Dean, Guy’s Hospital and Great Ormond Street
Cyril Chantler is a distinguished medical administrator. He also likes to talk and we have discussed the quackery problem several times. He kindly sent me the slides that he used. Slide 18 says that in order to do some good we “need to demonstrate that the treatment is clinically effective and cost effective for NHS use”. That’s impeccable, but throughout the rest of the slides he talks of integrating with complementary” therapies, the effectiveness of which is either already disproved or simply not known.
I remain utterly baffled by the reluctance of some quite sensible people to grasp the nettle of deciding what works. Chantler fails to grasp the nettle, as does the Department of Health. Until they do so, I don’t see how they can be taken seriously.
10.05 Panel discussion
The Awards
10:20 Integrated Health Awards 2009 Introduction: a review of the short-listed applications
10:45 Presentations to the Award winners by the special guest speaker
11:00 Keynote address by special guest speaker
Getting integrated
Dr David Peters
12:00 Integration, long term disease and creating a sustainable NHS. Professor David Peters, Clinical Director and Professor of Integrated Healthcare, University of Westminster
I first met David Peters after Nature ran my article, Science Degrees without the Science. .One of the many media follow-ups of that article was on Material World (BBC Radio 4). This excellent science programme, presented by Quentin Cooper, had a discussion between me and David Peters ( listen to the mp3 file).
There was helpful intervention from Michael Marmot who had talked, in the first half of the programme, about his longitudinal population studies.
Marmot stressed the need for proper testing. In the case of
homeopathy and acupuncture, that proper testing has largely been done. The tests were failed.
The University of Westminster has, of course, gained considerable notoriety as the university that runs more degree programmes in anti-scientific forms of medicine than any other. Their lecture on vibrational medicine teaches students that amethysts “emit high Yin energy so transmuting lower energies and clearing and aligning energy disturbances at all levels of being”. So far their vice-chancellor, Professor Geoffrey Petts, has declined to answer enquiries about whether he thinks such gobbledygook is appropriate for a BSc degree.
But he did set up an internal enquiry into the future of their alternative activities. Sadly that enquiry seems to have come to the nonsensical conclusion that the problem can be solved by injection of good science into the courses, as reported here and in the Guardian.
It seems obvious that if you inject good science into their BSc in homeopathy the subject will simply vanish in a puff of smoke.
In 2007, the University of Westminster did respond to earlier criticism in Times Higher Education, but their response seemed to me to serve only to dig themselves deeper into a hole.
Nevertheless, Westminster has now closed down its homeopathy degree (the last in the country to go) and there is intense internal discussion going on there. I have the impression that Dr Peters’ job is in danger. The revelation of more slides from their courses on homeopathy, naturopathy and Chinese herbal medicine shows that these courses are not only barmy, but also sometimes dangerous.
Professor Chris Fowler
12:10 Educating tomorrow’s integrated doctors. Professor Chris Fowler, Dean for Education, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
I first came across Dr Fowler when I noticed him being praised for his teaching of alternative medicine to students at Barts and the London Medical School on the web site of the Prince’s Foundation. I wrote him a polite letter to ask if he really thought that the Prince of Wales was the right person to consult about the education of medical students. The response I got was, ahem, unsympathetic. But a little while later I noticed that two different Barts students had set up public blogs that criticised strongly the nonsense that was being inflicted on them.
At that point, I felt it was necessary to support the students who, it seemed to me, knew more about medical education than Professor Fowler. It didn’t take long to uncover the nonsense that was being inflicted on the students: read about it here.
There is a follow-up to this story here. Fortunately, Barts’ Director of Research, and, I’m told, the Warden of Barts, appear to agree with my view of the harm that this sort of thing can do to the reputation of Barts, so things may change soon,
Dame Donna Kinnair
12:30 Educating tomorrow’s integrated nurses.
Dame Donna Kinnair, Director of Nursing, Southwark PCT
As far as I can see, Donna Kinnair has no interest in alternative medicine. She is director of nursing at Southwark primary care trust and was an adviser to Lord Laming throughout his inquiry into the death of Victoria Climbié. I suspect that her interest is in integrating child care services (they need it, judging by the recent death of ‘Baby P’). Perhaps her presence shows the danger of using euphemisms like ‘integrated medicine’ when what you really mean is the introduction of unproven or disproved forms of medicine.
Michael Dooley
12:40 Integrating the care of women: an example of the new paradigm. Michael Dooley, Consultant Obstetrician and Gynecologist
DC’s rule 2. Never trust anyone who uses the word ‘paradigm’. It is a sure-fire sign of pseudoscience. In this case, the ‘new paradigm’ seems to be the introduction of disproven treatment. Dooley is a gynaecologist and Medical Director of the Poundbury Clinic. His clinic offers a whole range of unproven and disproved treatments. These include acupuncture as an aid to conception in IVF. This is not recommended by the Cochrane review, and one report suggests that it hinders conception rather than helps.
12.40 Discussion
13.00 – 14.00 Lunch and Exhibition
15.30 Tea
Boo Armstrong and Get Well UK
16.00 Integrated services in action: The Northern
Ireland experience: what has it shown us and what are its implications?
Boo Armstrong of Get Well UK with a team from the NI study
I expect that much will be made of this “study”, which, of course, tells you absolutely nothing whatsoever about the effectiveness of the alternative treatments that were used in it. This does not appear to be the view of Boo Armstrong, On the basis of the “study”, her company’s web site proclaims boldly
“Complementary Medicine Works
Get Well UK ran the first government-backed complementary therapy project in the UK, from February 2007 to February 2008″
This claim appears, prima facie, to breach the Unfair Trading Regulations of May 2008. The legality of the claim is, at the moment, being judged by a Trading Standards Officer. In any case, the “study” was not backed by the government as a whole, but just by Peter Hain’s office. It is not even clear that it had ethical approval.
The study consisted merely of asking people who had seen an alternative medicine practitioner whether they felt better or worse. There was no control group; no sort of comparison was made. It is surely obvious to the most naive person that a study like this cannot even tell you if the treatment has a placebo effect, never mind that it has any genuine effects of its own. To claim that it does so seems to be simply dishonest. There is no reason at all to think that the patients would not have got better anyway.
It is not only Get Well UK who misrepresent the evidence. The Prince’s
Foundation itself says
“Now a new, year long trial supported by the Northern Ireland health service has . . . demonstrated that integrating complementary and conventional medicine brings measurable benefits to patients’ health.”
That is simply not true. It is either dishonest or stupid. Don’t ask me which, I have no idea.
This study is no more informative than the infamous Spence (2005) ‘study’ of the same type, which seems to be the only thing that homeopaths can produce to support their case.
There is an excellent analysis of the Northern Ireland ‘study’ by Andy Lewis, The Northern Ireland NHS Alternative Medicine ‘Trial’. He explains patiently, yet again, what constitutes evidence and why studies like this are useless.
His analogy starts
” . . . the Apple Marketing Board approach the NHS and ask for £200,000 to do a study to show the truth behind the statement ‘An apple a day keeps the doctor away’. The Minister, being particularly fond of apples, agrees and the study begins.”
16.30 Social enterprise and whole systems integrated care. Dee Kyne, Sandwell PCT and a GP. Developing an integrated service in secondary care
Dee Kyne appears to be CEO of KeepmWell Ltd (a financial interest that is not mentioned).
Peter Mackereth, Clinical Lead, Supportive Services, Christie Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
I had some correspondence with Mackereth when the Times (7 Feb 2007) published a picture of the Prince of Wales inspecting an “anti-MRSA aromatherapy inhaler” in his department at the Christie. It turned out that the trial they were doing was not blind No result has been announced anyway, and on enquiry, I find that the trial has not even started yet. Surprising, then to find that the FIH is running the First Clinical Aromatherapy Conference at the Christie Hospital, What will there be to talk about?
Much of what they do at the Christie is straightforward massage, but they also promote the nonsensical principles of “reflexology” and acupuncture.
The former is untested. The latter is disproven.
Parallel Sessions
Developing a PCT funded musculoskeletal service Dr Roy Welford, Glastonbury Health Centre
Roy Welford is a Fellow of the Faculty of Homeopathy, and so promotes disproven therapies. The Glastonbury practice also advertises acupuncture (disproven), osteopathy and herbal medicine (largely untested so most of it consists of giving patients an unknown dose of an ill-defined drug, of unknown effectiveness and unknown safety).
Making the best of herbal self-prescription in integrated practice: key remedies and principles. Simon Mills, Project Lead: Integrated Self Care in Family Practice, Culm Valley Integrated Centre for Health, Devon
Simon Mills is a herbalist who now describes himself as a “phytotherapist” (it sounds posher, but the evidence, or lack of it, is not changed by the fancy name). Mills likes to say things like “there are herbs for heating and drying”, “hot and cold” remedies, and to use meaningless terms like “blood cleanser”, but he appears to be immune to the need for good evidence that herbs work before you give them to sick people. He says, at the end of a talk, “The hot and the cold remain the trade secret of traditional medicine”. And this is the 21st Century.
Practical ways in which complementary approaches can improve the treatment of cancer. Professor Jane Plant, Author of “Your life in your hands” and Chief Scientist, British Geological Society and Professor Karol Sikora, Medical Director, Cancer Partners UK
Jane Plant is a geologist who, through her own unfortunate encounter with breast cancer, became obsessed with the idea that a dairy-free diet cured her. Sadly there is no good evidence for that idea, according to the World Cancer Research Fund Report, led by Professor Sir Michael Marmot. No doubt her book on the subject sells well, but it could be held that it is irresponsible to hold out false hopes to desperate people. She is a supporter of the very dubious CancerActive organisation (also supported by Michael Dixon OBE –see above) as well as the notorious pill salesman, Patrick Holford (see also here).
Karol Sikora, formerly an oncologist at the Hammersmith Hospital, is now Dean of Medicine at the University of Buckingham (the UK’s only private university). He is also medical director at CancerPartners UK, a private cancer company.
He recently shot to fame when he appeared in a commercial in the USA sponsored by “Conservatives for Patients’ Rights”, to pour scorn on the NHS, and to act as an advocate for the USA’s present health system. A very curious performance. Very curious indeed.
His attitude to quackery is a mystery wrapped in an enigma. One was somewhat alarmed to see him sponsoring a course at what was, at first, called the British College of Integrated Medicine, and has now been renamed the Faculty of Integrated Medicine That grand title makes it sound like part of a university. It isn’t.

The alarm was as result of the alliance with Dr Rosy Daniel (who promotes an untested herbal conconction, Carctol, for ‘healing’ cancer) and Dr Mark Atkinson (a supplement salesman who has also promoted the Qlink pendant. The Qlink pendant is a simple and obvious fraud designed to exploit paranoia about WiFi killing you.
The first list of speakers on the proposed diploma in Integrated Medicine was an unholy alliance of outright quacks and commercial interests. It turned out that, although Karol Sikora is sponsoring the course, he knew nothing about the speakers. I did and when I pointed this out to Terence Kealey, vice-chancellor of Buckingham, he immediately removed Rosy Daniel from directing the Diploma. At the moment the course is being revamped entirely by Andrew Miles. There is hope that he’ll do a better job. It has not yet been validated by the University of Buckingham. Watch this space for developments.
Stop press It is reported in the Guardian that Professor Sikora has been describing his previous job at Imperial College with less than perfect accuracy. Oh dear. More developments in the follow-up.
The role of happy chickens in healing: farms as producers of health as well as food – the Care Farm Initiative Jonathan Dover, Project Manager, Care Farming, West Midlands.
“Care farming is a partnership between farmers, participants and health & social care providers. It combines the care of the land with the care of people, reconnecting people with nature and their communities.”
Sounds lovely, I wonder how well it works?
What can the Brits learn from the Yanks when it comes to integrated health? Jack Lord, Chief Executive Humana Europe
It is worth noticing that the advisory board of Humana Europe includes Micheal Dixon OBE, a well known advocate of alternative medicine (see
above). Humana Europe is a private company, a wholly owned subsidiary of Humana Inc., a health benefits company with 11 million members and 22,000 employees and headquarters in Louisville, Kentucky. In 2005 it entered into a business partnership with Virgin Group. Humana was mentioned in the BBC Panorama programme “NHS for Sale”. The company later asked that it be pointed out that they provide commissioning services, not clinical services [Ed. well not yet anyway].
Humana’s document “Humana uses computer games to help people lead healthier lives” is decidedly bizarre. Hang on, it was only a moment ago that we were being told that computer games rewired your brain.
Day 2 Integrated health in action
09.00 Health, epidemics and the search for new solutions. Sir Michael Marmot, Professor of Epidemiology and Public Health, Royal Free and University College Medical School
It is a mystery to me that a distinguished epidemiologist should be willing to keep such dubious company. Sadly I don’t know what he said, but judging my his publications and his appearence on Natural World, I can’t imagine he’d have much time for homeopaths.
9.25 Improving health in the workplace. Dame Carol Black, National Director, Health and Work, Department of Health
This is not the first time that Dame Carol has been comtroversial.
9.45 Integrated health in focus: defeating obesity. Professor Chris Drinkwater, President, NHS Alliance.
The NHS Alliance was mentioned above. Enough said.
10.00 Integrated healthcare in focus: new approaches to managing asthma, eczema and allergy. Professor Stephen Holgate, Professor of Immunopharmacology, University of Southampton
10.15 Using the natural environment to increase activity. The Natural England Project: the results from year one. Dr William Bird and Ruth Tucker, Natural England.
10.30 Panel discussion
10.45 Coffee
Self help in action
11.10 Your health, your way: supporting self care through care planning and the use of personal budgets. Angela Hawley, Self Care Lead, Department of Health
11.25 NHS Life Check: providing the signposts to
integrated health. Roy Lambley, Project Director, NHS LifeCheck Programme
This programme was developed with the University of Westminster’s “Health and Well-being Network”. This group, with one exception, is separate from Westminster’s extensive alternative medicine branch (it’s mostly psychologists).
11.45 The agony and the ecstasy of helping patients to help themselves: tips for clinicians, practices and PCTs. Professor
Ruth Chambers, FIH Foundation Fellow.
11.55 Providing self help in practice: Department of Health Integrated Self Help Information Project. Simon Mills, Project Lead: Integrated Self Care in Family Practice, Culm Valley Integrated Centre for Health, Devon and Dr Sam Everington, GP, Bromley by Bow.
The Culm Valley Integrated Centre for health is part of the College Surgery Partnership, associated with Michael Dixon OBE (yes, again!).
Simon Mills is the herbalist who says “The hot and the cold remain the trade secret of traditional medicine” .
Sam Everington, in contrast, seems to be interested in ‘integration’ in the real sense of the word, rather than quackery.
Integrated health in action
How to make sense of the evidence on complementary approaches: what works? What might work? What doesn’t work?
Dr Hugh MacPherson, Senior Research Fellow in Health Sciences, York University and Dr Catherine Zollman, Bravewell Fellow
Hugh MacPherson‘s main interest is in acupuncture and he publishes in alternative medicine journals. Since the recent analysis in the BMJ from the Nordic Cochrane Centre (Madsen et al., 2009) it seems that acupuncture is finally dead. Even its placebo effect is too small to be useful. Catherine Zollman is a Bristol GP who is into homeopathy as well as acupuncture. She is closely connected with the Prince’s Foundation via the Bravewell Fellowship. That fellowship is funded by the Bravewell Collaboration, which is run by Christie Mack, wife of John Mack (‘Mack the Knife’), head of Morgan Stanley (amazingly, they still seem to have money). This is the group which, by sheer wealth, has persuaded so many otherwise respectable US universities to embrace every sort of quackery (see, for example, Integrative baloney @ Yale)
The funding of integrated services
14.15 How to get a PCT or practice- based commissioner to fund your integrated service. A PCT Chief Executive and a Practice-Based Commissioning lead.
14.30 How I succeeded: funding an integrated service. Dr John Ribchester, Whitstable
14.45 How we created an acupuncture service in St Albans and Harpenden PBC group. Mo Girach, Chief Executive, STAHCOM
Uhuh Acupunture again. Have these people never read Bausell’s
book? Have they not read the BMJ? Acupuncture is now ell-established to be based on fraudulent principles, and not even to have a worthwhile placeobo effect. STAHCOM seem to be more interested in money than in what works.
Dragon’s Den. Four pitchers lay out their stall for the commissioning dragons
And at this stage there is no prize for guessing that all four are devoted to trying to get funds for discredited treatments
- An acupuncture service for long-term pain. Mike Cummings Chair, Medical Acupuncture Association
- Manipulation for the treatment of back pain Simon Fielding, Founder Chairman of the General Osteopathic Council
- Nigel Clarke, Senior Partner, Learned Lion Partners Homeopathy for long term conditions
- Peter Fisher, Director, Royal Homeopathic Hospital
Sadly it is not stated who the dragons are. One hopes they will be more interested in evidence than the supplicants.
Mike Cummings at least doesn’t believe the nonsense about meridians and Qi. It’s a pity he doesn’t look at the real evidence though.
You can read something about him and his journal at BMJ Group promotes acupuncture: pure greed.
Osteopathy sounds a bit more respectable than the others, but in fact it has never shaken off its cult-like origins. Still many osteopaths make absurd claims to cure all sorts of diseases. Offshoots of osteopathy like ‘cranial osteopathy’ are obvious nonsense. There is no reason to think that osteopathy is any better than any other manipulative therapy and it is clear that all manipulative therapies should be grouped into one.
Osteopathy and chiropractic provide the best ever examples of the folly of giving official government recognition to a branch of alternative medicine before the evidence is in.
Learned Lion Partners is a new one on me. It seems it is
part of Madsen Gornall Ashe Chambers (‘MGA Chambers’) “a grouping of top level, independent specialists who provide a broad range of management consultancy advice to the marketing community”. It’s a management consultant and marketing outfit. So don’t expect too much when it comes to truth and evidence. The company web site says nothing about alternative medicine, but only that Nigel Clarke
“. . . has very wide experience of public affairs issues and campaigns, having worked with clients in many sectors in Europe, North America and the Far East. He has particular expertise in financial, competition and healthcare issues. “
However, all is revealed when we see that he is a Trustee of the Prince’s Foundation where his entry says
“Nigel Clarke is senior partner of Learned Lion Partners. He is a director of Vidapulse Ltd, Really Easy Ltd, Newscounter Ltd and Advanced Transport Systems Ltd. He has worked on the interfaces of public policy for 25 years. He has been chair of the General Osteopathic Council since May 2001, having been a lay member since it was formed. He is now a member of the Council for Healthcare Regulatory Excellence”
The Council for Healthcare Regulatory Excellence is yet another quango that ticks boxes and fails absolutely to grasp the one important point, does it work?. I came across them at the Westminster Forum, and they seemed a pretty pathetic way to spend £2m per year.
Peter Fisher is the last supplicant to the Dragons. He is clinical director of the Royal London Homeopathic Hospital (RLHH), and Queen’s homeopathic physician, It was through him that I got an active interest in quackery. The TV programme QED asked me to check the statistics in a paper of his that claimed that homeopathy was good for fibrositis (there was an elementary mistake and no evidence for an effect). Peter Fisher is also remarkable because he agreed with me that BSc degrees in homeopathy were not justified (on TV –see the movie). And he condemned homeopaths who were caught out recommending their sugar pills for malaria. To that extent Fisher represents the saner end of the homeopathic spectrum. Nevertheless he still maintains that sugar pills work and have effects of their own, and tries to justify the ‘memory of water’ by making analogies with a memory stick or CD. This is so obviously silly that no more comment is needed.
Given Fisher’s sensible condemnation of the malaria fiasco, I was rather surprised to see that he appeared on the programme of a conference at the University of Middlesex, talking about “A Strategy To Research The Potential Of Homeopathy In Pandemic Flu”. The title of the conference was Developing Research Strategies in CAM. A colleague, after seeing the programme, thought it was more like “a right tossers’ ball”.
Much of the homeopathy has now vanished from the RLHH as a result of greatly reduced commissioning by PCTs (read about it in Fisher’s own words). And the last homeopathy degree in the UK has closed down. It seems an odd moment for the FIH to be pushing it so hard.
Follow-up
Stop press It is reported in the Guardian (22 May 2009) that Professor Sikora has been describing his previous job at Imperial College with less than perfect accuracy. Oh dear, oh dear.
This fascinating fact seems to have been unearthed first by the admirable NHS Blog Doctor, in his post ‘Imperial College confirm that Karol Sikora does not work for them and does not speak on their behalf‘.
This article has been reposted on The Winnower, and now has a digital object identifier DOI: 10.15200/winn.142934.47856
This post is not about quackery, nor university politics. It is about inference, How do we know what we should eat? The question interests everyone, but what do we actually know? Not as much as you might think from the number of column-inches devoted to the topic. The discussion below is a synopsis of parts of an article called “In praise of randomisation”, written as a contribution to a forthcoming book, Evidence, Inference and Enquiry.
About a year ago just about every newspaper carried a story much like this one in the Daily Telegraph,
|
Sausage a day can increase bowel cancer risk By Rebecca Smith, Medical Editor Last Updated: 1:55AM BST 31/03/2008
|
||||
What, I wondered, was the evidence behind these dire warnings. They did not come from a lifestyle guru, a diet faddist or a supplement salesman. This is nothing to do with quackery. The numbers come from the 2007 report of the World Cancer Research Fund and American Institute for Cancer Research, with the title ‘Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and the Prevention of Cancer: a Global Perspective‘. This is a 537 page report with over 4,400 references. Its panel was chaired by Professor Sir Michael Marmot, UCL’s professor of Epidemiology and Public Health. He is a distinguished epidemiologist, renowned for his work on the relation between poverty and health.
Nevertheless there has never been a randomised trial to test the carcinogenicity of bacon, so it seems reasonable to ask how strong is the evidence that you shouldn’t eat it? It turns out to be surprisingly flimsy.
In praise of randomisation
Everyone knows about the problem of causality in principle. Post hoc ergo propter hoc; confusion of sequence and consequence; confusion of correlation and cause. This is not a trivial problem. It is probably the main reason why ineffective treatments often appear to work. It is traded on by the vast and unscrupulous alternative medicine industry. It is, very probably, the reason why we are bombarded every day with conflicting advice on what to eat. This is a bad thing, for two reasons. First, we end up confused about what we should eat. But worse still, the conflicting nature of the advice gives science as a whole a bad reputation. Every time a white-coated scientist appears in the media to tell us that a glass of wine per day is good/bad for us (delete according to the phase of the moon) the general public just laugh.
In the case of sausages and bacon, suppose that there is a correlation between eating them and developing colorectal cancer. How do we know that it was eating the bacon that caused the cancer – that the relationship is causal? The answer is that there is no way to be sure if we have simply observed the association. It could always be that the sort of people who eat bacon are also the sort of people who get colorectal cancer. But the question of causality is absolutely crucial, because if it is not causal, then stopping eating bacon won’t reduce your risk of cancer. The recommendation to avoid all processed meat in the WCRF report (2007) is sensible only if the relationship is causal. Barker Bausell said:
[Page39] “But why should nonscientists care one iota about something as esoteric as causal inference? I believe that the answer to this question is because the making of causal inferences is part of our job description as Homo Sapiens.”
That should be the mantra of every health journalist, and every newspaper reader.
|
The essential basis for causal inference was established over 70 years ago by that giant of statistics Ronald Fisher, and that basis is randomisation. Its first popular exposition was in Fisher’s famous book, The Design of Experiments (1935). The Lady Tasting Tea has become the classical example of how to design an experiment. . |

|
Briefly, a lady claims to be able to tell whether the milk was put in the cup before or after the tea was poured. Fisher points out that to test this you need to present the lady with an equal number of cups that are ‘milk first’ or ‘tea first’ (but otherwise indistinguishable) in random order, and count how many she gets right. There is a beautiful analysis of it in Stephen Senn’s book, Dicing with Death: Chance, Risk and Health. As it happens, Google books has the whole of the relevant section Fisher’s tea test (geddit?), but buy the book anyway. Such is the fame of this example that it was used as the title of a book, The Lady Tasting Tea was published by David Salsburg (my review of it is here)
Most studies of diet and health fall into one of three types, case-control studies, cohort (or prospective) studies, or randomised controlled trials (RCTs). Case-control studies are the least satisfactory: they look at people who already have the disease and look back to see how they differ from similar people who don’t have the disease. They are retrospective. Cohort studies are better because they are prospective: a large group of people is followed for a long period and their health and diet is recorded and later their disease and death is recorded. But in both sorts of studies,each person decides for him/herself what to eat or what drugs to take. Such studies can never demonstrate causality, though if the effect is really big (like cigarette-smoking and lung cancer) they can give a very good indication. The difference in an RCT is that each person does not choose what to eat, but their diet is allocated randomly to them by someone else. This means that, on average, all other factors that might influence the response are balanced equally between the two groups. Only RCTs can demonstrate causality.
Randomisation is a rather beautiful idea. It allows one to remove, in a statistical sense, bias that might result from all the sources that you hadn’t realised were there. If you are aware of a source of bias, then measure it. The danger arises from the things you don’t know about, or can’t measure (Senn, 2004; Senn, 2003). Although it guarantees freedom from bias only in a long run statistical sense, that is the best that can be done. Everything else is worse.
Ben Goldacre has referred memorably to the newspapers’ ongoing “Sisyphean task of dividing all the inanimate objects in the world into the ones that either cause or cure cancer” (Goldacre, 2008). This has even given rise to a blog. “The Daily Mail Oncological Ontology Project“. The problem arises in assessing causality.
It wouldn’t be so bad if the problem were restricted to the media. It is much more worrying that the problem of establishing causality often seems to be underestimated by the authors of papers themselves. It is a matter of speculation why this happens. Part of the reason is, no doubt, a genuine wish to discover something that will benefit mankind. But it is hard not to think that hubris and self-promotion may also play a role. Anything whatsoever that purports to relate diet to health is guaranteed to get uncritical newspaper headlines.
At the heart of the problem lies the great difficulty in doing randomised studies of the effect of diet and health. There can be no better illustration of the vital importance of randomisation than in this field. And, notwithstanding the generally uncritical reporting of stories about diet and health, one of the best accounts of the need for randomisation was written by a journalist, Gary Taubes, and it appeared in the New York Times (Taubes, 2007).
The case of hormone replacement therapy
In the 1990s hormone replacement therapy (HRT) was recommended not only to relieve the unpleasant symptoms of the menopause, but also because cohort studies suggested that HRT would reduce heart disease and osteoporosis in older women. For these reasons, by 2001, 15 million US women (perhaps 5 million older women) were taking HRT (Taubes, 2007). These recommendations were based largely on the Harvard Nurses’ Study. This was a prospective cohort study in which 122,000 nurses were followed over time, starting in 1976 (these are the ones who responded out of the 170,000 requests sent out). In 1994, it was said (Manson, 1994) that nearly all of the more than 30 observational studies suggested a reduced risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) among women receiving oestrogen therapy. A meta-analysis gave an estimated 44% reduction of CHD. Although warnings were given about the lack of randomised studies, the results were nevertheless acted upon as though they were true. But they were wrong. When proper randomised studies were done, not only did it turn out that CHD was not reduced: it was actually increased.
The Women’s Health Initiative Study (Rossouw et al., 2002) was a randomized double blind trial on 16,608 postmenopausal women aged 50-79 years and its results contradicted the conclusions from all the earlier cohort studies. HRT increased risks of heart disease, stroke, blood clots, breast cancer (though possibly helped with osteoporosis and perhaps colorectal cancer). After an average 5.2 years of follow-up, the trial was stopped because of the apparent increase in breast cancer in the HRT group. The relative risk (HRT relative to placebo) of CHD was 1.29 (95% confidence interval 1.02 to 1.63) (286 cases altogether) and for breast cancer 1.26 (1.00 -1.59) (290 cases). Rather than there being a 44% reduction of risk, it seems that there was actually a 30% increase in risk. Notice that these are actually quite small risks, and on the margin of statistical significance. For the purposes of communicating the nature of the risk to an individual person it is usually better to specify the absolute risk rather than relative risk. The absolute number of CHD cases per 10,000 person-years is about 29 on placebo and 36 on HRT, so the increased risk of any individual is quite small. Multiplied over the whole population though, the number is no longer small.
Several plausible reasons for these contradictory results are discussed by Taubes,(2007): it seems that women who choose to take HRT are healthier than those who don’t. In fact the story has become a bit more complicated since then: the effect of HRT depends on when it is started and on how long it is taken (Vandenbroucke, 2009).
This is perhaps one of the most dramatic illustrations of the value of randomised controlled trials (RCTs). Reliance on observations of correlations suggested a 44% reduction in CHD, the randomised trial gave a 30% increase in CHD. Insistence on randomisation is not just pedantry. It is essential if you want to get the right answer.
Having dealt with the cautionary tale of HRT, we can now get back to the ‘Sisyphean task of dividing all the inanimate objects in the world into the ones that either cause or cure cancer’.
The case of processed meat
The WCRF report (2007) makes some pretty firm recommendations.
- Don’t get overweight
- Be moderately physically active, equivalent to brisk walking for at least 30 minutes every day
- Consume energy-dense foods sparingly. Avoid sugary drinks. Consume ‘fast foods’ sparingly, if at all
- Eat at least five portions/servings (at least 400 g or 14 oz) of a variety of non-starchy vegetables and of fruits every day. Eat relatively unprocessed cereals (grains) and/or pulses (legumes) with every meal. Limit refined starchy foods
- People who eat red meat to consume less than 500 g (18 oz) a week, very little if any to be processed.
- If alcoholic drinks are consumed, limit consumption to no more than two drinks a day for men and one drink a day for women.
- Avoid salt-preserved, salted, or salty foods; preserve foods without using salt. Limit consumption of processed foods with added salt to ensure an intake of less than 6 g (2.4 g sodium) a day.
- Dietary supplements are not recommended for cancer prevention.
These all sound pretty sensible but they are very prescriptive. And of course the recommendations make sense only insofar as the various dietary factors cause cancer. If the association is not causal, changing your diet won’t help. Note that dietary supplements are NOT recommended. I’ll concentrate on the evidence that lies behind “People who . . . very little if any to be processed.”
The problem of establishing causality is dicussed in the report in detail. In section 3.4 the report says
” . . . causal relationships between food and nutrition, and physical activity can be confidently inferred when epidemiological evidence, and experimental and other biological findings, are consistent, unbiased, strong, graded, coherent, repeated, and plausible.”
The case of processed meat is dealt with in chapter 4.3 (p. 148) of the report.
“Processed meats” include sausages and frankfurters, and ‘hot dogs’, to which nitrates/nitrites or other preservatives are added, are also processed meats. Minced meats sometimes, but not always, fall inside this definition if they are preserved chemically. The same point applies to ‘hamburgers’.
The evidence for harmfulness of processed meat was described as “convincing”, and this is the highest level of confidence in the report, though this conclusion has been challenged (Truswell, 2009) .
How well does the evidence obey the criteria for the relationship being causal?
Twelve prospective cohort studies showed increased risk for the highest intake group when compared to the lowest, though this was statistically significant in only three of them. One study reported non-significant decreased risk and one study reported that there was no effect on risk. These results are summarised in this forest plot (see also Lewis & Clark, 2001)
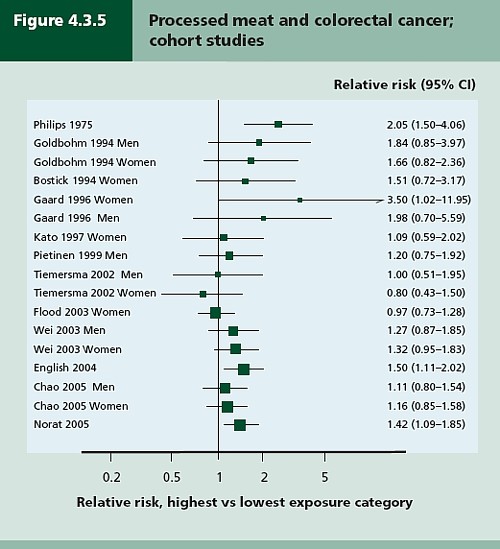
Each line represents a separate study. The size of the square represents the precision (weight) for each. The horizontal bars show the 95% confidence intervals. If it were possible to repeat the observations many times on the same population, the 95% CL would be different on each repeat experiment, but 19 out of 20 (95%) of the intervals would contain the true value (and 1 in 20 would not contain the true value). If the bar does not overlap the vertical line at relative risk = 1 (i.e. no effect) this is equivalent to saying that there is a statistically significant difference from 1 with P < 0.05. That means, very roughly, that there is a 1 in 20 chance of making a fool of yourself if you claim that the association is real, rather than being a result of chance (more detail here),
There is certainly a tendency for the relative risks to be above one, though not by much, Pooling the results sounds like a good idea. The method for doing this is called meta-analysis .
Meta-analysis was possible on five studies, shown below. The outcome is shown by the red diamond at the bottom, labelled “summary effect”, and the width of the diamond indicates the 95% confidence interval. In this case the final result for association between processed meat intake and colorectal cancer was a relative risk of 1.21 (95% CI 1.04–1.42) per 50 g/day. This is presumably where the headline value of a 20% increase in risk came from.
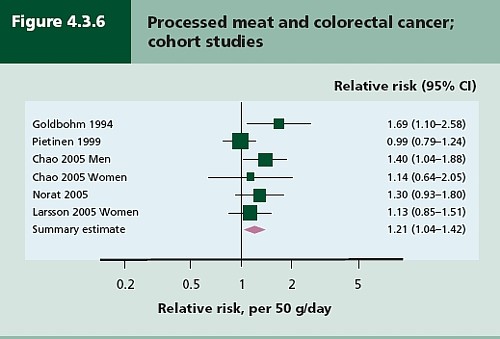
Support came from a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies, which reported a relative risk for processed meat of 1.09 (95% CI 1.05 – 1.13) per 30 g/day (Larsson & Wolk, 2006). Since then another study has come up with similar numbers (Sinha etal. , 2009). This consistency suggests a real association, but it cannot be taken as evidence for causality. Observational studies on HRT were just as consistent, but they were wrong.
The accompanying editorial (Popkin, 2009) points out that there are rather more important reasons to limit meat consumption, like the environmental footprint of most meat production, water supply, deforestation and so on.
So the outcome from vast numbers of observations is an association that only just reaches the P = 0.05 level of statistical significance. But even if the association is real, not a result of chance sampling error, that doesn’t help in the least in establishing causality.
There are two more criteria that might help, a good relationship between dose and response, and a plausible mechanism.
Dose – response relationship
|
It is quite possible to observe a very convincing relationship between dose and response in epidemiological studies, The relationship between number of cigarettes smoked per day and the incidence of lung cancer is one example. Indeed it is almost the only example. |
 Doll & Peto, 1978 |
There have been six studies that relate consumption of processed meat to incidence of colorectal cancer. All six dose-response relationships are shown in the WCRG report. Here they are.
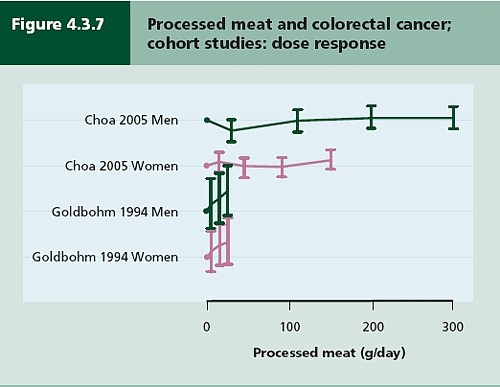
This Figure was later revised to
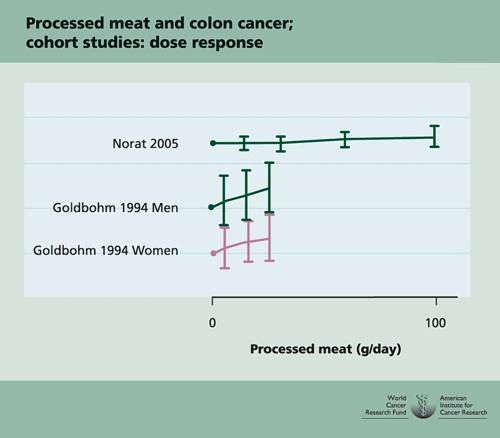
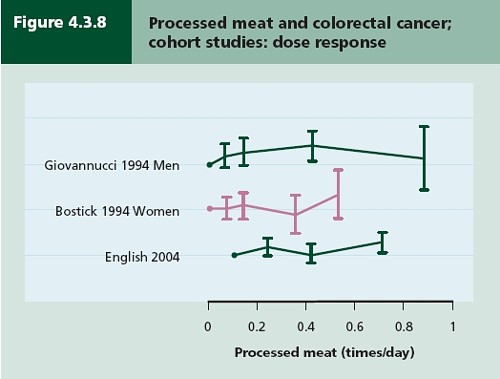
This is the point where my credulity begins to get strained. Dose – response curves are part of the stock in trade of pharmacologists. The technical description of these six curves is, roughly, ‘bloody horizontal’. The report says “A dose-response relationship was also apparent from cohort studies that measured consumption in times/day”. I simply cannot agree that any relationship whatsoever is “apparent”.
They are certainly the least convincing dose-response relationships I have ever seen. Nevertheless a meta-analysis came up with a slope for response curve that just reached the 5% level of statistical significance.
The conclusion of the report for processed meat and colorectal cancer was as follows.
“There is a substantial amount of evidence, with a dose-response relationship apparent from cohort studies. There is strong evidence for plausible mechanisms operating in humans. Processed meat is a convincing cause of colorectal cancer.”
But the dose-response curves look appalling, and it is reasonable to ask whether public policy should be based on a 1 in 20 chance of being quite wrong (1 in 20 at best –see Senn, 2008). I certainly wouldn’t want to risk my reputation on odds like that, never mind use it as a basis for public policy.
So we are left with plausibility as the remaining bit of evidence for causality. Anyone who has done much experimental work knows that it is possible to dream up a plausible explanation of any result whatsoever. Most are wrong and so plausibility is a pretty weak argument. Much play is made of the fact that cured meats contain nitrates and nitrites, but there is no real evidence that the amount they contain is harmful.
The main source of nitrates in the diet is not from meat but from vegetables (especially green leafy vegetables like lettuce and spinach) which contribute 70 – 90% of total intake. The maximum legal content in processed meat is 10 – 25 mg/100g, but lettuce contains around 100 – 400 mg/100g with a legal limit of 200 – 400 mg/100g. Dietary nitrate intake was not associated with risk for colorectal cancer in two cohort studies.(Food Standards Agency, 2004; International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2006).
To add further to the confusion, another cohort study on over 60,000 people compared vegetarians and meat-eaters. Mortality from circulatory diseases and mortality from all causes were not detectably different between vegetarians and meat eaters (Key et al., 2009a). Still more confusingly, although the incidence of all cancers combined was lower among vegetarians than among meat eaters, the exception was colorectal cancer which had a higher incidence in vegetarians than in meat eaters (Key et al., 2009b).
Mente et al. (2009) compared cohort studies and RCTs for effects of diet on risk of coronary heart disease. “Strong evidence” for protective effects was found for intake of vegetables, nuts, and “Mediterranean diet”, and harmful effects of intake of trans–fatty acids and foods with a high glycaemic index. There was also a bit less strong evidence for effects of mono-unsaturated fatty acids and for intake of fish, marine ω-3 fatty acids, folate, whole grains, dietary vitamins E and C, beta carotene, alcohol, fruit, and fibre. But RCTs showed evidence only for “Mediterranean diet”, and for none of the others.
As a final nail in the coffin of case control studies, consider pizza. According to La Vecchia & Bosetti (2006), data from a series of case control studies in northern Italy lead to: “An inverse association was found between regular pizza consumption (at least one portion of pizza per week) and the risk of cancers of the digestive tract, with relative risks of 0.66 for oral and pharyngeal cancers, 0.41 for oesophageal, 0.82 for laryngeal, 0.74 for colon and 0.93 for rectal cancers.”
What on earth is one meant to make of this? Pizza should be prescribable on the National Health Service to produce a 60% reduction in oesophageal cancer? As the authors say “pizza may simply represent a general and aspecific indicator of a favourable Mediterranean diet.” It is observations like this that seem to make a mockery of making causal inferences from non-randomised studies. They are simply uninterpretable.
Is the observed association even real?
The most noticeable thing about the effects of red meat and processed meat is not only that they are small but also that they only just reach the 5 percent level of statistical significance. It has been explained clearly why, in these circumstances, real associations are likely to be exaggerated in size (Ioannidis, 2008a; Ioannidis, 2008b; Senn, 2008). Worse still, there as some good reasons to think that many (perhaps even most) of the effects that are claimed in this sort of study are not real anyway (Ioannidis, 2005). The inflation of the strength of associations is expected to be bigger in small studies, so it is noteworthy that the large meta-analysis by Larsson & Wolk, 2006 comments “In the present meta-analysis, the magnitude of the relationship of processed meat consumption with colorectal cancer risk was weaker than in the earlier meta-analyses”.
This is all consistent with the well known tendency of randomized clinical trials to show initially a good effect of treatment but subsequent trials tend to show smaller effects. The reasons, and the cures, for this worrying problem are discussed by Chalmers (Chalmers, 2006; Chalmers & Matthews, 2006; Garattini & Chalmers, 2009)
What do randomized studies tell us?
The only form of reliable evidence for causality comes from randomised controlled trials. The difficulties in allocating people to diets over long periods of time are obvious and that is no doubt one reason why there are far fewer RCTs than there are observational studies. But when they have been done the results often contradict those from cohort studies. The RCTs of hormone replacement therapy mentioned above contradicted the cohort studies and reversed the advice given to women about HRT.
Three more illustrations of how plausible suggestions about diet can be refuted by RCTs concern nutritional supplements and weight-loss diets
Many RCTs have shown that various forms of nutritional supplement do no good and may even do harm (see Cochrane reviews). At least we now know that anti-oxidants per se do you no good. The idea that anti-oxidants might be good for you was never more than a plausible hypothesis, and like so many plausible hypotheses it has turned out to be a myth. The word anti-oxidant is now no more than a marketing term, though it remains very profitable for unscrupulous salesmen.
The randomised Women’s Health Initiative Dietary Modification Trial (Prentice et al., 2007; Prentice, 2007) showed minimal effects of dietary fat on cancer, though the conclusion has been challenged on the basis of the possible inaccuracy of reported diet (Yngve et al., 2006).
Contrary to much dogma about weight loss (Sacks et al., 2009) found no differences in weight loss over two years between four very different diets. They assigned randomly 811 overweight adults to one of four diets. The percentages of energy derived from fat, protein, and carbohydrates in the four diets were 20, 15, and 65%; 20, 25, and 55%; 40, 15, and 45%; and 40, 25, and 35%. No difference could be detected between the different diets: all that mattered for weight loss was the total number of calories. It should be added, though, that there were some reasons to think that the participants may not have stuck to their diets very well (Katan, 2009).
The impression one gets from RCTs is that the details of diet are not anything like as important as has been inferred from non-randomised observational studies.
So does processed meat give you cancer?
After all this, we can return to the original question. Do sausages or bacon give you colorectal cancer? The answer, sadly, is that nobody really knows. I do know that, on the basis of the evidence, it seems to me to be an exaggeration to assert that “The evidence is convincing that processed meat is a cause of bowel cancer”.
In the UK there were around 5 cases of colorectal cancer per 10,000 population in 2005, so a 20% increase, even if it were real, and genuinely causative. would result in 6 rather than 5 cases per 10,000 people, annually. That makes the risk sound trivial for any individual. On the other hand there were 36,766 cases of colorectal cancer in the UK in 2005. A 20% increase would mean, if the association were causal, about 7000 extra cases as a result of eating processed meat, but no extra cases if the association were not causal.
For the purposes of public health policy about diet, the question of causality is crucial. One has sympathy for the difficult decisions that they have to make, because they are forced to decide on the basis of inadequate evidence.
If it were not already obvious, the examples discussed above make it very clear that the only sound guide to causality is a properly randomised trial. The only exceptions to that are when effects are really big. The relative risk of lung cancer for a heavy cigarette smoker is 20 times that of a non-smoker and there is a very clear relationship between dose (cigarettes per day) and response (lung cancer incidence), as shown above. That is a 2000% increase in risk, very different from the 20% found for processed meat (and many other dietary effects). Nobody could doubt seriously the causality in that case.
The decision about whether to eat bacon and sausages has to be a personal one. It depends on your attitude to the precautionary principle. The observations do not, in my view, constitute strong evidence for causality, but they are certainly compatible with causality. It could be true so if you want to be on the safe side then avoid bacon. Of course life would not be much fun if your actions were based on things that just could be true.
My own inclination would be to ignore any relative risk based on observational data if it was less than about 2. The National Cancer Institute (Nelson, 2002) advises that relative risks less than 2 should be “viewed with caution”, but fails to explain what “viewing with caution” means in practice, so the advice isn’t very useful.
In fact hardly any of the relative risks reported in the WCRF report (2007) reach this level. Almost all relative risks are less than 1.3 (or greater than 0.7 for alleged protective effects). Perhaps it is best to stop worrying and get on with your life. At some point it becomes counterproductive to try to micromanage `people’s diet on the basis of dubious data. There is a price to pay for being too precautionary. It runs the risk of making people ignore information that has got a sound basis. It runs the risk of excessive medicalisation of everyday life. And it brings science itself into disrepute when people laugh at the contradictory findings of observational epidemiology.
The question of how diet and other ‘lifestyle interventions’ affect health is fascinating to everyone. There is compelling reason to think that it matters. For example one study demonstrated that breast cancer incidence increased almost threefold in first-generation Japanese women who migrated to Hawaii, and up to fivefold in the second generation (Kolonel, 1980). Since then enormous effort has been put into finding out why. The first great success was cigarette smoking but that is almost the only major success. Very few similar magic bullets have come to light after decades of searching (asbestos and mesothelioma, or UV radiation and skin cancer count as successes).
The WCRF report (2007) has 537 pages and over 4400 references and we still don’t know.
Sometimes I think we should say “I don’t know” rather more often.
More material
-
Listen to Ben Goldacre’s Radio 4 programmes. The Rise of the Lifetsyle Nutritionists. Part 1 and Part 2 (mp3 files), and at badscience.net.
-
Risk The Science and Politics of Fear, Dan Gardner. Virgin
Books, 2008 -
Some bookmarks about diet and supplements
Follow up
Dan Gardner, the author of Risk, seems to like the last line at least, according to his blog.
Report of the update, 2010
The 2010 report has been updated in WCRF/AICR Systematic Literature Review Continuous Update Project Report [big pdf file]. This includes studies up to May/June 2010.
The result of addition of the new data was to reduce slightly the apparent risk from eating processed meat from 1.21 (95% CI = 1.04-1.42) in the original study to 1.18 (95% CI = 1.10-1.28) in the update. The change is too small to mean much, though it is in direction expected for false correlations. More importantly, the new data confirm that the dose-response curves are pathetic. The evidence for causality is weakened somewhat by addition of the new data.
Dose-response graph of processed meat and colorectal cancer
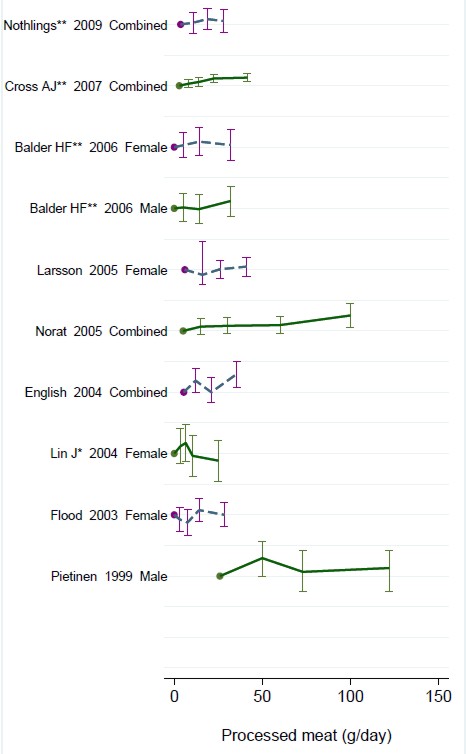
Alfred Joseph Clark FRS held the established chair of Pharmacology at UCL from 1919 to 1926, when he left for Edinburgh. In the 1920s and 30s, Clark was a great pioneer in the application of quantitative physical ideas to pharmacology. As well as his classic scientific works, like The Mode of Action of Drugs on Cells (1933) he wrote, and felt strongly, about the fraud perpetrated on the public by patent medicine salesmen. In 1938 (while in Edinburgh) he published a slim volume called Patent Medicines. The parallels with today are astonishing.
Alfred Joseph Clark FRS (1885 – 1941) |
 |
I was lucky to be given a copy of this book by David Clark, A.J. Clark’s eldest son, who is now 88. I visited him in Cambridge on 17 September 2008, because he thought that, as holder of the A.J. Clark chair at UCL from 1985 to 2004, I’d be a good person to look after this and several other books from his father’s library. They would have gone to the Department of Pharmacology if we still had one, but that has been swept away by mindless administrators with little understanding of how to get good science.
Quotations from the book are in italic, and are interspersed with comments from me.
The book starts with a quotation from the House of Commons Select Committee report on Patent Medicines. The report was submitted to the House on 4 August 1914, so there is no need to explain why it had little effect. The report differs from recent ones in that it is not stifled by the sort of political correctness that makes politicians refer to fraudsters as “professions”.
The problem
“2.2 The situation, therefore, as regards the sale and advertisement of proprietary medicines and articles may be summarised as follows:
For all practical purposes British law is powerless to prevent any person from procuring any drug, or making any mixture, whether patent or without any therapeutical activity whatever (as long as it does not contain a scheduled poison), advertising it in any decent terms as a cure for any disease or ailment, recommending it by bogus testimonials and the invented opinions and facsimile signatures of fictitious physicians, and selling it under any name he chooses, on payment of a small stamp duty. For any price he can persuade a credulous public to pay.”
Select Committee on Patent Medicines. 1914
“The writer has endeavoured in the present article to analyse the reasons for the amazing immunity of patent medicines form all attempts to curb their activity, to estimate the results and to suggest the obvious measures of reform that are needed.”
| Clark, writing in 1938, was surprised that so little had changed since 1914. What would he have thought if he had known that now, almost 100 years after the 1914 report, the fraudsters are still getting away with it? Chapter 2 starts thus. |
 |
THE LAW
The Select Committee appointed by the House of Commons in 1914 ‘to consider and inquire into the question of the sale of Patent and Proprietary Medicines’ stated its opinion in 28 pages of terse and uncompromising invective. Its general conclusions were as follows:
That the trade in secret remedies constituted a grave and widespread public evil.
That the existing law was chaotic and had proved inoperative and that consequently the traffic in secret remedies was practically uncontrolled.
In particular it concluded ‘”that this is an intolerable state of things and that new legislation to deal with it, rather than merely the amendment of existing laws, is urgently needed in the public interest.”
The “widespread public evil”continues almost unabated, and rather than introduce sensible legislation to cope with it, the government has instead given a stamp of approval for quackery by introducing utterly ineffective voluntary “self-regulation”.
Another Bill to deal with patent medicines was introduced in 1931, without success, and finally in 1936, a Medical and Surgical Appliances (Advertisement) Bill was introduced. This Bill had a very limited scope. Its purpose was to alleviate some of the worst abuses of the quack medicine trade by prohibiting the advertisement of cures for certain diseases such as blindness, Bright’s disease [nephritis] , cancer, consumption [tuberculosis], epilepsy, fits, locomotor ataxy, fits, lupus or paralysis.
The agreement of many interests was secured for this measure. The president of the Advertising Association stated that the proposed Bill would not affect adversely any legitimate trade interest. Opposition to the Bill was, however, whipped up amongst psychic healers, anti-vivisectionists and other opponents of medicine and at the second reading in March 1936, the Bill was opposed and the House was counted out during the ensuing debate. The immediate reason for this fate was that the Bill came up for second reading on the day of the Grand National! This is only one example of the remarkable luck that has attended the patent medicine vendors.
(Page 14).
The “remarkable luck” of patent medicine vendors continues to this day, Although, in principle, advertisement of cures for venereal diseases was banned in 1917, and for cancer in 1939, it takes only a few minutes with Google to find that these laws are regularly flouted by quacks, In practice quacks get away with selling vitamin pills for AIDS, sugar pills for malaria and homeopathic pills for rabies, polio anthrax and just about anything else you can think of. Most of these advertisements are contrary to the published codes of ethics of the organisations to which the quack in question belongs but nothing ever happens.
Self-regulation simply does not work, and there is still no effective enforcement even of existing laws..
“It has already been stated that British law allows the advertiser of a secret remedy to tell any lie or make any claim that he fancies will sell his goods and the completeness of this licence is best illustrated by the consideration of a few specific points.
Advertisements for secret remedies very frequently contain a list of testimonials from medical men, which usually are in an anonymous form, stating that ………….. M.D., F.R.C.S., has found the remedy infallible. Occasionally, however, the name and address of a doctor is given and anyone unaware of the vagaries of English law would imagine that such use of a doctor’s name and professional reputation could not be made with impunity without his consent. In 1899, however, the Sallyco Mineral Water Company advertised that ‘Dr. Morgan Dochrill, physician to St. John’s Hospital, London and many of the leading physicians are presenting ‘Sallyco’ as an habitual drink. Dr. Dochrill says nothing has done his gout so much good.
Dr. Dochrill, whose name and title were correctly stated above, sued the company but failed in his case. ”
“The statement that the law does not prevent the recommending of a secret remedy by the use of bogus testimonials and facsimile signatures of fictitious physicians is obviously an understatement since it is doubtful how far it interferes with the use of bogus testimonials from real physicians.”
Dodgy testimonials are still a mainstay of dodgy salesman. One is reminded of the unauthorised citation of testimonials from Dr John Marks and Professor Jonathan Waxman by Patrick Holford to aid his sales of unnecessary vitamin supplements. There is more on this at Holfordwatch.
The man in the street knows that the merits of any article are usually exaggerated in advertisements and is in the habit of discounting a large proportion of such claims, but, outside the realm of secret remedies, the law is fairly strict as regards definite misstatements concerning goods offered for sale and hence the everyday experience of the man in the street does not prepare him for dealing with advertisements which are not merely exaggerations but plain straightforward lies from beginning to end.
Scientific training is undoubtedly a handicap in estimating popular gullibility as regards nostrums. One imagines that no one today would be willing to spend money on pills guaranteed to prevent earthquakes but yet the claims of many of the remedies offered appear equally absurd to anyone with an elementary
knowledge of physiology or even of chemistry. A study of the successes and failures suggests that success depends chiefly on not over-rating the public intelligence. (Page 34)
This may have changed a bit since A.J. Clark was writing in 1938. Now the main clients of quacks seem to be the well-off “worried-well”. But it remains as true as ever that “Scientific training is undoubtedly a handicap in estimating popular gullibility as regards nostrums.” In 2008, it is perhaps more a problem of Ben Goldacre’s dictum ““My basic hypothesis is this: the people who run the media are humanities graduates with little understanding of science, who wear their ignorance as a badge of honour.”
Clark refers (page 36) to a successful conviction for fraud in the USA in 1917. The subject was a widely advertised ‘get fat quick’ pill that contained lecithin, proteins and sugar. The BMA analysis (in 1912)
suggested that the cost of the ingredients in a box of 30 tablets sold for 4/6 was 1 1/4 d. [4/6 meant 4 shillings and six pence, or 22.5 pence since 1971, and 1 1/4 old pence, a penny farthing, is 0.52 new pence]. He comments thus.
The trial revealed many interesting facts. The formula was devised after a short consultation with the expert of one of the largest drug manufacturers in the U.S.A. This firm manufactured the tablets and sold them to the proprietary medicine company at about 3/- per 1000, whilst they were retailed to the public at the rate of £7 10s. per 1000. The firm is estimated to have made a profit of about $3,000,000.
These trials in the U.S.A. revealed the fact that in a considerable proportion of cases the ‘private formula’ department of the large and well known drug firm already mentioned had first provided the formula for the nostrum and subsequently had prepared it wholesale.
Nothing much has changed here either. The alternative medicine industry (and it is a very big industry) is fond of denouncing the evils of the pharmaceutical industry, and sadly, occasionally they are right. One of the less honest practices of the pharmaceutical industry (though one never mentioned by quacks) is buying heavily into alternative medicine. Goldacre points out
“there is little difference between the vitamin and pharmaceutical industries. Key players in both include multinationals such as Roche and Aventis; BioCare, the vitamin pill producer that media nutritionist Patrick Holford works for, is part-owned by Elder Pharmaceuticals.”
And then. of course, there is the deeply dishonest promotion by Boots the Chemists of homeopathic miseducation, of vitamins and of CoQ10 supplements.
The manner in which secret remedies can survive repeated exposure is shown by the following summary of the life history of a vendor of a consumption [tuberculosis] cure.
1904, 1906: Convicted of violating the law in South Africa.
1908: Exposed in British Medical Association report and also attacked by Truth.
1910: Sued by a widow. The judge stated: ‘I think this is an intentional and well-considered fraud. It is a scandalous thing that poor people should be imposed upon and led to part with their money, and to hope that those dear to them would be cured by those processes which were nothing but quack remedies and had not the slightest value of any kind.’
1914: A libel action against the British Medical Association was lost.
1915 The cure was introduced into the United States.
1919 The cure was sold in Canada.
1924 Articles by men with medical qualifications appeared in the Swiss medical journal boosting
the cure.
Secret remedies have a vitality that resembles that of the more noxious weeds and the examples mentioned suggest that nothing can do them any serious harm.
Most of the time, quacks get away with claims every bit as outrageous today. But Clark does give one example of a successful prosecution. It resulted from an exposé in the newspapers -wait for it -in the Daily Mail.
There is, however, one example which proves that a proprietary remedy can be squashed by exposure if this is accompanied by adequate publicity.
The preparation Yadil was introduced as an antiseptic and was at first advertised to the medical profession. The proprietor claimed that the remedy was not secret and that the active principle was ‘tri-methenal allylic carbide’. The drug acquired popularity in the influenza epidemic of 1918 and the proprietor became more and more ambitious in his therapeutic claims. The special virtue claimed for Yadil was that it would kill any harmful organism that had invaded the body. A more specific claim was that consumption in the first stage was cured with two or three pints whilst advanced cases might require a little more. Other advertisements suggested that it was a cure for most known diseases from cancer downwards.
These claims were supported by an extraordinarily intense advertising campaign. Most papers, and even magazines circulating amongst the wealthier classes, carried full page and even double page advertisements. The Daily Mail refused these advertisements and in 1924 published a three column article by Sir William Pope, professor of Chemistry in the University of Cambridge. He stated that
the name ‘tri-methenal allylic carbide’ was meaningless gibberish and was not the chemical definition of any known substance. He concluded that Yadil consisted of :
‘About one per cent of the chemical compound formaldehyde.
About four per cent of glycerine.
About ninety-five per cent of water and, lastly, a smell.
He calculated that the materials contained in a gallon cost about 1/6, whilst the mixture was sold at £4 10s. per gallon.
This exposure was completely successful and the matter is of historic interest in that it is the only example of the career of a proprietary medicine being arrested by the action of the Press.
Clark goes on to talk of the law of libel.
“On the other hand the quack medicine vendor can pursue his advertising campaigns in the happy assurance that, whatever lies he tells, he need fear nothing from the interference of British law. The law does much to protect the quack medicine vendor because the laws of slander and libel are so severe.”
The law of libel to this day remains a serious risk to freedom of speech of both individuals and the media. Its use by rogues to suppress fair comment is routine. My first encounter was when a couple of herbalists
threatened to sue UCL because I said that the term ‘blood cleanser’ is gobbledygook. The fact that the statement was obviously true didn’t deter them for a moment. The herbalists were bluffing no doubt, but they caused enough nuisance that I was asked to take my pages off UCL’s server. A week later I was invited back but by then I’d set up a much better blog and the publicity resulted in an enormous increase in readership, so the outcome was good for me (but bad for herbalists).
It was also good in the end for Andy Lewis when his immortal page “The gentle art of homoeopathic killing” (about the great malaria scandal) was suppressed. The Society of Homeopaths’ lawyers didn’t go for him personally but for his ISP who gave in shamefully and removed the page. As a result the missing page reappeared in dozens of web sites round the world and shot to the top in a Google search.
Chiropractors are perhaps the group most likely to try to suppress contrary opinions by law not argument. The only lawyers’ letter that has been sent to me personally, alleged defamation in an editorial that I wrote for the New Zealand Medical Journal. That was a little scary, but the journal stuck up for its right to speak and the threat went away after chiropractors were allowed right of reply (but we got the last word).
Simon Singh, one of the best science communicators we have, has not been so lucky. He is going to have to defend in court an action brought by the British Chiropractic Association because of innocent opinions expressed in the Guardian.
Chapter 6 is about “The harm done by patent medicines”. It starts thus.
“The trade in secret remedies obviously represents a ridiculous waste of money but some may argue that, since we are a free country and it pleases people to waste their money in this particular way, there is no call for any legislative interference. The trade in quack medicines cannot, however, be regarded as a harmless one. The Poisons Acts fortunately prevent the sale of a large number of dangerous drugs, but there are numerous other ways in which injury can be produced by these remedies.”
The most serious harm, he thought, resulted from self-medication, and he doesn’t mince his words.
“The most serious objection to quack medicines is however that their advertisements encourage self-medication as a substitute for adequate treatment and they probably do more harm in this than in any other manner.
The nature of the problem can best be illustrated by considering a simple example such as diabetes. In this case no actual cure is known to medicine but, on the other hand, if a patient is treated adequately by insulin combined with appropriate diet, he can be maintained in practically normal health, in spite of his disability, for an indefinite period. The expectation of life of the majority of intelligent diabetics, who make no mistakes in their regime, is not much less than that of normal persons. The regime is both irksome and unpleasant, but anyone who persuades diabetics to abandon it, is committing manslaughter as certainly as if he fired a machine gun into a crowded street.
As regards serious chronic disease the influence of secret remedies may be said to range from murderous to merely harmful.
‘Cures’ for consumption, cancer and diabetes may fairly be classed as murderous, since they are likely to cause the death of anyone who is unfortunate enough to believe in their efficacy and thus delay adequate treatment until too late.
The phrase “‘Cures for consumption, cancer and diabetes may fairly be classed as murderous” made Clark himself the victim of suppression of freedom of speech by lawyers. His son, David Clark, wrote of his father in “Alfred Joseph Clark, A Memoir” (C. & J. Clark Ltd 1985 ISBN 0-9510401-0-3)
“Although tolerant of many human foibles, A. J. had always disapproved fiercely of quacks, particularly the charlatans who sold fraudulent medicines. During his visits to London he met Raymond Postgate, then a crusading left wing journalist, who persuaded A.J. to write a pamphlet which was published in an ephemeral series called ‘Fact‘ in March 1938. It was a lively polemical piece. . To A.J.’s surprise and dismay he was sued for libel by a notorious
rogue who peddled a quack cure for for tuberculosis. This man said that A.J.’s remarks (such as “‘Cures’ for consumption, cancer and diabetes may fairly be classed as murderous”) were libellous and would damage his business. A.J. was determined to fight, and he and Trixie decided to put their savings at stake if necessary. The B.M.A. and the Medical Defence Union agreed to support him and they all went to lawyers. He was shocked when they advised him that he would be bound to lose for he had damaged the man’s livelihood! Finally, after much heart searching, he made an apology, saying that he had not meant that particular man’s nostrum”
Talk about déjà vu!
On page 68 there is another very familiar story. It could have been written today.
“The fact that the public is acquiring more knowledge of health matters and is becoming more suspicious of the cruder forms of lies is also helping to weed out the worst types of patent medicine advertisements. For example, in 1751 a bottle of oil was advertised as a cure for scurvy, leprosy and consumption but today such claims would not be effective in promoting the sale of a remedy. The modern advertiser would probably claim that the oil was rich in all the vitamins and the elements essential for life and would confine his claims to a statement that it would alleviate all minor forms of physical or mental ill-health.
The average patent medicine advertised today makes plausible rather than absurd claims and in general the advertisements have changed to conform with a change in the level of the public’s knowledge.
It is somewhat misleading, however, to speak of this as an improvement, since the law has not altered and hence the change only means that the public is being swindled in a somewhat more skilful manner.
The ideal method of obtaining an adequate vitamin supply is to select a diet containing an abundant supply of fresh foods, but unfortunately the populace is accustomed to live very largely on preserved or partially purified food stuffs and such processes usually remove most of the vitamins.”
The first part of the passage above is reminiscent of something that A.J Clark wrote in the BMJ in 1927. Nowadays it is almost unquotable and I was told by a journal editor that it was unacceptable even with asterisks. That seems to me a bit silly. Words had different connotations in 1927.
“The less intelligent revert to the oldest form of belief and seek someone who will make strong magic for them and defeat the evil spirits by some potent charm. This is the feeling to which the quack appeals; he claims to be above the laws of science and to possess some charm for defeating disease of any variety.
The nature of the charm changes with the growth of education. A naked n****r howling to the beat of a tom-tom does not impress a European, and most modern Europeans would be either amused or disgusted by the Black mass that was popular in the seventeenth century. Today some travesty of physical science appears to be the most popular form of incantation.”
A.J. Clark (1927) The historical aspect of quackery, BMJ October 1st 1927
Apart from some of the vocabulary, what better description could one have of the tendency of homeopaths to harp on meaninglessly about quantum theory or the “scienciness” and “referenciness” of
modern books on nutritional therapy?
So has anything changed?
Thus far, the outcome might be thought gloomy. Judging by Clark’s account, remarkably little has changed since 1938, or even since 1914. The libel law in the UK is as bad now as it was then. Recently the United Nations Human Rights Committee said UK laws block matters of public interest and encourage libel tourism (report here, see also here). It is unfit for a free society and it should be changed.
But there are positive sides too. Firstly the advent of scientific bloggers has begun to have some real influence. People are no longer reliant on journalists to interpret (or, often, misinterpret) results for them. They can now get real experts and links to original sources. Just one of these, Ben Goldacre’s badscience.net, and his weekly column in the Guardian has worked wonders in educating the public and improving journalism. Young people can, and do, contribute to the debate because they can blog anonymously if they are frightened that their employer might object.
Perhaps still more important, the law changed this year. Now, at last, it may be possible to prosecute successfully those who make fraudulent health claims. Sad to say, this was not an initiative of the UK government, which remains as devoted as ever to supporting quacks. Remember that, quite shamefully, the only reason given by the Medicines and Health Regulatory Authority (MHRA) gave for allowing false labelling of homeopathic pills was to support the “homeopathic industry”. They suggested (falsely) that the EU required them to take this irresponsible step, which was condemned by just about every scientific organisation. But the new unfair trading regulations did come from the EU. After almost 100 years since the 1914 report, we have at last some decent legislation. Let’s hope it’s enforced.
Postcript
The back cover of the series of ‘Fact‘ books in which A.J. Clark’s article appeared is reproduced below, simply because of the historical portrait of the 1930s that it gives.
Follow-up
This post got a lot of hits from Ben Goldacre’s miniblog which read
- Prof David Colquhoun gets into a time machine and meets himself
A truly classic DC post.
Thanks, Ben.