nutribollocks
‘We know little about the effect of diet on health. That’s why so much is written about it’. That is the title of a post in which I advocate the view put by John Ioannidis that remarkably little is known about the health effects if individual nutrients. That ignorance has given rise to a vast industry selling advice that has little evidence to support it.
The 2016 Conference of the so-called "College of Medicine" had the title "Food, the Forgotten Medicine". This post gives some background information about some of the speakers at this event. I’m sorry it appears to be too ad hominem, but the only way to judge the meeting is via the track record of the speakers.


Quite a lot has been written here about the "College of Medicine". It is the direct successor of the Prince of Wales’ late, unlamented, Foundation for Integrated Health. But unlike the latter, its name is disguises its promotion of quackery. Originally it was going to be called the “College of Integrated Health”, but that wasn’t sufficently deceptive so the name was dropped.
For the history of the organisation, see
Don’t be deceived. The new “College of Medicine” is a fraud and delusion
The College of Medicine is in the pocket of Crapita Capita. Is Graeme Catto selling out?
The conference programme (download pdf) is a masterpiece of bait and switch. It is a mixture of very respectable people, and outright quacks. The former are invited to give legitimacy to the latter. The names may not be familiar to those who don’t follow the antics of the magic medicine community, so here is a bit of information about some of them.
The introduction to the meeting was by Michael Dixon and Catherine Zollman, both veterans of the Prince of Wales Foundation, and both devoted enthusiasts for magic medicne. Zollman even believes in the battiest of all forms of magic medicine, homeopathy (download pdf), for which she totally misrepresents the evidence. Zollman works now at the Penny Brohn centre in Bristol. She’s also linked to the "Portland Centre for integrative medicine" which is run by Elizabeth Thompson, another advocate of homeopathy. It came into being after NHS Bristol shut down the Bristol Homeopathic Hospital, on the very good grounds that it doesn’t work.
Now, like most magic medicine it is privatised. The Penny Brohn shop will sell you a wide range of expensive and useless "supplements". For example, Biocare Antioxidant capsules at £37 for 90. Biocare make several unjustified claims for their benefits. Among other unnecessary ingredients, they contain a very small amount of green tea. That’s a favourite of "health food addicts", and it was the subject of a recent paper that contains one of the daftest statistical solecisms I’ve ever encountered
"To protect against type II errors, no corrections were applied for multiple comparisons".
If you don’t understand that, try this paper.
The results are almost certainly false positives, despite the fact that it appeared in Lancet Neurology. It’s yet another example of broken peer review.
It’s been know for decades now that “antioxidant” is no more than a marketing term, There is no evidence of benefit and large doses can be harmful. This obviously doesn’t worry the College of Medicine.
Margaret Rayman was the next speaker. She’s a real nutritionist. Mixing the real with the crackpots is a standard bait and switch tactic.
Eleni Tsiompanou, came next. She runs yet another private "wellness" clinic, which makes all the usual exaggerated claims. She seems to have an obsession with Hippocrates (hint: medicine has moved on since then). Dr Eleni’s Joy Biscuits may or may not taste good, but their health-giving properties are make-believe.
Andrew Weil, from the University of Arizona
gave the keynote address. He’s described as "one of the world’s leading authorities on Nutrition and Health". That description alone is sufficient to show the fantasy land in which the College of Medicine exists. He’s a typical supplement salesman, presumably very rich. There is no excuse for not knowing about him. It was 1988 when Arnold Relman (who was editor of the New England Journal of Medicine) wrote A Trip to Stonesville: Some Notes on Andrew Weil, M.D..
“Like so many of the other gurus of alternative medicine, Weil is not bothered by logical contradictions in his argument, or encumbered by a need to search for objective evidence.”
This blog has mentioned his more recent activities, many times.
Alex Richardson, of Oxford Food and Behaviour Research (a charity, not part of the university) is an enthusiast for omega-3, a favourite of the supplement industry, She has published several papers that show little evidence of effectiveness. That looks entirely honest. On the other hand, their News section contains many links to the notorious supplement industry lobby site, Nutraingredients, one of the least reliable sources of information on the web (I get their newsletter, a constant source of hilarity and raised eyebrows). I find this worrying for someone who claims to be evidence-based. I’m told that her charity is funded largely by the supplement industry (though I can’t find any mention of that on the web site).
Stephen Devries was a new name to me. You can infer what he’s like from the fact that he has been endorsed byt Andrew Weil, and that his address is "Institute for Integrative Cardiology" ("Integrative" is the latest euphemism for quackery). Never trust any talk with a title that contains "The truth about". His was called "The scientific truth about fats and sugars," In a video, he claims that diet has been shown to reduce heart disease by 70%. which gives you a good idea of his ability to assess evidence. But the claim doubtless helps to sell his books.
Prof Tim Spector, of Kings College London, was next. As far as I know he’s a perfectly respectable scientist, albeit one with books to sell, But his talk is now online, and it was a bit like a born-again microbiome enthusiast. He seemed to be too impressed by the PREDIMED study, despite it’s statistical unsoundness, which was pointed out by Ioannidis. Little evidence was presented, though at least he was more sensible than the audience about the uselessness of multivitamin tablets.
Simon Mills talked on “Herbs and spices. Using Mother Nature’s pharmacy to maintain health and cure illness”. He’s a herbalist who has featured here many times. I can recommend especially his video about Hot and Cold herbs as a superb example of fantasy science.
Annie Anderson, is Professor of Public Health Nutrition and
Founder of the Scottish Cancer Prevention Network. She’s a respectable nutritionist and public health person, albeit with their customary disregard of problems of causality.
Patrick Holden is chair of the Sustainable Food Trust. He promotes "organic farming". Much though I dislike the cruelty of factory farms, the "organic" industry is largely a way of making food more expensive with no health benefits.
The Michael Pittilo 2016 Student Essay Prize was awarded after lunch. Pittilo has featured frequently on this blog as a result of his execrable promotion of quackery -see, in particular, A very bad report: gamma minus for the vice-chancellor.
Nutritional advice for patients with cancer. This discussion involved three people.
Professor Robert Thomas, Consultant Oncologist, Addenbrookes and Bedford Hospitals, Dr Clare Shaw, Consultant Dietitian, Royal Marsden Hospital and Dr Catherine Zollman, GP and Clinical Lead, Penny Brohn UK.
Robert Thomas came to my attention when I noticed that he, as a regular cancer consultant had spoken at a meeting of the quack charity, “YestoLife”. When I saw he was scheduled tp speak at another quack conference. After I’d written to him to point out the track records of some of the people at the meeting, he withdrew from one of them. See The exploitation of cancer patients is wicked. Carrot juice for lunch, then die destitute. The influence seems to have been temporary though. He continues to lend respectability to many dodgy meetings. He edits the Cancernet web site. This site lends credence to bizarre treatments like homeopathy and crystal healing. It used to sell hair mineral analysis, a well-known phony diagnostic method the main purpose of which is to sell you expensive “supplements”. They still sell the “Cancer Risk Nutritional Profile”. for £295.00, despite the fact that it provides no proven benefits.
Robert Thomas designed a food "supplement", Pomi-T: capsules that contain Pomegranate, Green tea, Broccoli and Curcumin. Oddly, he seems still to subscribe to the antioxidant myth. Even the supplement industry admits that that’s a lost cause, but that doesn’t stop its use in marketing. The one randomised trial of these pills for prostate cancer was inconclusive. Prostate Cancer UK says "We would not encourage any man with prostate cancer to start taking Pomi-T food supplements on the basis of this research". Nevertheless it’s promoted on Cancernet.co.uk and widely sold. The Pomi-T site boasts about the (inconclusive) trial, but says "Pomi-T® is not a medicinal product".
There was a cookery demonstration by Dale Pinnock "The medicinal chef" The programme does not tell us whether he made is signature dish "the Famous Flu Fighting Soup". Needless to say, there isn’t the slightest reason to believe that his soup has the slightest effect on flu.
In summary, the whole meeting was devoted to exaggerating vastly the effect of particular foods. It also acted as advertising for people with something to sell. Much of it was outright quackery, with a leavening of more respectable people, a standard part of the bait-and-switch methods used by all quacks in their attempts to make themselves sound respectable. I find it impossible to tell how much the participants actually believe what they say, and how much it’s a simple commercial drive.
The thing that really worries me is why someone like Phil Hammond supports this sort of thing by chairing their meetings (as he did for the "College of Medicine’s" direct predecessor, the Prince’s Foundation for Integrated Health. His defence of the NHS has made him something of a hero to me. He assured me that he’d asked people to stick to evidence. In that he clearly failed. I guess they must pay well.
Follow-up
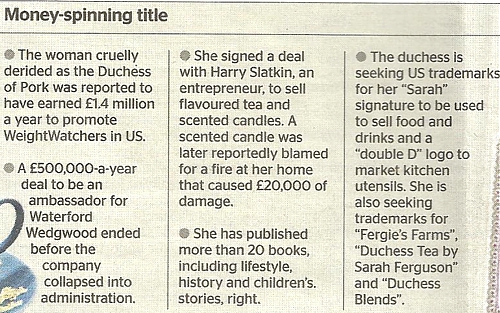
Sarah Ferguson, ex-wife of Prince Andrew, Duke of York, seems to need a lot of money. Some of her wheezes are listed in today’s Times. That’s behind a paywall, as is the version reproduced in The Australian (Murdoch connection presumably). You can read it (free) here, with more details below the article.
|
Thomas Ough and David Brown Published at 12:01AM, January 15 2015 In her seemingly endless quest to make money, Sarah, Duchess of York, has had little hesitation using her title to generate sales. This week, though, she landed herself in trouble after appearing to use the name of Britain’s foremost scientific university to lend credibility to a promotion for her new diet system. The duchess told NBC’s Today show during an interview to promote her “emulsifier” programme that she was aware of the dangers of obesity through her work as an ambassador for the Institute of Global Health Improvement at Imperial College London. Last night she apologised for “any misunderstanding” after Imperial College, ranked the joint second-best university in the world, sought to distance itself from the duchess’s promotion. A spokesman said: “The commercial activities promoted by Sarah Ferguson in the interview with Today are not connected in any way to Imperial’s staff or research activities, and the college does not endorse the suggestion of any possible link.” The institute, which has more than 160 specialists, including clinicians, engineers, scientists and psychologists, is headed by Lord Darzi of Denham, a former Labour health minister. The duchess told the Today presenter Matt Lauer that she had been a comfort eater since the age of 12 but the “turning point” was when she realised that she was the same weight as when pregnant with Princess Beatrice, now 25. “I couldn’t bear looking at myself any minute longer,” she confided. “In fact, the size of my ass probably saved my life.” She said she discovered that the “emulsifier” was “a solution for behavioural change” and helped her to lose 55lbs. The $99 kit, which includes a blender, a couple of recipe books and some workout DVDs, is produced by Tristar Products, a direct marketing company for home and health items. The duchess told the breakfast show: “I have just found out on my discoveries with Imperial College London . . . I’m an ambassador for the Institute for Global Health Innovation, and I found out that children, little children, are going to die before their parents because of obesity.” The benefits of the kit were questioned yesterday by Ayela Spiro, a senior scientist at the British Nutrition Foundation. She said: “In terms of the particular product, no juicer or blender on their own can enhance how much nutrition your body will absorb. Any claims made about such products such that it accelerates weight loss, boosts energy and strengthens the immune system need to be treated with caution.” Professor David Colquhoun of University College London, said: “I find it pretty amazing that Imperial chose someone like her to be an ‘ambassador’. Imperial does have an interest in appetite suppression but hasn’t come up with any usable product yet and this research has nothing to do with blenders. “[Her television appearance] was sheer name-dropping, something she’s quite good at. The only ‘discovery’ she seems to have made is that if you eat less you’ll lose weight. The $100 blender has nothing to do with it.” A spokesman for the duchess said: “She is not trying to use her association with the institute to promote her personal interests. She was talking about ‘behavioural change’, which is endorsed by the institute, and her own behavioural change.” |
With the article there’s an inset that gives details of other ways in which Sarah Ferguson has exploited her title to make money.
Fergie’s latest wheeze, Duchess Discoveries is being promoted heavily on US television. It bears a close resemblance to those ghastly daytime TV advertising channels. Watch her interview on a US TV programme, "Today".
It’s partly promoting her latest diet scam, and partly a vigorous defence of her ex-husbands innocence in the face of allegations of sexual shenanigans. Of course she doesn’t know whether the allegations are true. The Queen doesn’t know (so why bother with the denial from Buckingham Palace?). And I don’t know. We know plenty about Prince Andrew’s bad behaviour, but we don’t know whether he’s had sex with minors.
Worse still is the promotional video on the “Duchess Discoveries” site itself.
I quote:
“I’m SO excited about my fusion accelerator system, accelerates weight loss, accelerates your energy, accelerates and strengthens your immune system.”
"accelerates weight loss" is certainly unproven. Mere hype
"accelerates your energy" is totally meaningless. It’s the sort of sciencey-sounding words that are loved by all quacks.
"accelerates and strengthens your immune system". Sigh. "strengthening the immune system is the perpetual mantra of just about every quack. It’s totally meaningless. Just made-up nutribollocks.
The promotional video is fraudulent nonsense. If it were based in the UK I have no doubt that it would be quickly slapped down by the Advertising Standards Authority. But in the USA the first amendment allows people to lie freely about nutrition, which is why it’s such big business.
It bothers me that the most that the best that the British Nutrition Foundation could manage was to say that such claims "need to be treated with caution". They are mendacious nonsense. Why not just say so?
Follow-up
One of my scientific heroes is Bernard Katz. The closing words of his inaugural lecture, as professor of biophysics at UCL, hang on the wall of my office as a salutory reminder to refrain from talking about ‘how the brain works’. After speaking about his discoveries about synaptic transmission, he ended thus.
|
"My time is up and very glad I am, because I have been leading myself right up to a domain on which I should not dare to trespass, not even in an Inaugural Lecture. This domain contains the awkward problems of mind and matter about which so much has been talked and so little can be said, and having told you of my pedestrian disposition, I hope you will give me leave to stop at this point and not to hazard any further guesses." |
The question of what to eat for good health is truly a topic about "which so much has been talked and so little can be said"
That was emphasized yet again by an editorial in the British Medical Journal written by my favourite epidemiologist. John Ioannidis. He has been at the forefront of debunking hype. Its title is “Implausible results in human nutrition research” (BMJ, 2013;347:f6698.
Get pdf).
The gist is given by the memorable statement
"Almost every single nutrient imaginable has peer reviewed publications associating it with almost any outcome."
and the subtitle
“Definitive solutions won’t come from another million observational papers or small randomized trials“.
Being a bit obsessive about causality, this paper is music to my ears. The problem of causality was understood perfectly by Samuel Johnson, in 1756, and he was a lexicographer, not a scientist. Yet it’s widely ignored by epidemiologists.
The problem of causality is often mentioned in the introduction to papers that describe survey data, yet by the end of the paper, it’s usually forgotten, and public health advice is issued.
Ioannidis’ editorial vindicates my own views, as an amateur epidemiologist, on the results of the endless surveys of diet and health.
- Diet and health. What can you believe: or does bacon kill you (2009) in which I look at the World Cancer Research Fund’s evidence for causality (next to none in my opinion). Through this I got to know Gary Taubes, whose explanation of causality in the New York Times is the best popular account I’ve ever seen.
- How big is the risk from eating red meat now: an update (2012) This was based on the WCRF update – the risk was roughly halved though it didn’t say that in the press release.
- Another update. Red meat doesn’t kill you, but the spin is fascinating (2013). Update after the EPIC results in which the risk essentially vanished: good news which you could find only by digging into Table 3.
There is nothing new about the problem. It’s been written about many times. Young & Karr (Significance, 8, 116 – 120, 2011: get pdf) said "Any claim coming from an observational study is most likely to be wrong". Out of 52 claims made in 12 observational studies, not a single one was confirmed when tested by randomised controlled trials.
Another article cited by Ioannidis, "Myths, Presumptions, and Facts about Obesity" (Casazza et al , NEJM, 2013), debunks many myths, but the list of conflicts of interests declared by the authors is truly horrendous (and at least one of their conclusions has been challenged, albeit by people with funding from Kellogg’s). The frequent conflicts of interest in nutrition research make a bad situation even worse.
The quotation in bold type continues thus.
"On 25 October 2013, PubMed listed 291 papers with the keywords “coffee OR caffeine” and 741 with “soy,” many of which referred to associations. In this literature of epidemic proportions, how many results are correct? Many findings are entirely implausible. Relative risks that suggest we can halve the burden of cancer with just a couple of servings a day of a single nutrient still circulate widely in peer reviewed journals.
However, on the basis of dozens of randomized trials, single nutrients are unlikely to have relative risks less than 0.90 for major clinical outcomes when extreme tertiles of population intake are compared—most are greater than 0.95. For overall mortality, relative risks are typically greater than 0.995, if not entirely null. The respective absolute risk differences would be trivial. Observational studies and even randomized trials of single nutrients seem hopeless, with rare exceptions. Even minimal confounding or other biases create noise that exceeds any genuine effect. Big datasets just confer spurious precision status to noise."
And, later,
"According to the latest burden of disease study, 26% of deaths and 14% of disability adjusted life years in the United States are attributed to dietary risk factors, even without counting the impact of obesity. No other risk factor comes anywhere close to diet in these calculations (not even tobacco and physical inactivity). I suspect this is yet another implausible result. It builds on risk estimates from the same data of largely implausible nutritional studies discussed above. Moreover, socioeconomic factors are not considered at all, although they may be at the root of health problems. Poor diet may partly be a correlate or one of several paths through which social factors operate on health."
Another field that is notorious for producing false positives, wirh false attribution of causality, is the detection of biomarkers. A critical discussion can be found in the paper by Broadhurst & Kell (2006), "False discoveries in metabolomics and related experiments".
"Since the early days of transcriptome analysis (Golub et al., 1999), many workers have looked to detect different gene expression in cancerous versus normal tissues. Partly because of the expense of transcriptomics (and the inherent noise in such data (Schena, 2000; Tu et al., 2002; Cui and Churchill, 2003; Liang and Kelemen, 2006)), the numbers of samples and their replicates is often small while the number of candidate genes is typically in the thousands. Given the above, there is clearly a great danger that most of these will not in practice withstand scrutiny on deeper analysis (despite the ease with which one can create beautiful heat maps and any number of ‘just-so’ stories to explain the biological relevance of anything that is found in preliminary studies!). This turns out to be the case, and we review a recent analysis (Ein-Dor et al., 2006) of a variety of such studies."
The fields of metabolomics, proteomics and transcriptomics are plagued by statistical problems (as well as being saddled with ghastly pretentious names).
What’s to be done?
Barker Bausell, in his demolition of research on acupuncture, said:
[Page39] “But why should nonscientists care one iota about something as esoteric as causal inference? I believe that the answer to this question is because the making of causal inferences is part of our job description as Homo Sapiens.”
The problem, of course, is that humans are very good at attributing causality when it does not exist. That has led to confusion between correlation and cause on an industrial scale, not least in attempts to work out the effects of diet on health.
More than in any other field it is hard to do the RCTs that could, in principle, sort out the problem. It’s hard to allocate people at random to different diets, and even harder to make people stick to those diets for the many years that are needed.
We can probably say by now that no individual food carries a large risk, or affords very much protection. The fact that we are looking for quite small effects means that even when RCTs are possible huge samples will be needed to get clear answers. Most RCTs are too short, and too small (under-powered) and that leads to overestimation of the size of effects.
That’s a problem that plagues experimental pyschology too, and has led to a much-discussed crisis in reproducibility.
"Supplements" of one sort and another are ubiquitous in sports. Nobody knows whether they work, and the margin between winning and losing is so tiny that it’s very doubtful whether we ever will know. We can expect irresponsible claims to continue unabated.
The best thing that can be done in the short term is to stop doing large observational studies altogether. It’s now clear that inferences made from them are likely to be wrong. And, sad to say, we need to view with great skepticism anything that is funded by the food industry. And make a start on large RCTs whenever that is possible. Perhaps the hardest goal of all is to end the "publish or perish" culture which does so much to prevent the sort of long term experiments which would give the information we want.
Ioannidis’ article ends with the statement
"I am co-investigator in a randomized trial of a low carbohydrate versus low fat diet that is funded by the US National Institutes of Health and the non-profit Nutrition Science Initiative."
It seems he is putting his money where his mouth is.
Until we have the results, we shall continue to be bombarded with conflicting claims made by people who are doing their best with flawed methods, as well as by those trying to sell fad diets. Don’t believe them. The famous "5-a-day" advice that we are constantly bombarded with does no harm, but it has no sound basis.
As far as I can guess, the only sound advice about healthy eating for most people is
- don’t eat too much
- don’t eat all the same thing
You can’t make much money out of that advice.
No doubt that is why you don’t hear it very often.
Follow-up
Two relevant papers that show the unreliability of observational studies,
"Nearly 80,000 observational studies were published in the decade 1990–2000 (Naik 2012). In the following decade, the number of studies grew to more than 260,000". Madigan et al. (2014)
“. . . the majority of observational studies would declare statistical significance when no effect is present” Schuemie et al., (2012)
20 March 2014
On 20 March 2014, I gave a talk on this topic at the Cambridge Science Festival (more here). After the event my host, Yvonne Noblis, sent me some (doubtless cherry-picked) feedback she’d had about the talk.
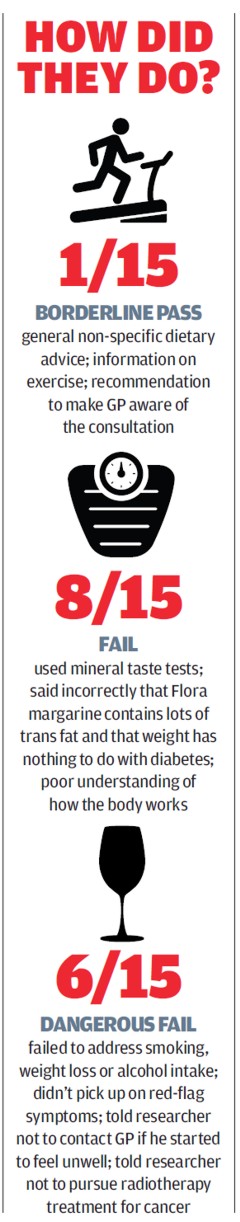
Our undercover investigation finds evidence of nutritional therapists giving out advice that could seriously harm patients’ health
That’s the title of an article in February’s Which? magazine. (That’s similar to Consumer Reports in the USA).
“When Which? sent researchers to investigate the quality of advice from nutritional therapists, some was so bad that patients’ health was put at risk. One nutritional therapist advised against surgery and radiotherapy to treat cancer, while another ‘diagnosed’ a problem with adrenal glands without any blood-test results. Some also used unproven testing, such as iridology or mineral testing, to identify problems or diagnose conditions.”
"We sent five undercover researchers to visit three nutritional therapists each. Every researcher was equipped with a specific health-related scenario: Helen (46) and Sarah (40), recently diagnosed with Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS), the most common type of non-invasive breast cancer; Mark (56) and Linda (52), suffering with serious fatigue for the past three months; and Emily (31), trying unsuccessfully to conceive for more than a year."
|
Sarah, posing as a patient diagnosed with DCIS, visited a nutritional therapist who advised her to delay treatment recommended by her oncologist (a lumpectomy and a course of radiotherapy). The therapist suggested that Sarah follow a no-sugar diet for three to six months and told her, ‘cancer lives off sugar; if you feed it sugar it’s going to thrive. If we starve the cancer of sugar then you have a better opportunity of the cancer going away’. When Sarah asked whether the cancer could progress during this time the therapist said it was a ‘gamble’. Dr Margaret McCartney, from our panel of experts, says: ‘If cancer treatment were as simplistic as cutting out sugar, surely we would have discovered a cure. This advice is highly irresponsible.’ Our experts rated this consultation as a ‘dangerous fail’." The Patients’ Guide to magic medicine defined “Nutritional therapy: self-styled ‘nutritionists’ making untrue claims about diet in order to sell you unnecessary supplements”. That turned out to be pretty accurate. They are part of the alternative medicine fringe. The Universities Admission Service (UCAS) no longer lists any BSc/MSc degrees in "Nutritional Therapy" or "Nutritional medicine". Westminster University closed its BSc Nutritional Therapy during last year. We still don’t know the fate of the notorious (or should I say hilarious) course run at the Northern College of Acupuncture and validated (after a fashion) by the late University of Wales, but it isn’t listed for entry in 2012. [We do now: see follow-up‘] But there are a large number of university courses called "Nutrition". How many of them teach properly, and how many of them teach the nonsense that prevails in "nutritional therapy", I don’t know. The term ‘nutrition’ has turned into a dangerous minefield. It can mean almost anything, because the term is undefined. Anyone can, and does, describe themselves as a nutritionist. At one extreme you have slick pills salesman like ‘not-a-Dr’ Gillian McKeith and Patrick Holford. At the other extreme you have a fascinating and respectable subject for study. The one thing that you need to get clear is that if you want advice about nutrition, go to a dietitian not a "nutritionist". Dietitians are the properly qualified people who work in the NHS, and who are (mostly) free of crackpot ideas. |
I suppose that one should not be surprised at the poor, and sometimes dangerous, advice that was given by nutritional therapists. Their training contains much nonsense so it isn’t surprising that they did so badly. Some of it has been revealed here. See, for example,
Another worthless validation: the University of Wales and nutritional therapy
Nutritional Fairy Tales from Thames Valley University
College of Natural Nutrition: bizarre teaching revealed
Nutriprofile: useful aid or sales scam?
Response to a threatening letter from Mr Holford
Food for the Brain: Child Survey. A proper job?
Teaching bad science to children: OfQual and Edexcel are to blame
The last BSc (Hons) Homeopathy closes! But look at what they still teach at Westminster University.
The level of knowledge of both physiology and chemistry shown my some of the therapists was shocking. One recommended avoiding margarine, because it’s “two chemical bonds away from pure plastic”. Another said that Flora margarine contains lots of trans fat, which has not been true for a long time.
One graduate ot the late Thames Valley University course said “”advantage of the wholemeal or the wholegrain … is that they contain more fibre and the fibre stops the sugars being absorbed quite as quickly”. Not so. Brown and white bread have much the same glycaemic index (60 – 70).
Quack diagnosis
One alarming fact was that several therapists offered methods of diagnosis for allergy and for deficiencies that have been known for many years not to work. There isn’t anything controversial about iridology, hair mineral analysis, taste tests. kinesiology. or the Vega test. They are pure quackery.
“Professor David Colquhoun, from our panel of experts, said: ‘Sadly, nutritional therapy is plagued by “diagnostic tests” that are little more than quackery; they are tools to aid sales, rather than tools to diagnose deficiencies. Iridology and hair analysis simply don’t work.”
Unnecessary treatments
One therapist advised a researcher to have an optimum nutritional evaluation test, costing £312, and a cellular nutrition profile, costing £156. Apparently, these would allow the therapist to give a
more targeted service by establishing what vitamin and mineral deficiencies he had.
Our experts were not convinced by these tests and certainly didn’t think they were worth the money; any necessary testing
could be done by a GP for free.
In 12 of the 15 consultations, researchers were prescribed a huge range of supplements, costing up to £70 per month. It was not revealed whether or not the prescriber made money from this, but usually you were asked to give the prescriber’s name "to get a discount". So it’s a fair guess that they got kickbacks.
British Association for Applied Nutrition & Nutritional Therapy (BANT)
Despite the low standards of advice, 13 out of the 14 therapists who were visited were registered with BANT, the British Association for Applied Nutrition & Nutritional Therapy. This is what passes for a professional association for nutritional therapists, though like all such bodies in alternative medicine, it is entirely ineffective as a regulator. Rather it serves to protect whatever untrue claims they make. BANT’s code of practice says that its members won’t diagnose, but in fact many of the therapists diagnosed conditions and created treatment plans. You can be confident that BANT will do nothing to stop this bad practice.
You can find out a lot about BANT from these sources:
British Association for Nutritional Therapy – when an organisation looks like a regulator, quacks like a regulator, but isn’t a regulator
Why it is easy to get the incorrect impression that BANT is a regulator
Nutritional Therapists Fail to Join Ofquack
BANT: A Profile
Matthias Rath drops his million pound legal case against me and the Guardian.
Only 3 of the 14 therapists were registered with the Complementary and Natural Healthcare Council (the CNHC, more commonly know as Ofquack). They are meant to be the official regulator, launched with a good chunk of taxpayers’ money, but registration is voluntary and not many have volunteered. As a requlator, Ofquack is a bad joke.
Conclusion
|
"Dr Margaret McCartney says: ‘This investigation appears to show that high street nutritional therapists are a waste of money. If you have symptoms please see your GP, not someone who can’t diagnose accurately.’ If you’re looking for tailored dietary advice, visit a registered dietitian.
" |
There is a discussion of this topic on the Which? magazine site.
Follow-up
The excellent Quackometer has posted simultaneously on the great nutritional therapy scam.
16 January 2012 The British Dietetic Association issued a press release that describes very clearly the many differences between a real dietitian and a "nutritional therapist". Download Leading UK Nutrition Association Urges Awareness Between Dietitians and Nutritionists (pdf).
16 January 2012 BANT issued a press release. Download Are Nutritional Therapists Gambling with Your Health?. It answers none of the serious questions raised by the Which? investigation. BANT moans that that Which? “did not provide all the promised transcripts/questionnaires in a timely fashion”. In fact they got them before Christmas and were given until January 15th to respond.
16 January 2012. BBC Radio 4 programme, You and Yours, had an item with Jenny Driscoll from Which? magazine and BANT chairperson, Catherine Honeywell. She did, inter alia, admit that some of the behaviour of the therapists were irresponsible. It remains to be seen if they do anything about it. don’t hold your breath. Hear it on BBC iPlayer.
16 January 2012. There was pretty god coverage of the story, even in the Daily Mail.
17 January 2012 Another question answered. I just learned that the ludicrous course in Nutritional Therapy, previously validated by the University of Wales (and a contributor to its downfall), is now being validated by, yes, you guessed, Middlesex University. Professor Driscoll seems determined to lead his univerity to the bottom of the academic heap. His new partnership with the Northern college of Acupuncture is just one of a long list of validations that almost rivals that of the late University of Wales. The course has, of course, an enthusiastic testimonial, from a student. It starts
I work full time as a team leader for a pension company but I am also a kinesiologist and work in my spare time doing kinesiology, reiki and Indian head massage.
Evidently she’s a believer in the barmiest and totally disproved forms of magic medicine. And Middlesex University will give her a Master of Science degree. I have to say I find it worrying that she’s a team leader for a pension company. Does she also believe in the value of worthless derivatives. I wonder?
17 January 2012 The discussion is going on at the Which? web site. A Chris James cast doubt on the reaults because ot the small sample size, and asked for confidence limits, so I gave them.
Chris James
It is easy enough to calculate limits yourself -you don’t even need to be able to do the maths -there are web calculators that do it for you, e.g. http://www.causascientia.org/math_stat/ProportionCI.html
14/15 = 93% failed. 95% confidence limits for this are 69.8% to 98.4%
6/15 = 40% gave dangerous advice 95% confidence limits 19.7% to 64.6%
So despite the small sample size we can say that it’s likely that at least 70% (and possibly 98%) of nutritional therapists fail.
And it is likely that at least 20% (and possibly 65%) of nutritional therapists give dangerous advice.
These results give real cause for concern, despite the small sample size.
For statistical enthusiasts, these limits are Bayesian with a uniform prior. Very much the same result is given by the standard analysis which is explained in section 7.7 of Lectures on Biostatistics [download pdf 10.5 Mb]
18 January 2012. BANT has, at last, produced an “updated response”. The good thing is that it starts by saying
” . . it is completely outside the BANT Code of Practice to advise a client to withhold any treatment for cancer for any period of time in order to follow a nutritional approach. Were a client to be advised in such a way we would expect to receive a complaint against the practitioner.”
I hope that this will happen. This statement, the only admission of guilt in BANT’s response, is rather spoiled by a later suggestion that no such recommendation was made. It looked very clear to both Which? magazine and to the three members of the expert panel.
The rest of the response admits no fault of any sort.
I’m sorry to say that the response by BANT shows very clearly what is wrong in nutritional therapy. Any organisation which can see nothing wrong in the advice given in 14 of the 15 consultations is, I’d argue, a threat to the health of the nation. Rather than saying we’ll try to improve, they just deny everything.
The response seems to show that the professional organisation for nutritional therapists is not part of the solution. Rather it is part of the problem.
There is no topic more widely discussed than what one should eat in order to stay healthy. And there are few topics where there evidence is so lacking in quality. This post isn’t about quackery, but about something much more important. it is about the real science (if it merits that description) behind dietary advice. I’m not an expert in nutrition, but I do know a bit about the nature of evidence. I’m continually astonished by the weakness of the evidence for some things that have become received truths, and nowhere is that more true than in nutrition.
|
The BMJ used my review of Gary Taube’s book, The Diet Delusion, to start off their new Round Table feature [full text link to BMJ]. The published version had some big cuts so I publish the original version here. Taubes was kind enough to send me a copy of the book after I’d mentioned his wonderful New York Times piece in my previous excursion into the murky world of diet and health, Diet and health. What can you believe: or does bacon kill you? |

|
The biggest omission in the BMJ version was Taubes’ own ten point summary of his conclusions (on page 454).
"“As I emerge from this research, though, certain conclusions seem inescapable to me, based on existing knowledge
- Dietary fat, whether saturated or not, is not a cause of obesity, heart disease, or any other chronic disease of civilization
- The problem is the carbohydrates in the diet, their effect on insulin secretion, and thus the hormonal regulation of homeostasis – the entire harmonic ensemble of the human body. The more easily digestible and refined the carbohydrates, the greater the effect on our health, weight, and well-being.
- Sugars – sucrose and high-fructose corn syrup specifically – are particularly harmful, probably because the combination of fructose and glucose simultaneously elevates insulin levels while overloading the liver with carbohydrates.
- Through their direct effect on insulin and blood sugar, refined carbohydrates, starches, and sugars are the dietary cause of coronary heart disease and diabetes. They are the most likely dietary causes of cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and the other chronic diseases of civilization.
- Obesity is a disorder of excess fat accumulation, not overeating, and not sedentary behaviour.
- Consuming excess calories does not cause us to grow fatter, any more than it causes a child to grow taller. Expending more energy than we consume does not lead to long-term weight loss; it leads to hunger.
- Fattening and obesity are caused by an imbalance – a disequilibrium – in the hormonal regulation of adipose tissue and fat metabolism. Fat synthesis and storage exceed the mobilization of fat from the adipose tissue and its subsequent oxidation. We become leaner when the hormonal regulation of the fat tissue reverses this balance.
- Insulin is the primary regulator of fat storage. When insulin levels are elevated – either chronically or after a meal – we accumulate fat in our fat tissue. When insulin levels fall, we release fat from our fat tissue and use it for fuel.
- By stimulating insulin secretion, carbohydrates make us fat and ultimately cause obesity. The fewer carbohydrates we consume, the leaner we will be.
- By driving fat accumulation, carbohydrates also increase hunger and decrease the amount of energy we expend in metabolism and physical activity.”
It is on these bases that Taubes suggests that the increase in obesity is, in part, a consequence of the recommendation of a low fat, and hence high sugar diet.
|
The Diet Delusion [ pp 601] (published in the USA as Good Calories, Bad Calories) Gary Taubes 2008 There is no topic more widely discussed than what one should eat in order to stay healthy. And there are few topics where the evidence is so lacking in quality. It is also a topic that is besieged by gurus, cranks and supplement hucksters. You need to beware of misleading titles. Dietitians are good. Nutritionists are sometimes good. But titles like ‘nutritional therapist’ and ‘nutritional medicine’ are usually warning signs of alternative therapists and/or pill salespeople. Gary Taubes is a journalist, but he is quite an exceptional journalist. His account of the importance of randomisation for the establishment of causality is one of the best ever and it was published not in an academic journal, but in the New York Times [1]. His book, The Diet Delusion, is in the same mould. It is more complete and more scholarly than most professional scientists could manage. Not only does it cover the literature right back to Samuel Johnson, but it is also particularly good at unravelling what one might call the politics of science. And by politics I don’t mean the vast lobbying industry that has built up with the aim of selling you unnecessary supplements, but the politics of academia. Obesity sounds simple. If you are fat it is because you eat too much or exercise too little, right? Well no, it’s not as simple as that. For a start, it has been shown time and time again that low fat diets, and exercise, have small and temporary effects on weight. The problem with diet and health revolves round causality. The law of conservation of energy is an inevitable truth, but says nothing about causality. It could imply that you get fat because you eat too much, or equally the causal arrow could point the other way and “we eat more, move less and have less energy to expend because we are metabolically or hormonally driven to get fat”. The assumption that positive caloric balance is the cause of weight gain has predominated since the 1970s and “this simple misconception has led to a century of misguided obesity research”. At the heart of the problem is the paucity of randomised trials, which are the only way to establish causality. Those that there are have usually shown that diet does not matter as much as we are told. Taubes concludes
I think it can certainly be argued that the problem of causality has been greatly underestimated. We are warned constantly of the dangers of processed meat, on the basis of very unconvincing evidence [2]. This is one reason why we still know so little about the causes of obesity, diabetes and heart disease. For Taubes, a major villain was the US nutritionist Ancel Keys (1904 – 2004). His It is quite possible that there was rather more to be said for the Atkins diet than was apparent at the time. The fact that Atkins was not a university scientist, that his views were extreme and that he was so obviously out to make a lot of money from it, gave him all the appearance of being yet another profiteering diet guru. He was dismissed by the medical establishment as a quack. Taubes points out that conflict of interest cuts both ways. Atkins’ sternest critics at Harvard were funded by General Foods, Coca-Cola and the sugar industry. It adds up to a sorry story of a conflict of vested interests and scientific vanity. Taubes’ final judgement is harsh. He quotes Robert Merton’s description [4] of what science is, or should be.
He then comments
It took Taubes five years to write this book, and he has nothing to sell apart from his ideas. No wonder it is so much better than a scientist can produce. Such is the corruption of science by the cult of managerialism that no university would allow you to spend five years on a book [5]. I find all ten points in his summary convincing. But his most important conclusion is that you cannot have any certainty without randomised trials. The business of nutrition is greatly at fault for not having put more effort into organising randomised trials. Until they are done, we’ll never really know, and we shouldn’t pretend that we do. 1. Taubes G. Do we really know what makes us healthy? New York Times 2007 Sep 16.[full text link] [pdf file] 2. Colquhoun, D. (3 May 2009) Diet and health. What can you believe: or does bacon kill you?. 3. Greenberg, S.A.. 2009 How citation distortions create unfounded authority: analysis of a citation network. BMJ ;339:b2680 [pdf file]. 4. Merton, R. K. Behavior Patterns of Scientists . Leonardo, Vol.3 1970; 3(2):213-220. From Jstor [or pdf file] 5. Lawrence PA. The mismeasurement of science. Curr Biol 2007; 17(15):R583-R585.PM:17686424 [pdf file] [commentary] |
If length had allowed, there should certainly have been a reference here to Robert Lustig of UCSF. He is an academic nutritionist who supports the main thesis of Taubes’ book. See, for example, his 2005 review, Childhood obesity: behavioral aberration or biochemical drive? Reinterpreting the First Law of Thermodynamics [full
text link]. Lustig’s slide show, The Trouble with Fructose is available in the NIH web site.
There are a couple of other articles by Taubes that are well worth reading. The Scientist and the Stairmaster Why most of us believe that exercise makes us thinner—and why we’re wrong. Gary Taubes, in New York Magazine, and We can’t work it out, in the Guardian.
You can see Taubes in action on YouTube, for example in “on Cholesterol and Science Practices“, and “on Carbohydrates and Degenerative Diseases“. There is also a video of Taubes on medical grand rounds at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center in June 2009. You can see Robert Lustig on YouTube too: “Sugar: The Bitter Truth“.
Follow-up
22 December.2009, Unlike the serious questions dealt with in the Diet Delusion, this concerns merely another bit of the ubiquitous nutribollocks that crops up in the media, While writing this I was listening to the excellent early evening news programme, PM, run by Eddie Mair, when a diet-related topic came up, it was nonsense about how a cocktail made with vodka, cointreau, acai juice and pomegranate juice would not give you a hangover. I suppose it was meant as christmas fun but whenever I hear the words ‘antioxidant‘ or ‘superfood; I feel an email coming on. It seems that Eddie Mair liked the fact that the email contained the words ‘quack’ and ‘codswallop’ because the next thing I knew I was asked to give an interview on next day’s programme. The mp3 is here.
We have listed many reasons hear why you should never trust Boots. Here are the previous ones.
Can you trust Boots?
Don’t Trust Boots
Boots reaches new level of dishonesty with CoQ10 promotion
This post is about a "functional food". That is about something a bit more serious than homeopathy, though I’ll return to that standing joke in the follow-up, because of Boots’ latest shocking admission..
Alternative medicine advocates love to blame Big Pharma for every criticism of magic medicine. In contrast, people like me, Ben Goldacre and a host of others have often pointed out that the differences seem to get ever smaller between the huge Alternative industry (about $60 billion per year), and the even huger regular pharmaceutical industry (around $600 billion per year),
Boots are as good an example as any. While representing themselves as ethical pharmacists, they seem to have no compunction at all in highly deceptive advertising of medicines and supplements which are utterly useless rip-offs.
The easiest way to make money is to sell something that is alleged to cure a common, but ill-defined problem, that has a lot of spontaneous variability.. Like stress, for example.
The Times carried a piece Is Boots’s new Lactium pill the solution to stress?. Needless to say the question wasn’t answered. It was more like an infomercial than serious journalism. Here is what Boots say.
 |
What does it do? This product contains Lactium, a unique ingredient which is proven to help with the stresses of every day life, helping you through a stressful day. Also contains B vitamins, magnesium and vitamin C, which help to support a healthy immune system and energy levels. Why is it different? This one a day supplement contains the patented ingredient Lactium. All Boots vitamins and suppliers are checked to ensure they meet our high quality and safety standards. |
So what is this "unique ingredient", Lactium? It is a produced by digestion of cow’s milk with trypsin. It was patented in 1995 by the French company, Ingredia, It is now distributed in the USA and Canada by Pharmachem. which describes itself as “a leader in the nutraceutical industry.” Drink a glass of milk and your digestive system will make it for you. Free. Boots charge you £4.99 for only seven capsules.
What’s the evidence?
The search doesn’t start well. A search of the medical literature with Pubmed for "lactium" produces no results at all. Search for "casein hydrolysate" gives quite a lot, but "casein hydrolysate AND stress" gives only seven, of which only one looks at effects in man, Messaoudi M, Lefranc-Millot C, Desor D, Demagny B, Bourdon L. Eur J Nutr. 2005.
There is a list of nineteen "studies" on the Pharmachem web site That is where Boots sent me when I asked about evidence, so let’s take a look.
Of the nineteen studies, most are just advertising slide shows or unpublished stuff. Two appear to be duplicated. There are only two proper published papers worth looking at, and one of these is in
rats not man. The human paper first.
Paper 1 Effects of a Bovine Alpha S1-Casein Tryptic Hydrolysate (CTH) on Sleep Disorder in Japanese General Population, Zara de Saint-Hilaire, Michaël Messaoudi, Didier Desor and Toshinori Kobayashi [reprint here] The authors come from France, Switzerland and Japan.
This paper was published in The Open Sleep Journal, 2009, 2, 26-32, one of 200 or so open access journals published by Bentham Science Publishers.
It has to be one of the worst clinical trials that I’ve encountered. It was conducted on 32 subjects, healthy Japanese men and women aged 25-40 and had reported sleeping disorders. It was double blind and placebo controlled, so apart from the fact that only 12 of the 32 subjects were in the control group, what went wrong?
The results were assessed as subjective sleep quality using the Japanese Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index (PSQI-J). This gave a total .score and seven component scores: sleep quality, sleep latency, sleep duration, habitual sleep efficiency, sleep disturbances, use of sleeping medication, and daytime dysfunction.
In the results section we read, for total PSQI score
"As shown in Table 2, the Mann-Whitney U-test did not show significant differences between CTH [casein tryptic hydrolysate] and Placebo groups in PSQI-J total scores at D0 (U=85; NS), D14 (U=86.5; NS), D28 (U=98.5; NS) and D35 (U=99.5; NS)."
Then we read exactly similar statements for the seven component scores. For example,. for Sleep Quality
As shown in Table 3, the Mann-Whitney U-test did not show significant differences between the sleep quality scores of CTH and Placebo groups at D0 (U=110.5; NS), D14 (U=108.5; NS), D28 (U=110; NS) and D35 (U=108.5; NS).
The discussion states
"The comparisons between the two groups with the test of Mann-Whitney did not show significant differences, probably because of the control product’s placebo effect. Despite everything, the paired comparisons with the test of Wilcoxon show interesting effects of CTH on sleep disorders of the treated subjects. "
Aha, so those pesky controls are to blame! But despite this negative result the abstract of the paper says
"CTH significantly improves the PSQI total score of the treated subjects. It particularly improves the sleep quality after two weeks of treatment, decreases the sleep latency and the daytime dysfunction after four weeks of treatment.
Given the antistress properties of CTH, it seems possible to relate the detected improvement of sleep aspects to a reduction of stress following its’ chronic administration."
So there seems to be a direct contradiction between the actual results and the announced outcome of the trial. How could this happen? The way that the results are presented make it hard to
tell. As far as I can tell, the answer is that, having failed to find evidence of real differences between CTH and placebo, the authors gave up on the placebo control and looked simply at the change
from the day 0 basleine values within the CTH group and, separately, within the placebo group. Some of these differences did pass statistical significance but if you analyse it
that way. there is no point in having a control group at all.
How on earth did such a poor paper get published in a peer-reviewed journal? One answer is that there are now so many peer-reviewed journals, that just about any paper, however poor, can get published
in some journal that describes itself as ‘peer-reviewed’. At the lower end of the status hierarchy, the system is simply broken.
Bentham Science Publishers are the publishers of the The Open Sleep Journal. (pity they saw fit to hijack the name of UCL’s spiritual founder, Jeremy Bentham). They publish 92 online and print journals, 200 plus open access journals, and related print/online book series. This publsher has a less than perfect reputation. There can be no scientist of any age or reputation who hasn’t had dozens of emails begging them to become editors of one or other of their journals or to write something for them. They have been described as a "pyramid scheme” for open access. It seems that every Tom, Dick and Harry has been asked. They have been described under the heading Black sheep among Open Access Journals and Publishers. More background can be found at Open Access News..
Most telling of all, a spoof paper was sent to a Bentham journal, The Open Information Science Journal. . There is a good account of the episode the New Scientist, under the title “CRAP paper accepted by journal”. It was the initiative if a graduate student at Cornell University. After getting emails from Bentham, he said “”It really painted a picture of vanity publishing”. The spoof paper was computer-generated rubbish, but it was accepted anyway, without comment. Not only did it appear that is was never reviewed but the editors even failed to notice that the authors said the paper came from the "Center for Research in Applied Phrenology", or CRAP. .The publication fee was $800, to be sent to a PO Box in the United Arab Emirates. Having made the point, the authors withdrew the paper.
Paper 5 in the list of nineteen stidies is also worth a look. It’s about rats not humans but it is in a respectable journal The FASEB Journal Express Article doi:10.1096/fj.00-0685fje (Published online June 8, 2001) [reprint here].
Characterization of α-casozepine, a tryptic peptide from bovine αs1-casein with benzodiazepine-like activity. Laurent Miclo et al.
This paper provides the basis for the claim that digested milk has an action like the benzodiazepine class of drugs, which includes diazepam (Valium). The milk hydrolysate, lactium was tested in rats and found to have some activity in tests that are alleged to measure effects on anxiety (I haven’t looked closely at the data, since the claims relate to humans).. The milk protein, bovine αS1 casein contains 214 amino acids. One of the many products of its digestion is a 10-amino-acid fragment (residues 91 -100) known as α-casozepine and this is the only product that was found to have an affinity for the γ-amino-butyric acid (GABA) type A receptors, which is where benzodiazepines are thought to act. There are a few snags with this idea.
- The affinity of α-casozepine peptide had 10,000-fold lower affinity for the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA than did diazepam, whereas allegedly the peptide was 10-fold more potent than diazepam in one of the rat tests.
- The is no statement anywhere of how much of the α-casozepine peptide is present in the stuff sold my Boots, or whether it can be absorbed
- And if digested milk did act like diazepam, it should clearly be callled a drug not a food.
What’s the conclusion about lactium?
Here is what I make of it.
Does it relieve stress? The evidence that it works any better than drinking a glass of milk is negligible. Tha advertising is grossly misleading and the price is extortionate.
Corruption of science. There is a more interesting aspect than that though. The case of lactium isn’t quite like the regular sort of alternative medicine scam. It isn’t inherently absurd, like homeopathy. The science isn’t the sort of ridiculous pseudo-scientific ramblings of magic medicine advocates who pretend it is all quantum theory The papers cited here are real papers, using real instruments and published in real journals,
What is interesting about that is that they show very clearly the corruption of real science that occurs at its fringes, This is science in the service of the dairy industry and in the service of the vast supplements industry. These are people who want to sell you a supplement for everything.
Medical claims are made for supplements, yet loopholes in the law are exploited to maintain that they are foods not drugs. The law and the companies that exploit it are deeply dishonest. That’s bad enough. but the real tragedy is when science itself is corrupted in the service of sales.
Big Pharma and the alternative industry. Nowhere is the slose alliance between Big Pharma and the alternative medicine industry more obvious than in the supplement and nutriceutical markets. Often the same companies run both. Their aim is to sell you thinks that you don’t need, for conditions that you may well not have, and to lighten your wallet in the process. Don’t believe for a moment that the dark-suited executives give a bugger about your health. You are a market to be exploited.
If you doubt that, look from time to time at one of the nutraceutical industry web sites, like nutraingredients.com. They even have a bit to say about lactium. They are particularly amusing at the moment because the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has had the temerity to demand that when health claims are made for foods, there is actually some small element of truth in the claims. The level of righteous indignation caused in the young food industry executives at the thought that they might have to tell the truth is everywhere to see. For example, try Life in a European health claims wasteland. Or, more relevant to Lactium, Opportunity remains in dairy bioactives despite departures. Here’s
a quotation from that one.
“Tage Affertsholt, managing partner at 3A Business Consulting, told NutraIngredients.com that the feedback from industry is that the very restrictive approach to health claims adopted by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) will hamper growth potential.”
“Affertsholt said: “Some companies are giving up and leaving the game to concentrate on more traditional dairy ingredients.”
Science and government policy
It may not have escaped your notice that the sort of low grade, corrupted, fringe science described here, is precisely the sort that is being encouraged by government policies. You are expected to get lots of publications, so never mind the details, just churn ’em out; The hundreds of new journals that have been created will allow you to get as meny peer-reviwed publications as you want without too much fuss, and you can very easily put an editorship of one of them on your CV when you fill in that bit about indicators of esteem. The box tickers in HR will never know that it’s a mickey mouse journal.
Follow-up
Boots own up to selling crap
Although this post was nothing to do with joke subjects like homeopathy, it isn’t possible to write about Boots without mentioning the performance of their professional standards director, Paul Bennett, when he appeared before the Parliamentary Select Committee for Science and Technology.. This committee was holding an “evidence check” session on homeopathy (it’s nothing short of surreal that this should be happening in 2009, uh?). The video can be seen here, and an uncorrected transcript. It is quite fun in places. You can also read the written evidence that was submitted.
Even the Daily Mail didn’t misss this one. Fioana Macrae wrote Boots boss admits they sell homeopathic remedies ‘because they’re popular, not because they work’
“It could go down as a Boot in Mouth moment.
Yesterday, the company that boasts shelf upon shelf of arnica, St John’s wort, flower remedies and calendula cream admitted that homeopathy doesn’t necessarily work.
But it does sell. Which according to Paul Bennett, the man from Boots, is why the pharmacy chain stocks such products in the first place.
Mr Bennett, professional standards director for Boots, told a committee of MPs that there was no medical evidence that homeopathic pills and potions work.
‘There is certainly a consumer demand for these products,’ he said. ‘I have no evidence to suggest they are efficacious.
‘It is about consumer choice for us and a large number of our customers believe they are efficacious.’
His declaration recalls Gerald Ratner’s infamous admission in 1991 that one of the gifts sold by his chain of jewellers was ‘total crap’.”
The Times noticed too, with Boots ‘labels homeopathy as effective despite lack of evidence‘.
Now you know that you can’t trust Boots. You heard it from the mouth of their professional standards director.
A commentary on the meeting by a clinical scientist summed up Bennett’s contribution thus
"Paul Bennett from Boots had to admit that there was no evidence, but regaled the committee with the mealy-mouthed flannel about customer choice that we have come to expect from his amoral employer."
Well said
The third session of the Scitech evidence check can be seen here, and the uncorrected transcript is here. It is, in a grim way, pure comedy gold, More of that later.
First the MHRA lets down the public by allowing deceptive labelling of sugar pills (see here, and this this blog). Now it is the turn of NICE to betray its own principles.
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) describes its job thus
“NICE is an independent organisation responsible for providing national guidance on promoting good health and preventing and treating ill health.”
Its Guidance document on Low Back Pain will be published on Wednesday 27 May 2009, but the newspapers have already started to comment, presumably on the assumption that it will have changed little from the Draft Guidance of September 2008. These comments may have to be changed as soon as the final version becomes available.
The draft guidance, though mostly sensible, has two recommendations that I believe to be wrong and dangerous. The recommendations include (page 7) these three.
- Consider offering a course of manual therapy including spinal manipulation of up to 9 sessions over up to 12 weeks.
- Consider offering a course of acupuncture needling comprising up to 10 sessions over a period of up to 12 weeks.
- Consider offering a structured exercise programme tailored to the individual.
All three of this options are accompanied by a footnote that reads thus.
“A choice of any of these therapies may be offered, taking into account patient preference.”
On the face if it, this might seem quite reasonable. All three choices seem to be about as effective (or ineffective) as each other, so why not let patients choose between them?
Actually there are very good reasons, but NICE does not seem to have thought about them. In the past I have had a high opinion of NICE but it seems that even they are now getting bogged down in the morass of political correctness and officialdom that is the curse of the Department of Health. It is yet another example of DC’s rule number one.
Never trust anyone who uses the word ‘stakeholder’.
They do use it, often.
So what is so wrong?
For a start, I take it that the reference to “spinal manipulation” in the first recommendation is a rather cowardly allusion to chiropractic. Why not say so, if that’s whar you mean? Chiropractic is mentioned in the rest of the report but the word doesn’t seem to occur in the recommendations. Is NICE perhaps nervous that it would reduce the credibility of the report if the word chiropractic were said out loud?
Well, they have a point, I suppose. It would.
That aside, here’s what’s wrong.
The Evidence
I take as my premise that the evidence says that no manipulative therapy has any great advantage over the others. They are all more or less equally effective. Perhaps I should say, more or less equally ineffective, because anyone who claims to have the answer to low back pain is clearly deluded (and I should know: nobody has fixed mine yet). So for effectiveness there are no good grounds to choose between exercise, physiotherapy, acupuncture or chiropractic. There is, though, an enormous cultural difference. Acupuncture and chiropractic are firmly in the realm of alternative medicine. They both invoke all sorts of new-age nonsense for which there isn’t the slightest good evidence. That may not poison your body, but it certainly poisons your mind.
Acupuncturists talk about about “Qi”, “meridians”, “energy flows”. The fact that “sham” and “real” acupuncture consistently come out indistinguishable is surely all the evidence one needs to dismiss such nonsense. Indeed there is a small group of medical acupuncturists who do dismiss it. Most don’t. As always in irrational subjects, acupuncture is riven by internecine strife between groups who differ in the extent of their mystical tendencies,
Chiropractors talk of “subluxations”, an entirely imaginary phenomenon (but a cause of much unnecessary exposure to X-rays). Many talk of quasi-religious things like “innate energy”. And Chiropractic is even more riven by competing factions than acupuncture. See, for example, Chiropractic wars Part 3: internecine conflict.
The bait and switch trick
This is the basic trick used by ‘alternative therapists’ to gain respectability.
There is a superb essay on it by the excellent Yale neurologist Steven Novella: The Bait and Switch of Unscientific Medicine. The trick is to offer some limited and reasonable treatment (like back manipulation for low back pain). This, it seems, is sufficient to satisfy NICE. But then, once you are in the showroom, you can be exposed to all sorts of other nonsense about “subluxations” or “Qi”. Still worse, you will also be exposed to the claims of many chiropractors and acupuncturists to be able to cure all manner of conditions other than back pain. But don’t even dare to suggest that manipulation of the spine is not a cure for colic or asthma or you may find yourself sued for defamation. The shameful legal action of the British Chiropractic Association against Simon Singh (follow it here) led to an addition to DC’s Patients’ Guide to Magic Medicine.
(In the face of such tragic behaviour, one has to be able to laugh).
Libel: A very expensive remedy, to be used only when you have no evidence. Appeals to alternative practitioners because truth is irrelevant.
NICE seems to have fallen for the bait and switch trick, hook line and sinker.
The neglected consequences
Once again, we see the consequences of paying insufficient attention to the Dilemmas of Alternative Medicine.
The lying dilemma
If acupuncture is recommended we will have acupuncturists telling patients about utterly imaginary things like “Qi” and “meridians”. And we will have chiropractors telling them about subluxations and innate energy. It is my opinion that these things are simply make-believe (and that is also the view of a minority of acupuncturist and chiropractors). That means that you have to decide whether the supposed benefits of the manipulation are sufficient to counterbalance the deception of patients.
Some people might think that it was worth it (though not me). What is unforgivable is not to consider even the question. The NICE guidance says not a word about this dilemma. Why not?
The training dilemma
The training dilemma is even more serious. Once some form of alternative medicine has successfully worked the Bait and Switch trick and gained a toehold in the NHS, there will be an army of box-ticking HR zombies employed to ensure that they have been properly trained in “subluxations” or “Qi”. There will be quangos set up to issue National Occupational Standards in “subluxations” or “Qi”. Skills for Health will issue “competences” in “subluxations” or “Qi” (actually they already do). There will be courses set up to teach about “subluxations” or “Qi”, some even in ‘universities’ (there already are).
The respectability problem
But worst of all, it will become possible for aupuncturists and chiropractors to claim that they now have official government endorsement from a prestigious evidence-based organisation like NICE for “subluxations” or “Qi”. Of course this isn’t true. In fact the words “subluxations” or “Qi” are not even mentioned in the draft report. That is the root of the problem. They should have been. But omitting stuff like that is how the Bait and Switch trick works.
Alternative medicine advocates crave, above all, respectability and acceptance. It is sad that NICE seems to have given them more credibility and acceptance without having considered properly the secondary consequences of doing so,
How did this failure of NICE happen?
It seems to have been a combination of political correctness, failure to consider secondary consequences, and excessive influence of the people who stand to make money from the acceptance of alternative medicine.
Take, for example, the opinion of the British Pain Society. This organisation encompasses not just doctors. It
includes “doctors, nurses, physiotherapists, scientists, psychologists, occupational therapists and other healthcare professionals actively engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of pain and in pain research for the benefit of patients”. Nevertheless, their response to the draft guidelines pointed out that the manipulative therapies as a whole were over-represented.
|
Manipulation The guidelines assess 9 large groups of interventions of which manual therapies are only one part. The full GDG members panel of 13 individuals included two proponents of spinal manipulation/mobilisation (P Dixon and S Vogel). In addition, the chair of the panel (M Underwood) is the lead author of the UKBEAM trial on which the positive recommendation for |
It seems that the Pain Society were quite right.
LBC 97.3 Breakfast Show (25 May 2009) had a quick discussion on acupuncture (play mp3 file). After I had my say, the other side was put by Rosey Grandage. She has (among other jobs) a private acupuncture practice so she is not quite as unbiassed as me). As usual, she misrepresents the evidence by failing to distinguish between blind and non-blind studies. She also misrepresented what I said by implying that I was advocating drugs. That was not my point and I did not mention drugs (they, like all treatments, have pretty limited effectiveness, and they have side effects too). She said “there is very good evidence to show they (‘Qi’ and ‘meridians’] exist”. That is simply untrue.
There can’t be a better demonstration of the consequences of falling for bait and switch than the defence mounted by Rosey Grandage. NICE may not mention “Qi” and “meridians”; but the people they want to allow into the NHS have no such compunctions.
I first came across Rosey Grandage when I discovered her contribution to the Open University/BBC course K221. That has been dealt with elsewhere. A lot more information about acupuncture has appeared since then. She doesn’t seem to have noticed it. Has she not seen the Nordic Cochrane Centre report? Nor read Barker Bausell, or Singh & Ernst? Has she any interest in evidence that might reduce her income? Probably not.
Where to find out more
An excellent review of chiropractic can be found at the Layscience site. It was written by the indefatigable ‘Blue Wode’ who has provided enormous amounts of information at the admirable ebm-first site (I am authorised to reveal that ‘Blue Wode’ is the author of that site). There you will also find much fascinating information about both acupuncture and about chiropractic.
I’m grateful to ‘Blue Wode’ for some of the references used here.
Follow-up
This article has been reposted on The Winnower, and now has a digital object identifier DOI: 10.15200/winn.142934.47856
This post is not about quackery, nor university politics. It is about inference, How do we know what we should eat? The question interests everyone, but what do we actually know? Not as much as you might think from the number of column-inches devoted to the topic. The discussion below is a synopsis of parts of an article called “In praise of randomisation”, written as a contribution to a forthcoming book, Evidence, Inference and Enquiry.
About a year ago just about every newspaper carried a story much like this one in the Daily Telegraph,
|
Sausage a day can increase bowel cancer risk By Rebecca Smith, Medical Editor Last Updated: 1:55AM BST 31/03/2008
|
||||
What, I wondered, was the evidence behind these dire warnings. They did not come from a lifestyle guru, a diet faddist or a supplement salesman. This is nothing to do with quackery. The numbers come from the 2007 report of the World Cancer Research Fund and American Institute for Cancer Research, with the title ‘Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and the Prevention of Cancer: a Global Perspective‘. This is a 537 page report with over 4,400 references. Its panel was chaired by Professor Sir Michael Marmot, UCL’s professor of Epidemiology and Public Health. He is a distinguished epidemiologist, renowned for his work on the relation between poverty and health.
Nevertheless there has never been a randomised trial to test the carcinogenicity of bacon, so it seems reasonable to ask how strong is the evidence that you shouldn’t eat it? It turns out to be surprisingly flimsy.
In praise of randomisation
Everyone knows about the problem of causality in principle. Post hoc ergo propter hoc; confusion of sequence and consequence; confusion of correlation and cause. This is not a trivial problem. It is probably the main reason why ineffective treatments often appear to work. It is traded on by the vast and unscrupulous alternative medicine industry. It is, very probably, the reason why we are bombarded every day with conflicting advice on what to eat. This is a bad thing, for two reasons. First, we end up confused about what we should eat. But worse still, the conflicting nature of the advice gives science as a whole a bad reputation. Every time a white-coated scientist appears in the media to tell us that a glass of wine per day is good/bad for us (delete according to the phase of the moon) the general public just laugh.
In the case of sausages and bacon, suppose that there is a correlation between eating them and developing colorectal cancer. How do we know that it was eating the bacon that caused the cancer – that the relationship is causal? The answer is that there is no way to be sure if we have simply observed the association. It could always be that the sort of people who eat bacon are also the sort of people who get colorectal cancer. But the question of causality is absolutely crucial, because if it is not causal, then stopping eating bacon won’t reduce your risk of cancer. The recommendation to avoid all processed meat in the WCRF report (2007) is sensible only if the relationship is causal. Barker Bausell said:
[Page39] “But why should nonscientists care one iota about something as esoteric as causal inference? I believe that the answer to this question is because the making of causal inferences is part of our job description as Homo Sapiens.”
That should be the mantra of every health journalist, and every newspaper reader.
|
The essential basis for causal inference was established over 70 years ago by that giant of statistics Ronald Fisher, and that basis is randomisation. Its first popular exposition was in Fisher’s famous book, The Design of Experiments (1935). The Lady Tasting Tea has become the classical example of how to design an experiment. . |

|
Briefly, a lady claims to be able to tell whether the milk was put in the cup before or after the tea was poured. Fisher points out that to test this you need to present the lady with an equal number of cups that are ‘milk first’ or ‘tea first’ (but otherwise indistinguishable) in random order, and count how many she gets right. There is a beautiful analysis of it in Stephen Senn’s book, Dicing with Death: Chance, Risk and Health. As it happens, Google books has the whole of the relevant section Fisher’s tea test (geddit?), but buy the book anyway. Such is the fame of this example that it was used as the title of a book, The Lady Tasting Tea was published by David Salsburg (my review of it is here)
Most studies of diet and health fall into one of three types, case-control studies, cohort (or prospective) studies, or randomised controlled trials (RCTs). Case-control studies are the least satisfactory: they look at people who already have the disease and look back to see how they differ from similar people who don’t have the disease. They are retrospective. Cohort studies are better because they are prospective: a large group of people is followed for a long period and their health and diet is recorded and later their disease and death is recorded. But in both sorts of studies,each person decides for him/herself what to eat or what drugs to take. Such studies can never demonstrate causality, though if the effect is really big (like cigarette-smoking and lung cancer) they can give a very good indication. The difference in an RCT is that each person does not choose what to eat, but their diet is allocated randomly to them by someone else. This means that, on average, all other factors that might influence the response are balanced equally between the two groups. Only RCTs can demonstrate causality.
Randomisation is a rather beautiful idea. It allows one to remove, in a statistical sense, bias that might result from all the sources that you hadn’t realised were there. If you are aware of a source of bias, then measure it. The danger arises from the things you don’t know about, or can’t measure (Senn, 2004; Senn, 2003). Although it guarantees freedom from bias only in a long run statistical sense, that is the best that can be done. Everything else is worse.
Ben Goldacre has referred memorably to the newspapers’ ongoing “Sisyphean task of dividing all the inanimate objects in the world into the ones that either cause or cure cancer” (Goldacre, 2008). This has even given rise to a blog. “The Daily Mail Oncological Ontology Project“. The problem arises in assessing causality.
It wouldn’t be so bad if the problem were restricted to the media. It is much more worrying that the problem of establishing causality often seems to be underestimated by the authors of papers themselves. It is a matter of speculation why this happens. Part of the reason is, no doubt, a genuine wish to discover something that will benefit mankind. But it is hard not to think that hubris and self-promotion may also play a role. Anything whatsoever that purports to relate diet to health is guaranteed to get uncritical newspaper headlines.
At the heart of the problem lies the great difficulty in doing randomised studies of the effect of diet and health. There can be no better illustration of the vital importance of randomisation than in this field. And, notwithstanding the generally uncritical reporting of stories about diet and health, one of the best accounts of the need for randomisation was written by a journalist, Gary Taubes, and it appeared in the New York Times (Taubes, 2007).
The case of hormone replacement therapy
In the 1990s hormone replacement therapy (HRT) was recommended not only to relieve the unpleasant symptoms of the menopause, but also because cohort studies suggested that HRT would reduce heart disease and osteoporosis in older women. For these reasons, by 2001, 15 million US women (perhaps 5 million older women) were taking HRT (Taubes, 2007). These recommendations were based largely on the Harvard Nurses’ Study. This was a prospective cohort study in which 122,000 nurses were followed over time, starting in 1976 (these are the ones who responded out of the 170,000 requests sent out). In 1994, it was said (Manson, 1994) that nearly all of the more than 30 observational studies suggested a reduced risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) among women receiving oestrogen therapy. A meta-analysis gave an estimated 44% reduction of CHD. Although warnings were given about the lack of randomised studies, the results were nevertheless acted upon as though they were true. But they were wrong. When proper randomised studies were done, not only did it turn out that CHD was not reduced: it was actually increased.
The Women’s Health Initiative Study (Rossouw et al., 2002) was a randomized double blind trial on 16,608 postmenopausal women aged 50-79 years and its results contradicted the conclusions from all the earlier cohort studies. HRT increased risks of heart disease, stroke, blood clots, breast cancer (though possibly helped with osteoporosis and perhaps colorectal cancer). After an average 5.2 years of follow-up, the trial was stopped because of the apparent increase in breast cancer in the HRT group. The relative risk (HRT relative to placebo) of CHD was 1.29 (95% confidence interval 1.02 to 1.63) (286 cases altogether) and for breast cancer 1.26 (1.00 -1.59) (290 cases). Rather than there being a 44% reduction of risk, it seems that there was actually a 30% increase in risk. Notice that these are actually quite small risks, and on the margin of statistical significance. For the purposes of communicating the nature of the risk to an individual person it is usually better to specify the absolute risk rather than relative risk. The absolute number of CHD cases per 10,000 person-years is about 29 on placebo and 36 on HRT, so the increased risk of any individual is quite small. Multiplied over the whole population though, the number is no longer small.
Several plausible reasons for these contradictory results are discussed by Taubes,(2007): it seems that women who choose to take HRT are healthier than those who don’t. In fact the story has become a bit more complicated since then: the effect of HRT depends on when it is started and on how long it is taken (Vandenbroucke, 2009).
This is perhaps one of the most dramatic illustrations of the value of randomised controlled trials (RCTs). Reliance on observations of correlations suggested a 44% reduction in CHD, the randomised trial gave a 30% increase in CHD. Insistence on randomisation is not just pedantry. It is essential if you want to get the right answer.
Having dealt with the cautionary tale of HRT, we can now get back to the ‘Sisyphean task of dividing all the inanimate objects in the world into the ones that either cause or cure cancer’.
The case of processed meat
The WCRF report (2007) makes some pretty firm recommendations.
- Don’t get overweight
- Be moderately physically active, equivalent to brisk walking for at least 30 minutes every day
- Consume energy-dense foods sparingly. Avoid sugary drinks. Consume ‘fast foods’ sparingly, if at all
- Eat at least five portions/servings (at least 400 g or 14 oz) of a variety of non-starchy vegetables and of fruits every day. Eat relatively unprocessed cereals (grains) and/or pulses (legumes) with every meal. Limit refined starchy foods
- People who eat red meat to consume less than 500 g (18 oz) a week, very little if any to be processed.
- If alcoholic drinks are consumed, limit consumption to no more than two drinks a day for men and one drink a day for women.
- Avoid salt-preserved, salted, or salty foods; preserve foods without using salt. Limit consumption of processed foods with added salt to ensure an intake of less than 6 g (2.4 g sodium) a day.
- Dietary supplements are not recommended for cancer prevention.
These all sound pretty sensible but they are very prescriptive. And of course the recommendations make sense only insofar as the various dietary factors cause cancer. If the association is not causal, changing your diet won’t help. Note that dietary supplements are NOT recommended. I’ll concentrate on the evidence that lies behind “People who . . . very little if any to be processed.”
The problem of establishing causality is dicussed in the report in detail. In section 3.4 the report says
” . . . causal relationships between food and nutrition, and physical activity can be confidently inferred when epidemiological evidence, and experimental and other biological findings, are consistent, unbiased, strong, graded, coherent, repeated, and plausible.”
The case of processed meat is dealt with in chapter 4.3 (p. 148) of the report.
“Processed meats” include sausages and frankfurters, and ‘hot dogs’, to which nitrates/nitrites or other preservatives are added, are also processed meats. Minced meats sometimes, but not always, fall inside this definition if they are preserved chemically. The same point applies to ‘hamburgers’.
The evidence for harmfulness of processed meat was described as “convincing”, and this is the highest level of confidence in the report, though this conclusion has been challenged (Truswell, 2009) .
How well does the evidence obey the criteria for the relationship being causal?
Twelve prospective cohort studies showed increased risk for the highest intake group when compared to the lowest, though this was statistically significant in only three of them. One study reported non-significant decreased risk and one study reported that there was no effect on risk. These results are summarised in this forest plot (see also Lewis & Clark, 2001)
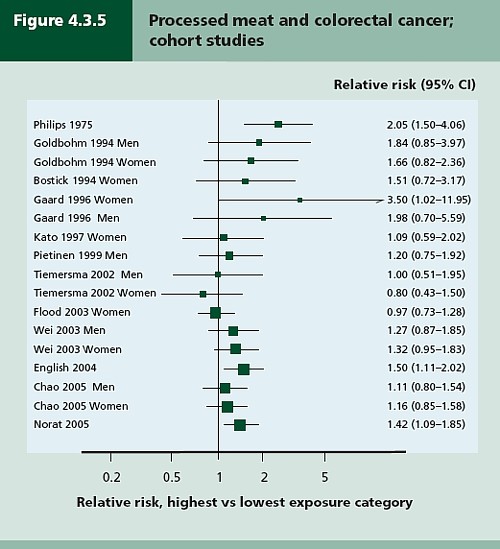
Each line represents a separate study. The size of the square represents the precision (weight) for each. The horizontal bars show the 95% confidence intervals. If it were possible to repeat the observations many times on the same population, the 95% CL would be different on each repeat experiment, but 19 out of 20 (95%) of the intervals would contain the true value (and 1 in 20 would not contain the true value). If the bar does not overlap the vertical line at relative risk = 1 (i.e. no effect) this is equivalent to saying that there is a statistically significant difference from 1 with P < 0.05. That means, very roughly, that there is a 1 in 20 chance of making a fool of yourself if you claim that the association is real, rather than being a result of chance (more detail here),
There is certainly a tendency for the relative risks to be above one, though not by much, Pooling the results sounds like a good idea. The method for doing this is called meta-analysis .
Meta-analysis was possible on five studies, shown below. The outcome is shown by the red diamond at the bottom, labelled “summary effect”, and the width of the diamond indicates the 95% confidence interval. In this case the final result for association between processed meat intake and colorectal cancer was a relative risk of 1.21 (95% CI 1.04–1.42) per 50 g/day. This is presumably where the headline value of a 20% increase in risk came from.
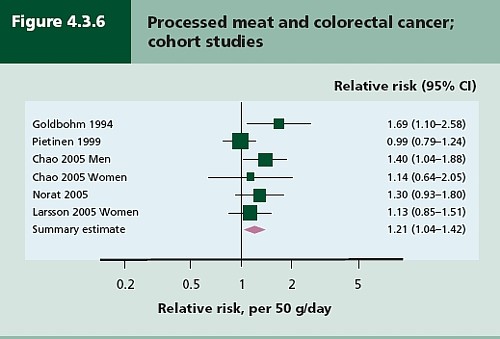
Support came from a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies, which reported a relative risk for processed meat of 1.09 (95% CI 1.05 – 1.13) per 30 g/day (Larsson & Wolk, 2006). Since then another study has come up with similar numbers (Sinha etal. , 2009). This consistency suggests a real association, but it cannot be taken as evidence for causality. Observational studies on HRT were just as consistent, but they were wrong.
The accompanying editorial (Popkin, 2009) points out that there are rather more important reasons to limit meat consumption, like the environmental footprint of most meat production, water supply, deforestation and so on.
So the outcome from vast numbers of observations is an association that only just reaches the P = 0.05 level of statistical significance. But even if the association is real, not a result of chance sampling error, that doesn’t help in the least in establishing causality.
There are two more criteria that might help, a good relationship between dose and response, and a plausible mechanism.
Dose – response relationship
|
It is quite possible to observe a very convincing relationship between dose and response in epidemiological studies, The relationship between number of cigarettes smoked per day and the incidence of lung cancer is one example. Indeed it is almost the only example. |
 Doll & Peto, 1978 |
There have been six studies that relate consumption of processed meat to incidence of colorectal cancer. All six dose-response relationships are shown in the WCRG report. Here they are.
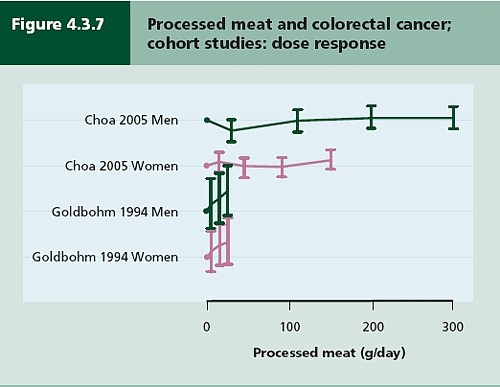
This Figure was later revised to
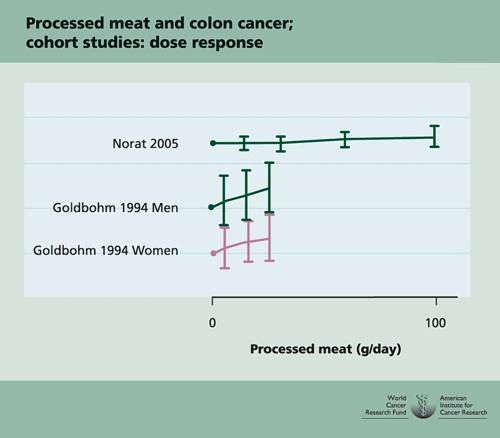
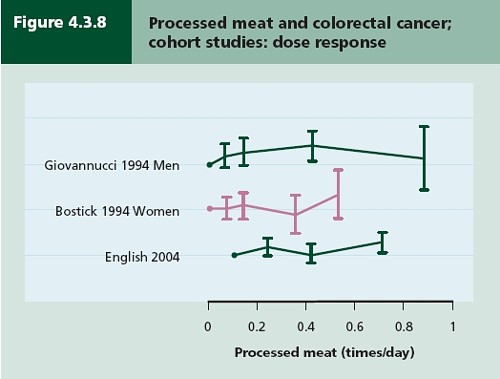
This is the point where my credulity begins to get strained. Dose – response curves are part of the stock in trade of pharmacologists. The technical description of these six curves is, roughly, ‘bloody horizontal’. The report says “A dose-response relationship was also apparent from cohort studies that measured consumption in times/day”. I simply cannot agree that any relationship whatsoever is “apparent”.
They are certainly the least convincing dose-response relationships I have ever seen. Nevertheless a meta-analysis came up with a slope for response curve that just reached the 5% level of statistical significance.
The conclusion of the report for processed meat and colorectal cancer was as follows.
“There is a substantial amount of evidence, with a dose-response relationship apparent from cohort studies. There is strong evidence for plausible mechanisms operating in humans. Processed meat is a convincing cause of colorectal cancer.”
But the dose-response curves look appalling, and it is reasonable to ask whether public policy should be based on a 1 in 20 chance of being quite wrong (1 in 20 at best –see Senn, 2008). I certainly wouldn’t want to risk my reputation on odds like that, never mind use it as a basis for public policy.
So we are left with plausibility as the remaining bit of evidence for causality. Anyone who has done much experimental work knows that it is possible to dream up a plausible explanation of any result whatsoever. Most are wrong and so plausibility is a pretty weak argument. Much play is made of the fact that cured meats contain nitrates and nitrites, but there is no real evidence that the amount they contain is harmful.
The main source of nitrates in the diet is not from meat but from vegetables (especially green leafy vegetables like lettuce and spinach) which contribute 70 – 90% of total intake. The maximum legal content in processed meat is 10 – 25 mg/100g, but lettuce contains around 100 – 400 mg/100g with a legal limit of 200 – 400 mg/100g. Dietary nitrate intake was not associated with risk for colorectal cancer in two cohort studies.(Food Standards Agency, 2004; International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2006).
To add further to the confusion, another cohort study on over 60,000 people compared vegetarians and meat-eaters. Mortality from circulatory diseases and mortality from all causes were not detectably different between vegetarians and meat eaters (Key et al., 2009a). Still more confusingly, although the incidence of all cancers combined was lower among vegetarians than among meat eaters, the exception was colorectal cancer which had a higher incidence in vegetarians than in meat eaters (Key et al., 2009b).
Mente et al. (2009) compared cohort studies and RCTs for effects of diet on risk of coronary heart disease. “Strong evidence” for protective effects was found for intake of vegetables, nuts, and “Mediterranean diet”, and harmful effects of intake of trans–fatty acids and foods with a high glycaemic index. There was also a bit less strong evidence for effects of mono-unsaturated fatty acids and for intake of fish, marine ω-3 fatty acids, folate, whole grains, dietary vitamins E and C, beta carotene, alcohol, fruit, and fibre. But RCTs showed evidence only for “Mediterranean diet”, and for none of the others.
As a final nail in the coffin of case control studies, consider pizza. According to La Vecchia & Bosetti (2006), data from a series of case control studies in northern Italy lead to: “An inverse association was found between regular pizza consumption (at least one portion of pizza per week) and the risk of cancers of the digestive tract, with relative risks of 0.66 for oral and pharyngeal cancers, 0.41 for oesophageal, 0.82 for laryngeal, 0.74 for colon and 0.93 for rectal cancers.”
What on earth is one meant to make of this? Pizza should be prescribable on the National Health Service to produce a 60% reduction in oesophageal cancer? As the authors say “pizza may simply represent a general and aspecific indicator of a favourable Mediterranean diet.” It is observations like this that seem to make a mockery of making causal inferences from non-randomised studies. They are simply uninterpretable.
Is the observed association even real?
The most noticeable thing about the effects of red meat and processed meat is not only that they are small but also that they only just reach the 5 percent level of statistical significance. It has been explained clearly why, in these circumstances, real associations are likely to be exaggerated in size (Ioannidis, 2008a; Ioannidis, 2008b; Senn, 2008). Worse still, there as some good reasons to think that many (perhaps even most) of the effects that are claimed in this sort of study are not real anyway (Ioannidis, 2005). The inflation of the strength of associations is expected to be bigger in small studies, so it is noteworthy that the large meta-analysis by Larsson & Wolk, 2006 comments “In the present meta-analysis, the magnitude of the relationship of processed meat consumption with colorectal cancer risk was weaker than in the earlier meta-analyses”.
This is all consistent with the well known tendency of randomized clinical trials to show initially a good effect of treatment but subsequent trials tend to show smaller effects. The reasons, and the cures, for this worrying problem are discussed by Chalmers (Chalmers, 2006; Chalmers & Matthews, 2006; Garattini & Chalmers, 2009)
What do randomized studies tell us?
The only form of reliable evidence for causality comes from randomised controlled trials. The difficulties in allocating people to diets over long periods of time are obvious and that is no doubt one reason why there are far fewer RCTs than there are observational studies. But when they have been done the results often contradict those from cohort studies. The RCTs of hormone replacement therapy mentioned above contradicted the cohort studies and reversed the advice given to women about HRT.
Three more illustrations of how plausible suggestions about diet can be refuted by RCTs concern nutritional supplements and weight-loss diets
Many RCTs have shown that various forms of nutritional supplement do no good and may even do harm (see Cochrane reviews). At least we now know that anti-oxidants per se do you no good. The idea that anti-oxidants might be good for you was never more than a plausible hypothesis, and like so many plausible hypotheses it has turned out to be a myth. The word anti-oxidant is now no more than a marketing term, though it remains very profitable for unscrupulous salesmen.
The randomised Women’s Health Initiative Dietary Modification Trial (Prentice et al., 2007; Prentice, 2007) showed minimal effects of dietary fat on cancer, though the conclusion has been challenged on the basis of the possible inaccuracy of reported diet (Yngve et al., 2006).
Contrary to much dogma about weight loss (Sacks et al., 2009) found no differences in weight loss over two years between four very different diets. They assigned randomly 811 overweight adults to one of four diets. The percentages of energy derived from fat, protein, and carbohydrates in the four diets were 20, 15, and 65%; 20, 25, and 55%; 40, 15, and 45%; and 40, 25, and 35%. No difference could be detected between the different diets: all that mattered for weight loss was the total number of calories. It should be added, though, that there were some reasons to think that the participants may not have stuck to their diets very well (Katan, 2009).
The impression one gets from RCTs is that the details of diet are not anything like as important as has been inferred from non-randomised observational studies.
So does processed meat give you cancer?
After all this, we can return to the original question. Do sausages or bacon give you colorectal cancer? The answer, sadly, is that nobody really knows. I do know that, on the basis of the evidence, it seems to me to be an exaggeration to assert that “The evidence is convincing that processed meat is a cause of bowel cancer”.
In the UK there were around 5 cases of colorectal cancer per 10,000 population in 2005, so a 20% increase, even if it were real, and genuinely causative. would result in 6 rather than 5 cases per 10,000 people, annually. That makes the risk sound trivial for any individual. On the other hand there were 36,766 cases of colorectal cancer in the UK in 2005. A 20% increase would mean, if the association were causal, about 7000 extra cases as a result of eating processed meat, but no extra cases if the association were not causal.
For the purposes of public health policy about diet, the question of causality is crucial. One has sympathy for the difficult decisions that they have to make, because they are forced to decide on the basis of inadequate evidence.
If it were not already obvious, the examples discussed above make it very clear that the only sound guide to causality is a properly randomised trial. The only exceptions to that are when effects are really big. The relative risk of lung cancer for a heavy cigarette smoker is 20 times that of a non-smoker and there is a very clear relationship between dose (cigarettes per day) and response (lung cancer incidence), as shown above. That is a 2000% increase in risk, very different from the 20% found for processed meat (and many other dietary effects). Nobody could doubt seriously the causality in that case.
The decision about whether to eat bacon and sausages has to be a personal one. It depends on your attitude to the precautionary principle. The observations do not, in my view, constitute strong evidence for causality, but they are certainly compatible with causality. It could be true so if you want to be on the safe side then avoid bacon. Of course life would not be much fun if your actions were based on things that just could be true.
My own inclination would be to ignore any relative risk based on observational data if it was less than about 2. The National Cancer Institute (Nelson, 2002) advises that relative risks less than 2 should be “viewed with caution”, but fails to explain what “viewing with caution” means in practice, so the advice isn’t very useful.
In fact hardly any of the relative risks reported in the WCRF report (2007) reach this level. Almost all relative risks are less than 1.3 (or greater than 0.7 for alleged protective effects). Perhaps it is best to stop worrying and get on with your life. At some point it becomes counterproductive to try to micromanage `people’s diet on the basis of dubious data. There is a price to pay for being too precautionary. It runs the risk of making people ignore information that has got a sound basis. It runs the risk of excessive medicalisation of everyday life. And it brings science itself into disrepute when people laugh at the contradictory findings of observational epidemiology.
The question of how diet and other ‘lifestyle interventions’ affect health is fascinating to everyone. There is compelling reason to think that it matters. For example one study demonstrated that breast cancer incidence increased almost threefold in first-generation Japanese women who migrated to Hawaii, and up to fivefold in the second generation (Kolonel, 1980). Since then enormous effort has been put into finding out why. The first great success was cigarette smoking but that is almost the only major success. Very few similar magic bullets have come to light after decades of searching (asbestos and mesothelioma, or UV radiation and skin cancer count as successes).
The WCRF report (2007) has 537 pages and over 4400 references and we still don’t know.
Sometimes I think we should say “I don’t know” rather more often.
More material
-
Listen to Ben Goldacre’s Radio 4 programmes. The Rise of the Lifetsyle Nutritionists. Part 1 and Part 2 (mp3 files), and at badscience.net.
-
Risk The Science and Politics of Fear, Dan Gardner. Virgin
Books, 2008 -
Some bookmarks about diet and supplements
Follow up
Dan Gardner, the author of Risk, seems to like the last line at least, according to his blog.
Report of the update, 2010
The 2010 report has been updated in WCRF/AICR Systematic Literature Review Continuous Update Project Report [big pdf file]. This includes studies up to May/June 2010.
The result of addition of the new data was to reduce slightly the apparent risk from eating processed meat from 1.21 (95% CI = 1.04-1.42) in the original study to 1.18 (95% CI = 1.10-1.28) in the update. The change is too small to mean much, though it is in direction expected for false correlations. More importantly, the new data confirm that the dose-response curves are pathetic. The evidence for causality is weakened somewhat by addition of the new data.
Dose-response graph of processed meat and colorectal cancer
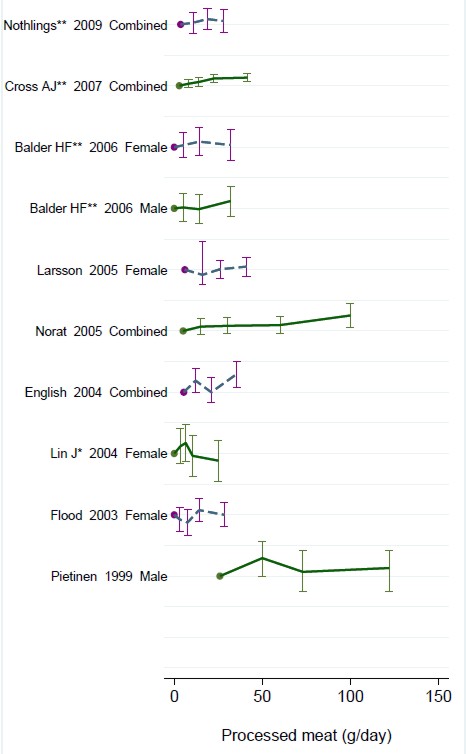
The Nutrition Society is the interim professional body for nutrition. It seems that, unlike so many ‘regulatory bodies’, it may actually take its responsibilities seriously. The following announcement has appeared on their web site.
|
The UK Voluntary Register of Nutritionists acts to protect the public and the reputation the nutrition profession On March 4th 2009, a Fitness to Practice Panel was convened to consider an allegation against a registrant, Dr Ann Walker, that her fitness to practise was impaired. The panel considered whether the registrant, in advocating the use of a web based personal nutritional profiling service had complied with the Code of Ethics’ clause 3: This expects all registered nutritionists to “maintain the highest standards of professionalism and scientific integrity”. In particular, the panel considered whether the registrant showed “knowledge, skills and performance of high quality, up-to-date, and relevant to their field of practice”, in keeping with the Statement of Professional Conduct (para 9). The Panel accepted the allegation of impaired fitness to practice. Mindful of its duty to protect the public, it recommended that Dr Walker be removed from the register. Dr Walker has a right of appeal. |
Well. well, this must be none other than the Dr Ann Walker who caused UCL,and me, such trouble a few years ago. And just because I described her use of the word “blood cleanser” as gobbledygook. She has appeared a few times on this blog.
- Nutribollocks: antioxidants useless, some are dangerous
- Red clover, herbal spin and vested interests
- The fallout from DC’s de-excommunication
- So what is a “blood cleanser”? Quinion speaks.
- Herbal medicines fail test
- Nutriprofile: useful aid or sales scam?
- She even gets a brief mention at Boots reaches new level of dishonesty with CoQ10 promotion

Presumably the “web-based personal nutritional profiling service” that is referred to is Nutriprofile, on which, with the help of a dietition, we had a bit of fun a while ago. However ideal your diet it still recommended at the end of the questionnaire that you should buy some expensive supplements. Read about it at Nutriprofile: useful aid or sales scam?
I have no idea who lodged the complaint (but it wasn’t me).
It is interesting to compare the high standards of the Nutrition Society with the quite different standards of BANT (the British Association for Applied Nutrition and Nutritional Therapy). They bill themselves as the “Professional Body for Nutritional Therapists”. Nutritional therapists are those fantasists who believe you can cure any ill by buying some supplement pills. Their standards can be judged by, for example, BANT ethics code: BANT nutritional therapists are allowed to earn commission from selling pills and tests.
It seems Dr Ann Walker may have joined the wrong society.
Follow-up
This letter appeared in the Times on Friday 30 January, 2009. It was prompted by the news from the University of Salford, but its main purpose was to try to point out to the Department of Health that you can’t hope to regulate alternative treatments in any sensible way while continuing to push under the carpet the crucial question of which ones work and which don’t.
| Sir
We would like to congratulate the vice-chancellor of the University of Salford, Professor Michael Harloe for his principled decision to drop “all the University’s programmes associated with complementary medicine within the School of Community, Health Sciences & Social Care”. This includes their “Homeopathy in Practice” degree. It is also encouraging that the University of Central Lancashire recently closed its BSc in Homeopathy to new students, and announced a review of all its activities in alternative medicine. Although universities are now taking sensible actions, government policy in the area of regulation of alternative medicine is in urgent need of revision. In May 2008 the Steering Group chaired by Professor Pittilo recommended to the Department of Health that entry into acupuncture, herbal medicine and traditional Chinese medicine should “normally be through a bachelor degree with honours”. But, in the same month, new regulations on Unfair Trading came into effect. One of the 31 commercial practices which are in all circumstances considered unfair is “falsely claiming that a product is able to cure illnesses, dysfunction or malformations”. One part of government seeks to endorse unproven and disproved treatments, at the same time as another part makes them illegal. The reason for this chaotic situation is simple. The Department of Health, and the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), have consistently failed to grasp the nettle of deciding which treatments work and which don’t. That is the first thing you want to know about any treatment. Vice-chancellors seem now to be asking the question, and the government should do so too. The ideal mechanism already exists. The question should be referred to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). That was recommended by a House of Lords report in 2000, and it was recommended again by the Smallwood report (commissioned by the Prince of Wales) in 2005. Now it should be done. Sir Walter Bodmer FRCPath, FRS, FMedSci, FRCP (hon) FRCS(hon) Professor David Colquhoun, FRS Dame Bridget Ogilvie , AC, DBE, FRS, FAA, Professor Dame Nancy Rothwell, FRS, FMedSci, FRCP (hon) |
(Actually, the Times removed the qualifications of the signatories, but left the titles!)
An earlier, longer, version of the letter tried to preempt the obvious criticism by including, as the second paragraph, this passage.
“It makes no sense to offer Bachelor of Science degrees in subjects that have no scientific basis. Not only is homeopathy scientifically absurd, but also the best quality clinical trials show that it is not distinguishable from placebo. From the point of view of the patient, there is nothing wrong with placebo effects. Conventional drugs benefit from them too. There is everything wrong with surrounding the placebo effect with mystical mumbo-jumbo and awarding degrees in it.”
Universities drop degree courses in alternative medicine
In the same issue, there was a related article by the Times’ education editor, Alexandra Frean: Universities drop degree courses in alternative medicine..
“Universities are increasingly turning their backs on homoeopathy and complementary medicine amid opposition from the scientific community to “pseudo-science” degrees.
The University of Salford has stopped offering undergraduate degrees in the subjects, and the University of Westminster announced yesterday that it plans to strengthen the “science base” content of its courses after an internal review which examined their scientific credibility.
Both universities are following the lead of the University of Central Lancashire, which last year stopped recruiting new students to its undergraduate degree in homoeopathic medicine.
The decisions by Salford and Westminster open a new chapter in the fierce debate about the place of awarding of Bachelor of Science degrees in subjects that are not science.”
The article ends thus.
“Other universities are more robust in their defence of their courses
Ian Appleyard, principal lecturer in acupuncture at London South Bank University, said that acupuncture should be studied for the very reason that it was not well understood from the standpoint of Western scientific medicine. Acupuncture had been used by a significant proportion of the world’s population for thousands of years.
“Recent large-scale clinical trials such Haake and meta-analysis from reputable institutions such as The Cochrane Collaboration, have shown that there is evidence to support the therapeutic benefits of acupuncture treatment for back pain and migraine,” he said.”
Uhuh, it seems that Ian Appleyard has been reading the misleading BBC report on the recent trials. In fact they show precisely the opposite of what he claims. The fact that advocates of alternative medicine can misinterpret the evidence so badly is, I guess, at the heart of the problem.
What’s happening at the University of Westminster?
Westminster has regularly been labelled as the University that has more quackery courses than any other.
It is also the only university for which we have much idea about what is taught. The university, like all others, has tried to keep secret what they teach. That itself shows that they aren’t very proud of it. But a surprising amount has leaked out from Westminster, nonetheless. The set of “vibrational medicine” slides, including “Amethysts emit high Yin energy”, have caused much hilarity. The Westminster “miasmatic” examination question gets some laughs too, after it was published in Nature. The set of homeopathic materia medica notes that have come into my possession are pretty good too (coming on line soon).
Recently it emerged that the University of Westminster had followed the example of the University of Central Lancashire (UCLAN), and set up a review of its activities in alternative medicine. But unlike UCLAN it was kept secret, and as far as one can tell, it asked for no input from critics.
Well the outcome of this review turned up in my mail recently. Click the picture to read the whole letter from the Vice-Chancellor.
There is no doubt that the outcome, so far, is rather disappointing. Here are some quotations from this letter, with my comments interleaved.
“The Audit was Chaired by Professor Alan Jago and carried out its review using a comprehensive evidence base”
Alan Jago is a pro- vice chancellor, and formerly from Westminster’s School of Architecture and the Built Environment, so no specialist knowledge there.
“The panel made a number of recommendations to me as a result of their Audit. Many of these recommendations concern the University’s processes for review and validation of courses and these will be passed to the Pro Vice Chancellor responsible for Quality to consider.”
Uhuh, sounds like box-ticking again When will universities learn that validation procedures are, on the whole, not worth the paper they are written on.
“The overarching aim of these actions then is to strengthen and make more explicit the ‘scientific’ nature of the Integrated Health undergraduate degrees.
In order to do this we will:
Strengthen learning outcomes particularly in discipline and clinical modules to reflect the science outcomes embedded in the courses.
Revise course specific regulations to explicitly identify that the core health sciences modules have to be passed to complete a degree of the BSc Scheme.
Strengthen the final year project offer to provide more scientific projects through working with Biosciences staff.
Strengthen the scientific/academic qualifications of staff through development
of existing staff and appointments where they become available.”
This seems to me to be whistling in the wind. Remember, we are talking about “bachelor of science” degrees in things like homeopathy and naturotherapy. These are things that are not science at all. In fact they are antiscience to their core.
If you were successful in raising the increasing the scientific level of the staff, many of the subjects they are meant to be teaching would vanish in a puff of smoke.
Certainly the responses of the Westminster staff to earlier enquiries (here, and here) showed little sign of scientific thinking.
And I wonder what Westminster’s admirable biomedical scientists think about taking on homeopathy students for projects?
“I am certain that this work will place Complementary therapies courses in an extremely strong position to meet the external challenges of the future.
I’m sorry to say, Professor Petts, that the scientific community is not likely to share your certainty.
Remember, Peter Fisher is on record as saying that there is not enough science in homeopathy to justifiy offering a BSc degree in it (watch the movie). He is the Queen’s Homeopathic Physician, and Clinical Director of the Royal London Homeopathic Hospital But Westminster still seems to know better.
It seems, so far, that Westminster has missed a chance to change for the better.
Follow-up
Times Higher Education published a pretty pathetic report on the Westminster audit. They did ask me for comments but then failed to publish most of them. I suppose a magazine like that is so dependent on advertising that they can’t afford to upset the authorities. Nevertheless, do they really have to be quite so bland?
I hear that the internal audit has made everyone at the University of Woominster Westminster more nervous and that staff and students have been advised not to share teaching material with people outside the university. Having seen some of them, I’m not surprised they are ashamed of them.
I’m perfectly happy to think of alternative medicine as being a voluntary, self-imposed tax on the gullible (to paraphrase Goldacre again). But only as long as its practitioners do no harm and only as long as they obey the law of the land. Only too often, though, they do neither.
When I talk about law, I don’t mean lawsuits for defamation. Defamation suits are what homeopaths and chiropractors like to use to silence critics. heaven knows, I’ve becomes accustomed to being defamed by people who are, in my view. fraudsters, but lawsuits are not the way to deal with it.

I’m talking about the Trading Standards laws Everyone has to obey them, and in May 2008 the law changed in a way that puts the whole health fraud industry in jeopardy.
The gist of the matter is that it is now illegal to claim that a product will benefit your health if you can’t produce evidence to justify the claim.
I’m not a lawyer, but with the help of two lawyers and a trading standards officer I’ve attempted a summary. The machinery for enforcing the law does not yet work well, but when it does, there should be some very interesting cases.
The obvious targets are homeopaths who claim to cure malaria and AIDS, and traditional Chinese Medicine people who claim to cure cancer.
But there are some less obvious targets for prosecution too. Here is a selection of possibilities to savour..
- Universities such as Westminster, Central Lancashire and the rest, which promote the spreading of false health claims
- Hospitals, like the Royal London Homeopathic Hospital, that treat patients with mistletoe and marigold paste. Can they produce any real evidence that they work?
- Edexcel, which sets examinations in alternative medicine (and charges for them)
- Ofsted and the QCA which validate these exams
- Skills for Health and a whole maze of other unelected and unaccountable quangos which offer “national occupational standards” in everything from distant healing to hot stone therapy, thereby giving official sanction to all manner of treatments for which no plausible evidence can be offered.
- The Prince of Wales Foundation for Integrated Health, which notoriously offers health advice for which it cannot produce good evidence
- Perhaps even the Department of Health itself, which notoriously referred to “psychic surgery” as a profession, and which has consistently refused to refer dubious therapies to NICE for assessment.
The law, insofar as I’ve understood it, is probably such that only the first three or four of these have sufficient commercial elements for there to be any chance of a successful prosecution. That is something that will eventually have to be argued in court.
But lecanardnoir points out in his comment below that The Prince of Wales is intending to sell herbal concoctions, so perhaps he could end up in court too.
The laws
We are talking about The Consumer Protection from Unfair Trading Regulations 2008. The regulations came into force on 26 May 2008. The full regulations can be seen here, or download pdf file. They can be seen also on the UK Statute Law Database.
The Office of Fair Trading, and Department for Business, Enterprise & Regulatory Reform (BERR) published Guidance on the Consumer Protection from Unfair Trading Regulations 2008 (pdf file),
Statement of consumer protection enforcement principles (pdf file), and
The Consumer Protection from Unfair Trading Regulations: a basic guide for business (pdf file).
Has The UK Quietly Outlawed “Alternative” Medicine?
On 26 September 2008, Mondaq Business Briefing published this article by a Glasgow lawyer, Douglas McLachlan. (Oddly enough, this article was reproduced on the National Center for Homeopathy web site.)
“Proponents of the myriad of forms of alternative medicine argue that it is in some way “outside science” or that “science doesn’t understand why it works”. Critical thinking scientists disagree. The best available scientific data shows that alternative medicine simply doesn’t work, they say: studies repeatedly show that the effect of some of these alternative medical therapies is indistinguishable from the well documented, but very strange “placebo effect” ”
“Enter The Consumer Protection from Unfair Trading Regulations 2008(the “Regulations”). The Regulations came into force on 26 May 2008 to surprisingly little fanfare, despite the fact they represent the most extensive modernisation and simplification of the consumer protection framework for 20 years.”
The Regulations prohibit unfair commercial practices between traders and consumers through five prohibitions:-
- General Prohibition on Unfair Commercial
Practices (Regulation 3)- Prohibition on Misleading Actions (Regulations 5)
- Prohibition on Misleading Omissions (Regulation 6)
- Prohibition on Aggressive Commercial Practices (Regulation 7)
- Prohibition on 31 Specific Commercial Practices that are in all Circumstances Unfair (Schedule 1). One of the 31 commercial practices which are in all circumstances considered unfair is “falsely claiming that a product is able to cure illnesses, dysfunction or malformations”. The definition of “product” in the Regulations includes services, so it does appear that all forms medical products and treatments will be covered.
Just look at that!
| One of the 31 commercial practices which are in all circumstances considered unfair is “falsely claiming that a product is able to cure illnesses, dysfunction or malformations” |
Section 5 is equally powerful, and also does not contain the contentious word “cure” (see note below)
Misleading actions
5.—(1) A commercial practice is a misleading action if it satisfies the conditions in either paragraph (2) or paragraph (3).
(2) A commercial practice satisfies the conditions of this paragraph—
(a) if it contains false information and is therefore untruthful in relation to any of the matters in paragraph (4) or if it or its overall presentation in any way deceives or is likely to deceive the average consumer in relation to any of the matters in that paragraph, even if the information is factually correct; and
(b) it causes or is likely to cause the average consumer to take a transactional decision he would not have taken otherwise.
These laws are very powerful in principle, But there are two complications in practice.
One complication concerns the extent to which the onus has been moved on to the seller to prove the claims are true, rather than the accuser having to prove they are false. That is a lot more favourable to the accuser than before, but it’s complicated.
The other complication concerns enforcement of the new laws, and at the moment that is bad.
Who has to prove what?
That is still not entirely clear. McLachlan says
“If we accept that mainstream evidence based medicine is in some way accepted by mainstream science, and alternative medicine bears the “alternative” qualifier simply because it is not supported by mainstream science, then where does that leave a trader who seeks to refute any allegation that his claim is false?
Of course it is always open to the trader to show that his the alternative therapy actually works, but the weight of scientific evidence is likely to be against him.”
On the other hand, I’m advised by a Trading Standards Officer that “He doesn’t have to refute anything! The prosecution have to prove the claims are false”. This has been confirmed by another Trading Standards Officer who said
“It is not clear (though it seems to be) what difference is implied between “cure” and “treat”, or what evidence is required to demonstrate that such a cure is false “beyond reasonable doubt” in court. The regulations do not provide that the maker of claims must show that the claims are true, or set a standard indicating how such a proof may be shown.”
The main defence against prosecution seems to be the “Due diligence defence”, in paragraph 17.
Due diligence defence
17. —(1) In any proceedings against a person for an offence under regulation 9, 10, 11 or 12 it is a defence for that person to prove—
(a) that the commission of the offence was due to—
(i) a mistake;
(ii) reliance on information supplied to him by another person;
(iii) the act or default of another person;
(iv) an accident; or
(v) another cause beyond his control; and
(b) that he took all reasonable precautions and exercised all due diligence to avoid the commission of such an offence by himself or any person under his control.
If “taking all reasonable precautions” includes being aware of the lack of any good evidence that what you are selling is effective, then this defence should not be much use for most quacks.
Douglas McLachlan has clarified, below, this difficult question
False claims for health benefits of foods
A separate bit of legislation, European regulation on nutrition and health claims made on food, ref 1924/2006, in Article 6, seems clearer in specifying that the seller has to prove any claims they make.
Article 6
Scientific substantiation for claims
1. Nutrition and health claims shall be based on and substantiated by generally accepted scientific evidence.
2. A food business operator making a nutrition or health claim shall justify the use of the claim.
3. The competent authorities of the Member States may request a food business operator or a person placing a product on the market to produce all relevant elements and data establishing compliance with this Regulation.
That clearly places the onus on the seller to provide evidence for claims that are made, rather than the complainant having to ‘prove’ that the claims are false.
On the problem of “health foods” the two bits of legislation seem to overlap. Both have been discussed in “Trading regulations and health foods“, an editorial in the BMJ by M. E. J. Lean (Professor of Human Nutrition in Glasgow).
“It is already illegal under food labelling regulations (1996) to claim that food products can treat or prevent disease. However, huge numbers of such claims are still made, particularly for obesity ”
“The new regulations provide good legislation to protect vulnerable consumers from misleading “health food” claims. They now need to be enforced proactively to help direct doctors and consumers towards safe, cost effective, and evidence based management of diseases.”
In fact the European Food Standards Agency (EFSA) seems to be doing a rather good job at imposing the rules. This, predictably, provoked howls of anguish from the food industry There is a synopsis here.
“Of eight assessed claims, EFSA’s Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) rejected seven for failing to demonstrate causality between consumption of specific nutrients or foods and intended health benefits. EFSA has subsequently issued opinions on about 30 claims with seven drawing positive opinions.”
“. . . EFSA in disgust threw out 120 dossiers supposedly in support of nutrients seeking addition to the FSD’s positive list.
If EFSA was bewildered by the lack of data in the dossiers, it needn’t hav been as industry freely admitted it had in many cases submitted such hollow documents to temporarily keep nutrients on-market.”
Or, on another industry site, “EFSA’s harsh health claim regime”
“By setting an unworkably high standard for claims substantiation, EFSA is threatening R&D not to mention health claims that have long been officially approved in many jurisdictions.”
Here, of course,”unworkably high standard” just means real genuine evidence. How dare they ask for that!
Enforcement of the law
Article 19 of the Unfair Trading regulations says
19. —(1) It shall be the duty of every enforcement authority to enforce these Regulations.
(2) Where the enforcement authority is a local weights and measures authority the duty referred to in paragraph (1) shall apply to the enforcement of these Regulations within the authority’s area.
Nevertheless, enforcement is undoubtedly a weak point at the moment. The UK is obliged to enforce these laws, but at the moment it is not doing so effectively.
A letter in the BMJ from Rose & Garrow describes two complaints under the legislation in which it appears that a Trading Standards office failed to enforce the law. They comment
” . . . member states are obliged not only to enact it as national legislation but to enforce it. The evidence that the government has provided adequate resources for enforcement, in the form of staff and their proper training, is not convincing. The media, and especially the internet, are replete with false claims about health care, and sick people need protection. All EU citizens have the right to complain to the EU Commission if their government fails to provide that protection.”
This is not a good start. A lawyer has pointed out to me
“that it can sometimes be very difficult to get Trading Standards or the OFT to take an interest in something that they don’t fully understand. I think that if it doesn’t immediately leap out at them as being false (e.g “these pills cure all forms of cancer”) then it’s going to be extremely difficult. To be fair, neither Trading Standards nor the OFT were ever intended to be medical regulators and they have limited resources available to them. The new Regulations are a useful new weapon in the fight against quackery, but they are no substitute for proper regulation.”
Trading Standards originated in Weights and Measures. It was their job to check that your pint of beer was really a pint. Now they are being expected to judge medical controversies. Either they will need more people and more training, or responsibility for enforcement of the law should be transferred to some more appropriate agency (though one hesitates to suggest the MHRA after their recent pathetic performance in this area).
Who can be prosecuted?
Any “trader”, a person or a company. There is no need to have actually bought anything, and no need to have suffered actual harm. In fact there is no need for there to be a complainant at all. Trading standards officers can act on their own. But there must be a commercial element. It’s unlikely that simply preaching nonsense would be sufficient to get you prosecuted, so the Prince of Wales is, sadly, probably safe.
Universities who teach that “Amethysts emit high Yin energy” make an interesting case. They charge fees and in return they are “falsely claiming that a product is able to cure illnesses”.
In my view they are behaving illegally, but we shan’t know until a university is taken to court. Watch this space.
The fact remains that the UK is obliged to enforce the law and presumably it will do so eventually. When it does, alternative medicine will have to change very radically. If it were prevented from making false claims, there would be very little of it left apart from tea and sympathy
Follow-up
New Zealand must have similar laws.
Just as I was about to post this I found that in New Zealand a
“couple who sold homeopathic remedies claiming to cure bird flu, herpes and Sars (severe acute respiratory syndrome) have been convicted of breaching the Fair Trading Act.”
They were ordered to pay fines and court costs totalling $23,400.
A clarification form Douglas McLachlan
On the difficult question of who must prove what, Douglas McLachlan, who wrote Has The UK Quietly Outlawed “Alternative” Medicine?, has kindly sent the following clarification.
“I would agree that it is still for the prosecution to prove that the trader committed the offence beyond a reasonable doubt, and that burden of proof is always on the prosecution at the outset, but I think if a trader makes a claim regarding his product and best scientific evidence available indicates that that claim is false, then it will be on the trader to substantiate the claim in order to defend himself. How will the trader do so? Perhaps the trader might call witness after witness in court to provide anecdotal evidence of their experiences, or “experts” that support their claim – in which case it will be for the prosecution to explain the scientific method to the Judge and to convince the Judge that its Study evidence is to be preferred.
Unfortunately, once human personalities get involved things could get clouded – I could imagine a small time seller of snake oil having serious difficulty, but a well funded homeopathy company engaging smart lawyers to quote flawed studies and lead anecdotal evidence to muddy the waters just enough for a Judge to give the trader the benefit of the doubt. That seems to be what happens in the wider public debate, so it’s easy to envisage it happening a courtroom.”
The “average consumer”.
(3) A commercial practice is unfair if—
(a) it contravenes the requirements of professional diligence; and
(b) it materially distorts or is likely to materially distort the economic behaviour of the average consumer with regard to the product.
It seems,therefore, that what matters is whether the “average consumer” would infer from what is said that a claim was being made to cure a disease. The legal view cited by Mojo (comment #2, below) is that expressions such as “can be used to treat” or “can help with” would be considered by the average consumer as implying successful treatment or cure.
The drugstore detox delusion. A nice analysis “detox” at .Science-based Pharmacy
Sense about Science have just produced a rather good pamphlet that exposes, yet again. the meaningless marketing slogan “detox”. You can download the pamphlet from their web site.
The pamphlet goes through the claims of eleven products. Needless to say, the claims are either meaningless, or simply untrue.
- Garnier Clean Detox Anti-Dullness Foaming Gel
“Detoxifies by cleansing the skin’s surface” - MG Detox Shampoo Trevor Sorbie
“Deep cleansing and clarifying shampoo” - Boots Detox Body Brush
“Ritualistic body brushing helps expel toxins through the skin” - Innocent Natural Detox Smoothie
“Helps neutralise nasty free radicals which can cause damage to your body’s cells” - Vitabiotics Detoxil 15 day support
“Helps the body cleanse itself of toxins and pollutants caused by the excesses of a busy life” - V-Water Detox
“Cleanse your system and whisk away the polluting nasties” - 4321 Shape Up and Detox
“To drain off water and toxins” and “purify the body” - Boots Detox 5 Day Plan
Works “in harmony with your body to flush away toxins” - Farmacia Spa Therapy Detox range
To “rid your body of these damaging toxins” - Crystal Spring Detox patches
“I’m the easy way to detox, just put me on one foot at night and take me off in the morning” - Fushi Holistic and Health Solutions Total Detox Patch
“it acts as a toxin sink and absorbs impurities through your feet”
One nice thing about the pamphlet is that each item is written by a young scientist (including my close neighbour, Daniella Muallem). They are all people at an early stage in their career, but they care enough to spend time dissecting the rubbish spread by companies in order to part you from your money.
Garnier, it’s true, is a cosmetics company, so one expects nothing but lies You won’t be disappointed on that score.
That least ethical of pharmaceutical companies, Boots, appears twice The Boots Detox Body Brush is reviewed by a young chemist, Tom Wells. It turns out (there’s a surprise) to be nothing more than an ordinary stiff brush. It seems that Boots’ definition of “detox”, for this purpose, is “removing dead skin cells” A totally shameless con, in other words.
The Boots Detox 5 day plan consists if 5 phials of apple or strawberry flavoured goo containing two vitamins and one mineral, mixed with glycerol. In this case the young investigator, Evelyn Harvey, elicited a quite remarkable response from Boots.
Well, have you tested the effects of that diet, with or without the detox product? Does the ‘goo’ stuff [the drink which forms part of the plan] add anything extra?
Well, it’s meant to kick start it.
But has is been tested like that?
No.
Ok, I’m thinking I’ll just try a healthy diet for a week, a bit more exercise, and not bother with buying the detox.
Yes, that sounds like a better idea, to be honest I’d never do this myself.
The media coverage
The Radio 4 Today programme interviewed Ben Goldacre and the managing director of yet another product “Detox in a box” (following their usual policy of equal time for the Flat Earth Society). Listen to the mp3. When Ben Goldacre asked the MD for evidence for the claim made on the web site of Detox in a box, that their diet could remove cadmium from the body, it was denied explicitly that any such claim had been made.
Not so.

But by 10.02 the site had already changed
![]()
So no apology for the mistake. Just a sneaky removal of a few words.
That seems to be the only change though. All the rest of the nutribollocks is still there. For example

There isn’t the slightest reason to believe that it will “improve our immune function”.
There isn’t the slightest reason to think that scavenging free radicals would do you any good, even if it happened.
There isn’t the slightest reason to think it will strengthen body’s fight against cancer cells (that looks like a breach of the Cancer Act to me).
“Cleansing mucous” doesn’t mean much, but whatever it is there isn’t any reason to think its true.
“Purify our blood”. Total meaningless bollocks. The words mean nothing at all. I’ve been here before.
Ben Goldacre’s own account is here “The barefaced cheek of these characters will never cease to amaze and delight me.”
The BBC web site does a good job too.
The Guardian gives an excellent account (James Randerson).
The Daily Mail writes “Detox diets to kick-start the New Year are a ‘total waste of money’ “.
Medical News Today write “Debunking The Detox Myth“.
The Daily Telegraph disgraces itself by not only failing to carry a decent account of the item, but it does run an article on “Detox holidays: New year, new you“. Mega-expensive holidays for the mega-stupid (not to mention the capital letter after the colon).
The Daily Mash provides a bit of cognate fun with “BRITAIN SIGNS UP FOR VORDERMAN’S 28-DAY PISS-DRINK DETOX“. That alludes to “Carol Vorderman’s 28-Day Detox Diet”. A woman who got an enormous salary for playing a parlour game on TV, and has done some good for maths education, is reduced to promoting nonsense for yet more money.
As Clive James pointed out, it’s a but like watching George Clooney advertising coffee for, of all unethical companies, Nestlé. They really look very silly.
Follow-up
Evening Standard 6th January. Nick Cohen writes “Give up detox – it’s bad for your health”
“Giving up on detox should not be painful, however. On the contrary, it should e a life-enhancing pleasure.”
The Times. rather later (January 18th) had a lovely one, “Detox
Debunked“, by the inimitable Ben Goldacre, His account of /detox; as a quasi-religious ‘cleansing ritual’, is spot on.
A really good bit of investigative journalism by BBC Inside Out South West.was shown on Wednesday 12th November 2008. Unfortunately it was shown only in the South West. If you are in the UK you can see it on BBC iPlayer. There is a clip on Youtube. It features some very sensible comments from a real dietitian, Catherine Collins, and from Ben Goldacre .
The College of Natural Nutrition is not a university. In fact it is an industrial building in Tiverton, Devon.

(Could that be a tutor in the window?)
But some of the courses are given in the far grander surroundings of Regent’s College in London.

The College of Natural Nutrition diploma (over £1300) is the only qualification of Barbara Nash. Nash is the ‘nutritionist’ who treated Dawn Page with a ‘hydration diet’, that resulted in organ failure, epilepsy and brain damage. Nash’s insurers paid £800 000. in damages, but didn’t admit liability.

Dr Ben Goldacre pointed out that it perhaps isn’t surprising that people like Nash so often act far beyond their competence because they are being “aggrandised by the strange made-up colleges and bodies that are training and accrediting them”.

When you see some of the things she was taught, it isn’t surprising. Secret video recording revealed some totally bizarre teaching by the College principle, Barbara Wren.

She claimed to have cured thyroid cancer by applying external compresses, half an hour with castor oil and half an hour with your own urine. Claiming to be able to cure cancer is illegal. Of course that isn’t done in public, just in private (a bit like Boots’ advice on useless supplements)). The BBC did some secret filming.


And what caused the cancer? A computer stored under the bed.

Catherine Collins commented “It would be laughable if it wasn’t so serious.

In another lecture, Barbara Wren sounds very peevish because she is going to be prevented from “prescribing” 25 times the safe dose of iodine. She advises her hapless customers to go to a pet shop and buy Lugol’s (iodine) solution, used to treat fish tank water, so they can poison themselves in peace.
The College of Natural Nutrition, and Barbara Nash, are both still in business The web site of the former has the disclaimer
“People who take the information and make decisions regarding their health or medical care, which they believe are based on ideas contained in this website, do so at their own risk. The author and publisher are not responsible for any adverse effects or consequences resulting from the use of any of the suggestions or information contained in the website “
I doubt if that is enough to exempt you from the Cancer Act. Anybody who does make medical decisions based on this utterly batty advice might be thought to deserve what they get.
Alternatively, if you are daft enough, buy the course..

Postscript. Some other blogs that give good information about this topic include Thinking is Dangerous and NHS Blog doctor
It seems that validation committees often don’t look beyond the official documents. As a result, the validations may not be worth the paper they are written on. Try this one.


One of the best bits of news recently was the downfall of Matthias Rath. He’s the man who peddled vitamin pills for AIDS in Africa, and encouraged the AIDS denialists in the South African government. Thabo Mbeki and his Health Minister, Mrs Beetroot, have gone now, thank heavens.
Rath was one of the best illustrations of the murderous effect of selling ineffective treatments. The fact that nobody in the “nutritional therapy” industry has uttered a word of condemnation for this man illustrates better than anything one can imagine the corrupt state of “nutritional therapy”. The people who kept silent include the British Association of Nutritional Therapists (BANT).
It might be surprising, then, to find the Northern College of Acupuncture proudly adding a course in alternative nutrition to its courses in acupuncture (now known to be a theatrical placebo) and Chinese herbal medicine (largely untested and sometimes toxic). It might be even more surprising to find the boast that the course is validated by the University of Wales. It seemed a good idea to find out a bit more about how this came about. Thanks to the Freedom of Information Act, some interesting things can be discovered.
Polly Toynbee’s superb article, Quackery and superstition – available soon on the NHS, written in January 2008, mentioned diplomas and degrees in complementary therapies offered by, among others, the University of Wales. This elicited a letter of protest to Toynbee from the Vice-Chancellor of the University of Wales, Professor Marc Clement BSc, PhD, MInstP, CEng,CPhys,FIET. He invited her to visit the university to see their “validation and monitoring procedures (including the University’s very specific guidelines on health studies disciplines”.
So let’s take a look at these validation procedures and guidelines.
The validation process
The Northern College of Acupuncture submitted a 148 page proposal for the course in October 2007. The document has all the usual edu-bollocks jargon, but of course doesn’t say much about clinical trials, though it does boast about an unblinded trial of acupuncture published in 2006 which, because of lack of appropriate controls, served only to muddy the waters. : This submission was considered by the University’s validation committee last December.

|
The whole validation document is only four pages long [download it]. The most interesting thing about it is that the words ‘evidence’ or ‘critical’ do not occur in it a single time. It has all the usual bureaucratic jargon of such documents but misses entirely the central point.
Does that mean that the University of Wales doesn’t care about evidence or critical thinking? Well, not on paper. Two years previously a short document called Health Studies Guidelines had been written by Dr Brian Spriggs (Health Studies Validation Consultant, since retired) for the Health Studies Committee, and it was approved on 21 April 2005. It starts well.
“Degrees in the Health Studies field are expected to promote an understanding of the importance of the scientific method and an evidence-base to underpin therapeutic interventions and of research to expand that base.”
It even goes on to say that a BSc degree in homeopathy is “unacceptable”. Don’t get too excited though, because it also says that acupuncture and Chinese herbal stuff is quite OK. How anyone can imagine they live up to the opening sentence beats me. And it gets worse. It says that all sorts of rather advanced forms of battiness are OK if they form only part of another degree. They include Homeopathy, Crystal therapy. Dowsing, Iridology; Kinesiology, Radionics, Reflexology, Shiatsu, Healing, and Maharishi Ayurvedic Medicine.
Dowsing? Crystal therapy? Just let me remind you. We are living in 2008. It is easy to forget that when ploughing through all this new age junk.
The Validation Handbook of Quality Assurance: Health Studies (2007) runs to an astonishing 256 pages [download the whole thing]. On page 12 we find the extent of the problem.
“The University of Wales validates a number of schemes in the Health Studies field. At the current time we have undergraduate and/or postgraduate degree schemes in Acupuncture, Animal Manipulation, Chiropractic, Herbal Medicine, Integrative Psychotherapy, Osteopathy, Osteopathic Studies, Traditional Chinese Medicine and Regulatory Affairs, both in the UK and overseas.”
That sounds pretty shocking. Further down on page 12, though, we find this.
“Degrees in the Health Studies field are expected to promote an understanding of the importance of the scientific method and an evidence-base to underpin therapeutic interventions and of research to expand that base. The mission is to promote and require the critical evaluation of the practices, doctrines, beliefs, theories and hypotheses that underlie the taught therapeutic measures of the discipline.”
They are indeed fine words. The problem is that I can detect no sign in the submission, nor in its consideration by the validation committee, that any attempt whatsoever was made to ensure that the course complied with these requirements.
The only sign of concern I could detect of any concern about the quality of what was being taught came in a minute to a meeting of the Health Studies Committee meeting on 24th April 2008.
“Members received a copy of an article entitled Quackery and superstition available soon on the NHS which appeared in The Guardian newspaper in January 2008, and a copy of the Vice- Chancellors response. Members agreed that this article was now historical but felt that if/when the issue were to arise again; the key matter of scientific rigour should be stressed. The Committee agreed that this was the most critical element of all degree schemes in the University of Wales portfolio of health studies schemes. It was felt it would be timely to re-examine the schemes within the portfolio as well as the guidelines for consideration of Health Studies schemes at the next meeting. The Committee might also decide that Institutions would be required to include literature reviews (as part of their validation submission) to provide evidence for their particular profession/philosophy. It was agreed that the guidelines would be a vital document in the consideration of new schemes and during preliminary visits to prospective Institutions. “
The Press Office had passed Polly Toynbee’s article to them. Curiously the Health Studies Committee dismissed it as “historical”, simply because it was written three months earlier. That is presumably “historical” in the sense that the public will have forgotten about it, rather than in the sense that the facts of the matter have changed since January. So, at least for the nutrition degree, Toynbee’s comments were simply brushed under the carpet.
After a few cosmetic changes of wording the validation was completed on 16th January 2008. For example the word “diagnosis” was removed in 43 places and “rewritten in terms of evaluation and assessment”. There was, needless to say, no indication that the change in wording would change anything in what was taught to students.
You may think that I am being a bit too harsh. Perhaps the course is just fine after all? The problem is that the submission and the reaction of the validation committee tell you next to nothing about what actually matters, and that is what is taught. There is only a vague outline of that in the submission (and part of it was redacted on the grounds that if it were made public somebody might copy ;it. Heaven forbid).
That is why I have to say, yet again, that this sort of validation exercise is not worth the paper it’s written on.
How can we find out a bit more? Very easily as it happens. Just Google. What matters is not so much formal course outlines but who teaches them.
The nutrition course
The title of the course is just “Nutrition”, not ‘Nutritional Therapy’ or ‘Alternative Nutrition’. That sounds quite respectable but a glance at the prospectus shows immediately that it is full-blown alternative medicine.
Already in July 2007, the glowing press releases for the course had attracted attention from the wonderfully investigative web site HolfordWatch. I see no sign that the validation committee was aware of this. But if not, why not? I would describe is as dereliction of academic duty.
“This pioneering course is unique in that it is firmly rooted in both Western nutritional science and naturopathic medicine and also covers concepts of nutrition within traditional Chinese, Japanese, Tibetan and Ayurvedic medicine.
This means that graduates will gain comprehensive understanding of both modern scientific knowledge and ancient wisdom concerning nutrition and dietetics.”
Ancient wisdom, of course, means something that your are supposed to believe though there is no good reason to think it’s true. In the end, though, almost the only thing that really matters about any course is who is running it. The brochure shows that all of the people are heavily into every form of alternative nuttiness.
Course Director and Tutor: Jacqueline Young nutritionist, naturopath, clinical psychologist and Oriental medical practitioner
Nutrition Tutors:
Elaine Aldred (qualified as a chiropractor with the Anglo European Chiropractic College, as an acupuncturist with the British College of Acupuncture and as a Western Medical Herbalist with the College of Phytotherapy. She recently also qualified in Chinese herbal medicine with the Northern College of Acupuncture.)
Sue Russell (3 year diploma in nutritional therapy at the Institute of Optimum Nutrition. She currently practises as a nutritional therapist and also works part-time as a manager at the Northern College of Homeopathic Medicine.)
Anuradha Sharma (graduated as a dietician from Leeds Metropolitan University in 2002 and subsequently completed a Naturopathy certificate and a post-graduate diploma in acupuncture).
Guest Lecturers include : Dr John Briffa, Professor Jane Plant, M.B.E. (a geochemist turned quack), and, most revealingly, none other than the UK’s most notorious media celebrity and pill peddler, Patrick Holford.
So much has been written about Holford’s appalling abuse of science, one would have thought that not even a validation committee could have missed it.
“The course has been created by Jacqueline Young“, so let’s look a bit further at her track record.
Jacqueline Young has written a book, ‘Complementary Medicine for Dummies’ [Ed: ahem shouldn’t that be Dummies for Complementary Medicine?]. You can see parts of it on Google Books. Did the validation committee bother to look at it? As far as I can tell, the words ‘randomised’ or ‘clinical trial’ occur nowhere in the book.
The chapter on Tibetan medicine is not very helpful when it comes to evidence but for research we are referred to the Tibetan Medical and Astrology Institute. Guess what? That site gives no evidence either. So far not a single university has endorsed Astrology (there is a profitable niche there for some vice-chancellor).
Here are few samples from the book. The advice seems to vary from the undocumented optimism of this

Well researched? No. Safe? Nobody knows. Or this

Mandarin peel prevents colds and flu? Old wive’s tale. Then there are things that verge on the weird, like this one

or the deeply bizarre like this

The problem of Jacqueline Young’s fantasy approach to facts was pointed out at least as far back as 2004, by Ray Girvan., who wrote about it again in May 2005. The problems were brought to wider attention when Ben Goldacre wrote two articles in his Badscience column, Imploding Researchers (September 2005), and the following week, Tangled Webs.
“we were pondering the ethics and wisdom of Jacqueline Young dishing out preposterous, made-up, pseudoscientific nonsense as if it was authoritative BBC fact, with phrases such as: “Implosion researchers have found that if water is put through a spiral its electrical field changes and it then appears to have a potent, restorative effect on cells.” “
and later
“Take this from her article on cranial osteopathy, riddled with half truths: “Sutherland found that the cranial bones (the skull bones encasing the brain) weren’t fused in adulthood, as was widely believed, but actually had a cycle of slight involuntary movement.” In fact the cranial bones do fuse in adulthood.
She goes on: “This movement was influenced by the rhythmic flow of cerebrospinal fluid (the nourishing and protective fluid that circulates through the spinal canal and brain) and could become blocked.” There have now been five studies on whether “cranial osteopaths” can indeed feel these movements, as they claim, and it’s an easy experiment to do: ask a couple of cranial osteopaths to write down the frequency of the rhythmic pulses on the same person’s skull, and see if they give the same answer. They don’t. A rather crucial well-replicated finding to leave out of your story.
That was in 2005 and since then all of Young’s “preposterous, made-up, pseudoscientific nonsense” (along with most of the other stuff about junk medicine) has vanished from the BBC’s web site, after some people with a bit of common sense pointed out what nonsense it was. But now we see them resurfacing in a course validated by a serious university. The BBC had some excuse (after all, it is run largely by arts graduates). I can see no excuses for the University of Wales.
Incidentally, thanks to web archive you can still read Young’s nonsense, long after the BBC removed it. Here is a quotation.
“Implosion researchers have found that if water is put through a spiral its ,field changes and it then appears to have a potent, restorative effect on cells. In one study, seedlings watered with spiralised water grew significantly faster, higher and stronger than those given ordinary water.”
The vice-chancellor of the University of Wales, Marc Clement, is a physicist (Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering), so can he perhaps explain the meaning of this?
Selection committees for jobs (especially senior jobs) and validation committees for courses, might make fewer mistakes if they didn’t rely so much on formal documents and did a little more investigation themselves. That sort of thing is why the managerial culture not only takes a lot more time, but also gives a worse result.
It would have taken 10 minutes with Google to find out about Young’s track record, but they didn’t bother. As a result they have spent a long time producing a validation that isn’t worth the paper it’s written on. That makes the University of Wales a bit of a laughing stock. Worse still, it brings science itself into disrepute.
Follow-up
What does the University of Wales say? So far, nothing. Last week I sent brief and polite emails to Professor Palastanga and to Professor Clement to try to discover whether it is true that the validation process had indeed missed the fact that the course organiser’s writings had been described as “preposterous, made-up, pseudoscientific nonsense” in the Guardian.
So far I have had no reply from the vice-chancellor, but on .26 October I did get an answer from Prof Palastaga.
| As regards the two people you asked questions about – J.Young – I personally am not familiar with her book and nobody on the validation panel raised any concerns about it. As for P.Holford similarly there were no concerns expressed about him or his work. In both cases we would have considered their CV’s as presented in the documentation as part of the teaching team. In my experience of conducting degree validations at over 16 UK Universities this is the normal practice of a validation panel. |
I have to say this reply confirms my worst fears. Validation committees such as this one simply don’t do their duty. They don’t show the curiosity that is needed to discover the facts about the things that they are meant to be judging. How could they not have looked at the book by the very person that they are validating? After all that has been written about Patrick Holford, it is simply mind-boggling that the committee seems to have been quite unaware of any of it.
It is yet another example of the harm done to science by an unthinking, box-ticking approach.
Pharmacology. A Handbook for Complementary Healthcare Professionals
Elsevier were kind enough to send me an inspection copy of this book, which is written by one of the nutrition course tutors, Elaine Aldred. She admits that pharmacology is “considered by most students to be nothing more that a ‘hoop-jumping’ exercise in the process of becoming qualified”. She also says. disarmingly. that “I was certainly not the most adept scientist at school and found my university course a trial”.
The book has all the feel of a cut and paste job. It is mostly very simple (if not simplistic). though for no obvious reason it starts with a long (and very amateur) discussion of chemical bonding Then molecules are admitted to be indivisible (but, guess what, the subject of homeopathy is avoided). There is a very short section on ion channels, though, bizarrely, it appears under the heading “How do drugs get into cells?”. Since the author is clearly not able to make the distinction between volts and coulombs, the discussion is more likely to confuse the reader than to help.
Then a long section on plants. It starts of by asserting that “approximately a quarter of prescription drugs contain at least one chemical that was originally isolated and extracted from a plant”.. This cannot be even remotely correct. There are vast tables showing complicated chemical structures, but the usual inadequate
list of their alleged actions This is followed by a quick gallop through some classes of conventional drugs, illustrated again mainly by chemical structures not data. Hormone replacement therapy is mentioned, but the chance to point out that it is one of the best illustrations of the need for RCTs is missed.
The one thing that one would really like to see in such a book is a good account of how you tell whether or not a drug works in man. This is relegated to five pages at the end of the book, and it is, frankly, pathetic. It
is utterly uncritical in the one area that matters more than any other for people who purport to treat patients. All you get is a list of unexplained bullet points.
If this book is the source of the “scientific content” of the nutrition course, things are as bad as we feared.
Today is a good day for anyone who deplores dangerous confidence tricksters. In particular it is a good day for Ben Goldacre, and for the Guardian which defended him at potentially enormous expense.
| Matthias Rath, the Dutch (or is it German) vitamin salesman has dropped his libel action against the Guardian. He is the man who is, without doubt, responsible for many deaths form AIDS in Africa, as a result of peddling vitamin pills as cures. The action was taken after Goldacre said, in the Guardian, that Rath aggressively sells his message to Aids victims in South Africa that Rath vitamin pills are better than medication”. |  |
Here is some of what has appeared already today
Fall of the doctor who said his vitamins would cure Aids – from The Guardian, with a video of the villain.
Goldacre’s Badscience blog article on his victory .
Profile of Zackie Achmat – from The Guardian, Mr Achmat is the founder of the Treatment Action Campaign , instrumental in exposing Rath.
Extract from witness statements from the defence in the trial .
And a lot of publicity from Gimpyblog (“Ben Goldacre and The Guardian triumph over murderous Matthias Rath”), Holfordwatch , Quackometer and jdc325 blogs.
Then more in the Guardian the next day, Chris McGreal investigates the Rath Foundation
Nutritional therapist?
Let’s be clear about what the words mean. Nutritional therapists are not like dietitians, and they are not like nutritionists. Nutritional therapists are solidly in the camp of alternative medicine practitioners, Don’t
take my word for it. They say so themselves.
“For nutritional therapists (who practise Complementary and Alternative Medicine) optimum nutrition encompasses individual prescriptions for diet and lifestyle in order to alleviate or prevent ailments and to promote optimal gene expression through all life stages. Recommendations may include guidance on natural detoxification, procedures to promote colon health, methods to support digestion and absorption, the avoidance of toxins or allergens and the appropriate use of supplementary nutrients, including phytonutrients.”
They love to use imaginary words like “detoxification”, and, much more dangerously, they love to pretend that they can cure diseases by changes in diet. As long as you buy from them a stack of expensive “supplement” pills, of course. That means they are selling medicines, but by pretending they are selling food supplements they manage to evade the law that requires medicines to be safe and effective. That will not be so easy under new legislation though, and we can look forward to a few prosecutions soon.
Guess who runs an “Honours BSc degree” in Nutritional Therapy. No prizes for realising it is the UK’s leading university purveyor of woo.
The University of Westminster
On their web site we learn that the Course Leader is Heather Rosa, and the Deputy Course Leader is Val Harvey. Harvey qualified in the subject at the Institute of Optimum Nutrition, the private college run by none other than the famous pill-peddler, Patrick Holford, about whom so very much has been written (try Holfordwatch, or the masterly chapter in Goldacre’s Bad Science)
We don’t know much about what is taught on the Nutritional Therapy course because the University of Westminster has refused repeated requests to say (but watch this space).. One can only assume that, whatever it is, they are not very proud of it. It seems a little unlikely that they will go as far as Matthias Rath and claim to cure AIDS -we’ll just have to wait and see. Meanwhile we can get an inkling by looking elsewhere.
Course leader, Heather Rosa, pops up for example, on the expert panel of a web site called Supplements Compared.com. “Supplements Compared is designed to help you find the best dietary supplement product for your health needs.” And what sort of advice do you find there? Try the page that compares 10 brands of CoQ10 (that is the stuff I wrote about recently, in “Boots reaches new level of dishonesty with CoQ10 promotion” – their advertising was deemed improper by the ASA ). It isn’t a recommended treatment for anything at all, but you certainly wouldn’t guess that from what is written by the ‘expert panel’. The winners are, according to the ‘expert panel’, Boots’ CoQ10 and Holland and Barrett’s CoQ10. Winners? Perhaps the explanation for that comes elsewhere, under “How are we funded?”. “Manufacturers who are awarded “best product” and “worth a look” are given the opportunity to promote this fact throughout the site for an additional fee.”. Well well.
Deputy Course leader, Val Harvey has her own web site and business (I do hope thar Westminster does not pay these people a full time salary too). What can we glean from there? It has the usual scare tactics “Why
you are at risk?“. Never fear; buy enough vitamin pills and you’ll be saved.
Her home page makes some pretty drastic claims.
“Potential health benefits of your nutritional programme
An appropriate Nutritional Programme can benefit many conditions including:
Allergies
Arthritis
Asthma
Bloating, indigestion
Chronic degenerative diseases
Chronic fatigue, ME
Constipation, diarrhoea
Cystitis
Depression, mood swings
Digestive or bowel problems
Eczema, psoriasis, other skin problems
Food sensitivities
Frequent infections
Hormone imbalanceHypertension or elevated cholesterol
Irritable bowel syndrome
Low energy
Menopausal symptoms
Migraines, headaches
Parasitic and fungal infections
Pre-conceptual issues
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
Sinus congestion
Stress
Thrush
Weight problems
and many others ….
These are just some of the wide range of health problems that may be helped by nutritional therapy. Even those who consider themselves well and healthy may be able to enhance their physical and mental health, as well as their performance, including athletic performance, by improving their nutrition.”
There is, in my view, not the slightest bit of good evidence that swallowing vitamin pills can benefit most of these conditions.
But at least the list doesn’t contain AIDS, so is all this really relevant to the case of Matthias Rath?
Yes, I believe it is. The University of Westminster may well not support the views of Matthias Rath (they won’t say), but we have heard no choruses of protests about him from any nutritional therapists, as far as I’m aware. There is no mention of him at all on the web site of the British Association of Nutritional Therapists (BANT), the UK club for these people. BANT, by the way, has a rather curious code of ethics. It allows its members to take undisclosed financial kickbacks for the pills they prescribe to patients. If doctors were caught doing that they’d be struck off the register.
It is the existence of degrees in subjects like “nutritional therapy” that gives the subject a spurious air of respectability which allows seriously dangerous people like Rath to flourish with very little criticism. In an indirect way, the vice-chancellors who allow it to flourish (and Universities UK who do nothing about it) must bear some small part of the responsibility for the deaths of thousands of people from AIDS.
It is about time they did something about it.
Follow-up
ANH. The first reaction from the supplement-peddling industry comes from the Alliance for Natural Health on 16th September. It contains not one word of condemnation for Rath’s murderous activities. It’s hard to believe how low they will sink.
The Prince’s Foundation for Integrated Health remains totally silent about Rath. HRH’s concern for health seems to dry up if things don’t suit his views.
The British Association of Nutritional Therapists shows it’s total irresponsibility after a letter was sent to them to ask about their reaction. Their answer , on jdc325’s weblog was “The association has no opinion to offer on Dr Raths vitamin trials.”.